The development of new bipolar medication has been a significant focus of research in the field of psychiatry, driven by the need for more effective and safer treatments for this complex and debilitating condition. Bipolar disorder, characterized by extreme mood swings that range from manic highs to depressive lows, affects millions of people worldwide, with a significant impact on quality of life, relationships, and productivity. The current pharmacological landscape for bipolar disorder includes mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, each with its own set of benefits and limitations. However, the search for new bipolar medications is ongoing, aiming to address the unmet needs of patients who do not respond adequately to existing treatments or experience significant side effects.
Recent advancements in neurobiology and pharmacology have led to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder, paving the way for the development of novel therapeutic agents. These advancements include insights into the role of neurotransmitters, the impact of stress on brain function, and the potential of new molecular targets for intervention. For instance, research into the glutamatergic system has highlighted its potential as a target for new bipolar medications, given its role in mood regulation and synaptic plasticity. Similarly, the exploration of inflammatory pathways and their modulation has opened up new avenues for therapeutic development, considering the link between inflammation and bipolar disorder.
Key Points
- The need for new bipolar medications stems from the limitations of current treatments, including efficacy and side effect profiles.
- Advancements in understanding the neurobiology of bipolar disorder have identified potential new targets for therapeutic intervention.
- Research into the glutamatergic system, inflammatory pathways, and other molecular targets is ongoing.
- Novel therapeutic approaches, including psychedelic-assisted therapy and personalized medicine, are being explored.
- The development of new medications must consider the complex interplay between biological, psychological, and environmental factors in bipolar disorder.
Current Landscape and Unmet Needs
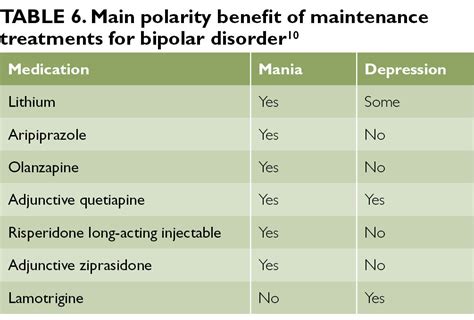
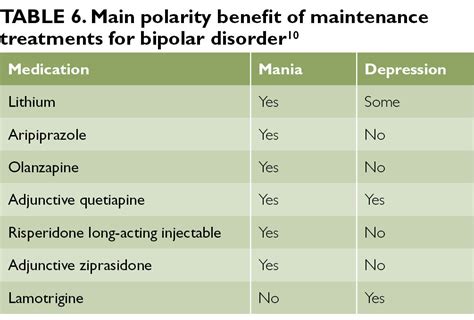
The current treatment landscape for bipolar disorder is characterized by a range of pharmacological options, each with its specific indications, efficacy, and side effect profile. Lithium, valproate, and lamotrigine are among the most commonly used mood stabilizers, while antipsychotics like olanzapine and quetiapine are often prescribed for their mood-stabilizing effects. However, despite these options, many patients continue to experience significant symptoms, and the search for new bipolar medications that can offer improved efficacy, better tolerability, and more personalized treatment approaches remains a pressing need.
Emerging Therapies and Targets
Among the emerging therapies for bipolar disorder, those targeting the glutamatergic system and inflammatory pathways have shown particular promise. The glutamatergic system, given its role in synaptic plasticity and mood regulation, presents a compelling target for novel therapeutic agents. Similarly, the exploration of anti-inflammatory drugs as potential treatments for bipolar disorder reflects the growing recognition of inflammation’s role in the pathophysiology of the condition. Other areas of research include the investigation of psychedelic-assisted therapies, which have garnered attention for their potential in treating resistant depression and other mood disorders.
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Action | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamatergic Modulators | Regulation of glutamate release and uptake | Improved mood stabilization, reduced side effects |
| Anti-inflammatory Agents | Modulation of inflammatory pathways | Addressing underlying inflammatory processes, potential for improved efficacy |
| Psychedelic-Assisted Therapies | Neuroplasticity enhancement, mood regulation | Rapid and sustained improvement in depressive symptoms, potential for novel therapeutic approach |
Challenges and Future Directions

Despite the progress in understanding bipolar disorder and the development of new therapeutic targets, several challenges remain. These include the complexity of the disorder itself, the need for more robust and consistent diagnostic criteria, and the ethical considerations surrounding novel therapeutic approaches, such as psychedelic-assisted therapy. Moreover, the translation of preclinical findings into clinical practice is a significant hurdle, requiring rigorous clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy. Future directions in the development of new bipolar medications will likely involve a multidisciplinary approach, combining insights from neurobiology, psychiatry, and pharmacology to create more effective and personalized treatments.
Personalized Medicine and Biomarkers
The integration of personalized medicine approaches into the treatment of bipolar disorder represents a promising direction for future research. This involves the use of genetic and other biomarkers to predict treatment response and tailor therapeutic strategies to the individual patient. While still in its early stages, the development of biomarkers for bipolar disorder could significantly enhance treatment outcomes by reducing trial-and-error approaches to medication and minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
What are the primary challenges in developing new bipolar medications?
+The primary challenges include the complexity and heterogeneity of bipolar disorder, the need for more consistent diagnostic criteria, and the ethical considerations surrounding novel therapeutic approaches.
How do emerging therapies like glutamatergic modulators and anti-inflammatory agents work?
+These therapies work by targeting specific molecular pathways implicated in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder, such as the regulation of glutamate release and uptake, and the modulation of inflammatory processes.
What role does personalized medicine play in the development of new bipolar medications?
+Personalized medicine involves the use of genetic and other biomarkers to predict treatment response and tailor therapeutic strategies to the individual patient, potentially leading to more effective and safer treatments.
In conclusion, the development of new bipolar medications is a complex and ongoing process, driven by advances in neurobiology, pharmacology, and personalized medicine. As research continues to uncover the underlying mechanisms of bipolar disorder and to explore novel therapeutic targets, there is hope for the creation of more effective, safer, and personalized treatments for this debilitating condition. The future of bipolar disorder treatment holds promise, with potential breakthroughs on the horizon that could significantly improve the lives of those affected by this condition.