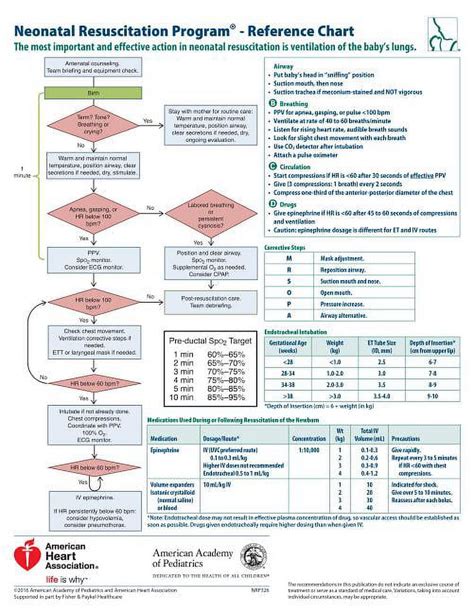
The Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) is a critical component of newborn care, designed to provide healthcare professionals with the skills and knowledge necessary to resuscitate newborns in distress. Developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American Heart Association (AHA), the NRP has undergone significant updates over the years, reflecting the latest research and best practices in neonatal care. As of 2022, the NRP has been revised to include new guidelines for resuscitation, emphasizing the importance of early intervention and individualized care.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 10% of newborns require some form of resuscitation at birth, with 1% requiring extensive resuscitative efforts. The NRP aims to equip healthcare professionals with the necessary skills to respond to these situations, reducing morbidity and mortality rates among newborns. By focusing on evidence-based practices and emphasizing the importance of teamwork and communication, the NRP has become a cornerstone of neonatal care, with over 3 million healthcare professionals trained worldwide.
Key Points
- The Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) is an evidence-based program designed to provide healthcare professionals with the skills and knowledge necessary to resuscitate newborns in distress.
- The NRP emphasizes the importance of early intervention, individualized care, and teamwork in reducing morbidity and mortality rates among newborns.
- According to the WHO, approximately 10% of newborns require some form of resuscitation at birth, with 1% requiring extensive resuscitative efforts.
- The NRP has undergone significant updates over the years, reflecting the latest research and best practices in neonatal care.
- Over 3 million healthcare professionals have been trained in the NRP worldwide, making it a critical component of newborn care.
Components of the Neonatal Resuscitation Program
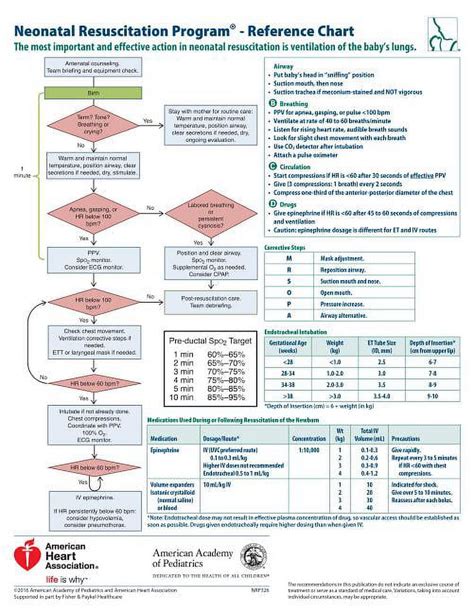
The NRP is comprised of several key components, including initial assessment, ventilation, chest compressions, and medication administration. Healthcare professionals are trained to evaluate the newborn’s condition, using the Apgar score to assess heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin color. The NRP also emphasizes the importance of proper ventilation techniques, including the use of positive pressure ventilation (PPV) and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Chest compressions are performed when the newborn’s heart rate remains below 60 beats per minute, despite adequate ventilation.
Initial Assessment and Stabilization
The initial assessment is a critical component of the NRP, as it allows healthcare professionals to quickly evaluate the newborn’s condition and determine the need for resuscitation. The Apgar score is used to assess the newborn’s heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin color, with scores ranging from 0 to 10. A score of 7 or above is generally considered normal, while a score below 4 indicates the need for immediate resuscitation. The NRP also emphasizes the importance of proper stabilization techniques, including the use of warmth, oxygen, and stimulation to promote comfort and reduce stress.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Assessment | Evaluation of the newborn's condition using the Apgar score |
| Ventilation | Use of positive pressure ventilation (PPV) and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) |
| Chest Compressions | Performance of chest compressions when the newborn's heart rate remains below 60 beats per minute |
| Medication Administration | Use of medications, such as epinephrine, to support cardiovascular function |
Benefits and Outcomes of the Neonatal Resuscitation Program

The NRP has been shown to improve outcomes for newborns in distress, reducing morbidity and mortality rates. Studies have demonstrated that healthcare professionals trained in the NRP are more likely to provide high-quality care, with improved adherence to guidelines and reduced errors. The NRP has also been associated with improved neonatal outcomes, including reduced rates of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and improved long-term neurological development.
Evidence-Based Practice and Quality Improvement
The NRP is grounded in evidence-based practice, with regular updates reflecting the latest research and best practices in neonatal care. The program emphasizes the importance of quality improvement, encouraging healthcare professionals to monitor and evaluate their practice, identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes to optimize care. By promoting a culture of safety and teamwork, the NRP has become a critical component of neonatal care, supporting the delivery of high-quality care to newborns in distress.
According to a study published in the Journal of Perinatology, implementation of the NRP was associated with a significant reduction in neonatal mortality rates, from 12.1 per 1,000 live births to 6.3 per 1,000 live births. The study also demonstrated improved adherence to guidelines, with a significant increase in the use of positive pressure ventilation and chest compressions. These findings highlight the importance of the NRP in improving outcomes for newborns in distress, emphasizing the need for ongoing training and education in neonatal resuscitation.
What is the primary goal of the Neonatal Resuscitation Program?
+The primary goal of the NRP is to provide healthcare professionals with the skills and knowledge necessary to resuscitate newborns in distress, reducing morbidity and mortality rates.
What are the key components of the NRP?
+The key components of the NRP include initial assessment, ventilation, chest compressions, and medication administration.
What are the benefits of the NRP?
+The NRP has been shown to improve outcomes for newborns in distress, reducing morbidity and mortality rates, and promoting high-quality care.
In conclusion, the Neonatal Resuscitation Program is a critical component of newborn care, providing healthcare professionals with the skills and knowledge necessary to resuscitate newborns in distress. By emphasizing the importance of early intervention, individualized care, and teamwork, the NRP has become a cornerstone of neonatal care, supporting the delivery of high-quality care to newborns in distress. As the program continues to evolve, reflecting the latest research and best practices in neonatal care, it is essential that healthcare professionals remain committed to ongoing training and education, ensuring the provision of optimal care to newborns in need.