Natural rights are fundamental principles that are considered inherent to human beings, regardless of the laws or norms of a particular society. These rights are often seen as universal and inalienable, meaning they cannot be taken away by any authority. The concept of natural rights has been explored and debated by philosophers, politicians, and scholars throughout history, with various interpretations and examples emerging over time. In this article, we will delve into the concept of natural rights, exploring their definition, historical context, and contemporary examples.
Historical Context of Natural Rights

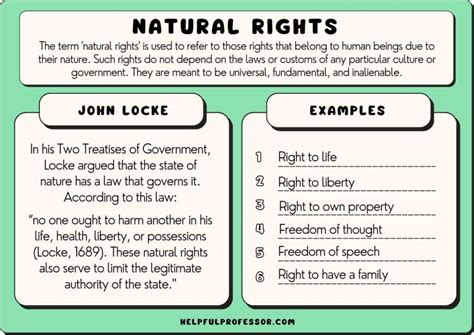
The idea of natural rights has its roots in ancient philosophy, with thinkers such as Aristotle and Cicero discussing the concept of natural law. However, it was not until the 17th and 18th centuries that the idea of natural rights as we understand it today began to take shape. Philosophers such as John Locke, Thomas Hobbes, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau wrote extensively on the subject, arguing that individuals have inherent rights that precede the establishment of governments. According to Locke, for example, individuals have the natural rights to life, liberty, and property, which governments are duty-bound to protect. This idea of natural rights as a foundation for political and social structures has had a profound impact on the development of modern democracy and human rights discourse.
Examples of Natural Rights
So, what are some examples of natural rights? While there is no consensus on a definitive list, some of the most commonly cited natural rights include the right to life, the right to freedom of speech and expression, the right to freedom of association, and the right to own property. These rights are considered fundamental because they are essential to human dignity and well-being. For instance, the right to life is considered a fundamental natural right because it is essential for the protection of human dignity and the realization of all other rights. Similarly, the right to freedom of speech and expression is crucial for the exchange of ideas, the promotion of democracy, and the protection of individual autonomy.
| Right | Description |
|---|---|
| Right to Life | The right to exist and to be protected from harm or violence. |
| Right to Liberty | The right to freedom of movement, thought, and expression. |
| Right to Property | The right to own and possess property, including land, goods, and other assets. |
| Right to Freedom of Speech | The right to express one's thoughts, opinions, and ideas without fear of censorship or retribution. |
| Right to Freedom of Association | The right to assemble, organize, and associate with others for social, political, or economic purposes. |

Key Points
- Natural rights are fundamental principles that are considered inherent to human beings, regardless of the laws or norms of a particular society.
- The concept of natural rights has its roots in ancient philosophy, but it was not until the 17th and 18th centuries that the idea began to take shape.
- Examples of natural rights include the right to life, the right to freedom of speech and expression, the right to freedom of association, and the right to own property.
- These rights are considered fundamental because they are essential to human dignity and well-being.
- The concept of natural rights provides a powerful framework for promoting human dignity, protecting individual autonomy, and advancing social justice.
Contemporary Relevance of Natural Rights

In contemporary times, the concept of natural rights continues to play a crucial role in shaping human rights discourse, informing policy debates, and guiding social justice movements. For instance, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), adopted by the United Nations in 1948, enshrines many of the natural rights discussed above, including the right to life, liberty, and security of person. Similarly, the concept of natural rights has been invoked in various social justice movements, such as the civil rights movement in the United States, the anti-apartheid movement in South Africa, and the feminist movement globally. By grounding their claims in the language of natural rights, these movements have been able to mobilize popular support, challenge unjust laws and institutions, and promote more inclusive and equitable societies.
Critiques and Challenges to Natural Rights
Despite the enduring importance of natural rights, the concept has faced various critiques and challenges over time. Some have argued that natural rights are too vague or ambiguous, making it difficult to determine what specific rights are entailed or how they should be prioritized. Others have pointed out that the concept of natural rights can be used to justify oppressive or discriminatory policies, such as the notion that certain groups are inherently inferior or less deserving of rights. Furthermore, the concept of natural rights has been challenged by alternative frameworks, such as cultural relativism, which argues that human rights and dignity are relative to cultural context, rather than being universal and absolute. In response to these critiques, scholars and advocates have sought to refine and revise the concept of natural rights, emphasizing the importance of context, nuance, and critical evaluation in applying these principles to real-world situations.
What are natural rights?
+Natural rights are fundamental principles that are considered inherent to human beings, regardless of the laws or norms of a particular society.
What are some examples of natural rights?
+Some examples of natural rights include the right to life, the right to freedom of speech and expression, the right to freedom of association, and the right to own property.
Why are natural rights important?
+Natural rights are important because they provide a framework for promoting human dignity, protecting individual autonomy, and advancing social justice.
In conclusion, the concept of natural rights remains a vital and contested idea in contemporary human rights discourse. By examining the historical context, examples, and critiques of natural rights, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and challenges involved in promoting human dignity and protecting individual autonomy. As we move forward, it is essential to continue refining and revising our understanding of natural rights, taking into account the nuances of cultural context, the complexities of power dynamics, and the evolving nature of human societies.