Negative punishment, a concept within the realm of operant conditioning, refers to the removal of a pleasant or desirable stimulus in response to an undesirable behavior, with the aim of decreasing the frequency of that behavior. This principle, first introduced by B.F. Skinner, is often misunderstood or misapplied, leading to ineffective or even harmful outcomes. Understanding negative punishment requires a nuanced approach, recognizing both its potential benefits and drawbacks. Let's delve into five examples that illustrate the application and implications of negative punishment in various contexts.
Negative Punishment in Everyday Life
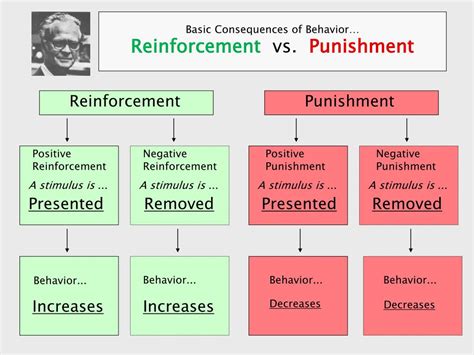
Negative punishment can be observed in numerous aspects of life, from parenting and education to workplace management and personal relationships. It’s essential to analyze these examples critically, considering the ethical implications and the potential for unintended consequences. The first example involves a parent taking away a child’s tablet as a response to the child not completing their homework. In this scenario, the removal of the tablet (a pleasant stimulus) is intended to reduce the likelihood of the child avoiding homework in the future. However, this approach may not address the underlying reasons for the child’s behavior, such as difficulty with the assignments or lack of interest, potentially leading to resentment rather than a positive change in behavior.
Negative Punishment in Educational Settings
In educational settings, negative punishment might be applied by removing privileges or freedoms as a consequence for misbehavior. For instance, a student who disrupts the class might lose their recess time. While the intention is to discourage disruptive behavior, this method can have negative effects on the student’s social and physical development, as recess is crucial for both. Furthermore, it may not teach the student alternative, more appropriate behaviors, thus failing to address the root cause of the misbehavior.
| Context | Application of Negative Punishment | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Parenting | Removing a child's privileges | Short-term compliance, potential long-term resentment |
| Education | Loss of recess or free time | Decrease in disruptive behavior, potential negative impact on physical and social development |
| Workplace | Reduction in benefits or privileges | Short-term increase in compliance, potential long-term decrease in job satisfaction |
| Personal Relationships | Withholding affection or attention | Potential for increased compliance, risk of damaging relationship trust and intimacy |
| Social Media | Blocking or limiting access | Immediate reduction in undesired behavior, potential for feelings of isolation or resentment |

Implications and Considerations

The application of negative punishment is not without its challenges and criticisms. One of the primary concerns is that it focuses on what not to do rather than teaching what to do. By simply removing a positive stimulus without providing an alternative behavior, individuals may not learn the desired behavior. Moreover, negative punishment can lead to a variety of unwanted side effects, including decreased self-esteem, especially in children, and a negative impact on relationships when used in personal or professional contexts.
Alternatives to Negative Punishment
Given the potential drawbacks of negative punishment, it’s beneficial to explore alternative strategies for behavior modification. Positive reinforcement, where desirable behaviors are rewarded with positive stimuli, can be an effective method. Additionally, providing clear expectations, feedback, and teaching alternative behaviors can promote a more positive and supportive environment for change. In educational settings, for example, instead of removing recess, a teacher could positively reinforce focused behavior during lessons with extra recess time or special activities, thus encouraging the desired behavior without the negative consequences associated with punishment.
Key Points
- Negative punishment involves the removal of a desirable stimulus to decrease undesired behavior.
- It can be applied in various contexts, including parenting, education, and the workplace.
- Potential outcomes include short-term compliance but also risk long-term negative effects such as resentment and decreased motivation.
- Alternatives like positive reinforcement and teaching alternative behaviors can be more effective and have fewer negative side effects.
- Consideration of the ethical implications and potential for unintended consequences is crucial when applying negative punishment.
In conclusion, while negative punishment can be a tool for modifying behavior, its application should be approached with caution and a deep understanding of its potential effects. By considering the complexities of human behavior and the importance of promoting positive, supportive environments, we can work towards more effective and humane methods of encouraging desirable behaviors and discouraging undesired ones.
What is the primary goal of negative punishment?
+The primary goal of negative punishment is to decrease the frequency of an undesired behavior by removing a pleasant or desirable stimulus following the behavior.
Can negative punishment have negative side effects?
+Yes, negative punishment can lead to a variety of unwanted side effects, including decreased self-esteem, resentment, and a negative impact on relationships.
What are some alternatives to negative punishment?
+Alternatives to negative punishment include positive reinforcement, where desirable behaviors are rewarded, and teaching alternative behaviors to replace undesired ones.