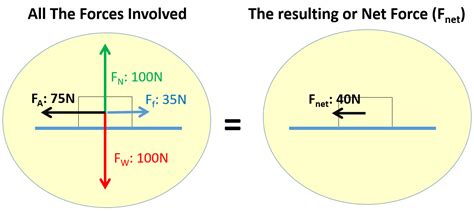
The concept of net force is a fundamental principle in physics, particularly in the field of mechanics. It refers to the overall force acting on an object, taking into account all the individual forces that are applied to it. The net force is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. To understand the net force definition, it's essential to consider the various types of forces that can act on an object, such as friction, gravity, and applied forces.
In everyday life, objects are subjected to multiple forces, and the net force is the resultant force that determines the object's motion or state of rest. For instance, when you push a box across the floor, the force you apply is countered by the force of friction. The net force in this case is the difference between the applied force and the force of friction. If the applied force is greater than the force of friction, the box will move, and the net force will be in the direction of the applied force.
Key Points
- The net force is the overall force acting on an object, considering all individual forces applied to it.
- Net force is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction.
- The net force determines an object's motion or state of rest.
- Multiple forces, such as friction, gravity, and applied forces, contribute to the net force.
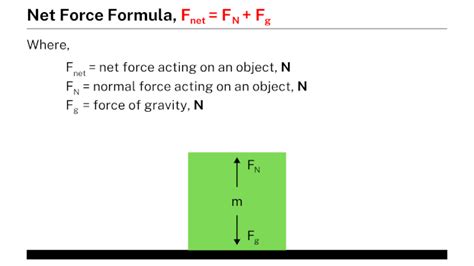
- The net force can be calculated using the formula: Net Force (F_net) = ΣF, where ΣF represents the sum of all forces acting on the object.
Understanding Net Force with Examples

To further illustrate the concept of net force, consider a skydiver jumping from a plane. Initially, the skydiver experiences a net force downward due to gravity, which is the primary force acting on them. As they reach a certain velocity, air resistance becomes significant, applying an upward force opposite to the direction of gravity. The net force in this scenario is the difference between the force of gravity and the force of air resistance. When the skydiver’s velocity reaches a point where the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity, the net force becomes zero, and the skydiver reaches terminal velocity, no longer accelerating downward.
Calculating Net Force
The calculation of net force involves summing up all the forces acting on an object. This can be represented by the formula: Net Force (F_net) = ΣF, where ΣF represents the sum of all forces acting on the object. For example, if a car is moving on a horizontal road with an applied force of 500 N forward and a frictional force of 200 N backward, the net force can be calculated as F_net = 500 N - 200 N = 300 N. This means the car is experiencing a net force of 300 N in the forward direction, causing it to accelerate.
| Force Type | Magnitude (N) | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Applied Force | 500 | Forward |
| Frictional Force | 200 | Backward |
| Net Force | 300 | Forward |
Net Force in Real-World Applications
The concept of net force has numerous real-world applications, from designing safer vehicles to understanding the motion of celestial bodies. In engineering, calculating the net force on a structure or machine component is vital to ensure it can withstand various types of loads without failing. Similarly, in sports, understanding the net force acting on athletes can help in optimizing their performance and reducing the risk of injury.
In conclusion, the net force definition is a critical concept in physics that explains how multiple forces acting on an object result in a single, overall force that determines the object's state of motion or rest. By understanding and applying the principles of net force, we can better analyze and predict the behavior of objects under various conditions, leading to advancements in technology, safety, and performance across different fields.
What is the net force acting on an object at rest?
+The net force acting on an object at rest is zero. According to Newton’s First Law of Motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force. If the net force is zero, it means that all forces acting on the object are balanced, resulting in no acceleration or change in motion.
How does the net force affect the motion of an object?
+The net force acting on an object determines its acceleration. According to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to its mass. The direction of the acceleration is in the direction of the net force.
Can the net force be negative?
+The concept of a negative net force might seem confusing because forces are vector quantities and do not have an intrinsic positive or negative value. However, when calculating the net force, a “negative” result simply indicates that the net force is acting in the opposite direction to what was initially considered positive. For example, if you consider forward as positive and calculate a net force of -300 N, it means the net force is 300 N in the backward direction.