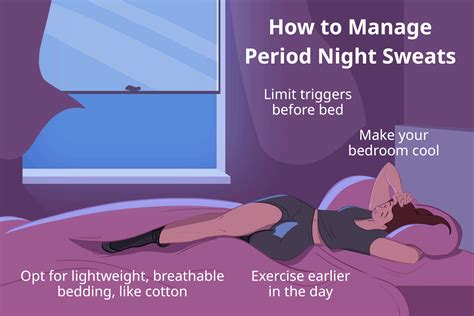
Night sweats during a woman's period can be a distressing and uncomfortable symptom, affecting the quality of life and sleep patterns. These hot flashes that occur at night, often accompanied by sweating, can be related to the hormonal changes that women experience during their menstrual cycle. The fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can influence the body's thermoregulation, leading to vasomotor symptoms like night sweats.
Estrogen plays a significant role in regulating body temperature. When estrogen levels drop, as they do right before and during menstruation, the body's thermostat can become imbalanced, leading to hot flashes and night sweats. Additionally, the shift in hormone levels can affect the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that controls body temperature, further contributing to these symptoms. Understanding the interplay between hormonal changes and thermoregulation is crucial in addressing night sweats during the menstrual cycle.
Key Points
- Hormonal fluctuations, particularly the drop in estrogen levels, contribute to night sweats during the menstrual cycle.
- The imbalance in body temperature regulation due to hormonal changes can lead to hot flashes and sweating.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a cool sleeping environment and avoiding triggers like spicy foods, can help alleviate symptoms.
- Dietary changes, including increasing omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B6 intake, may help reduce the severity of night sweats.
- In some cases, hormonal therapies or supplements, under the guidance of a healthcare provider, can be considered for managing severe symptoms.
Causes and Contributing Factors

Beyond the hormonal shifts, several other factors can contribute to or exacerbate night sweats during a woman’s period. These include stress, anxiety, and certain lifestyle choices. For instance, consuming hot or spicy foods close to bedtime can trigger night sweats. Similarly, wearing heavy or warm clothing to bed and having a high room temperature can make the body more prone to sweating. Stress and anxiety, which can be heightened during the premenstrual phase due to hormonal changes, can also lead to an increase in body temperature and sweating.
Impact of Lifestyle on Night Sweats
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in reducing the frequency and severity of night sweats. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation, and ensuring adequate sleep can help in managing stress and reducing symptoms. Dietary changes, such as increasing the intake of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts) and vitamin B6 (found in bananas, potatoes, and chicken), may also help in alleviating night sweats due to their potential effects on hormonal balance and stress reduction.
| Food Type | Nutritional Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fatty Fish | Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
| Bananas | High in Vitamin B6 |
| Flaxseeds | Good Source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
| Potatoes | Rich in Vitamin B6 |

Management and Treatment Options

For many women, making lifestyle adjustments and using home remedies can significantly reduce the discomfort caused by night sweats. However, in cases where night sweats are severe or disrupt daily life, seeking medical advice is recommended. A healthcare provider may suggest hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills, which can help stabilize hormonal fluctuations. Additionally, certain supplements like black cohosh or vitamin D may be recommended for their potential benefits in reducing hot flashes and night sweats, although their effectiveness can vary and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Importance of Medical Consultation
It’s crucial for women experiencing night sweats, especially if they are severe or accompanied by other symptoms like heavy bleeding, significant mood changes, or persistent discomfort, to consult with a healthcare provider. A medical professional can provide a comprehensive evaluation, considering the woman’s overall health, medical history, and the severity of symptoms, to determine the most appropriate management strategy. This might include prescribing medication, recommending lifestyle changes, or suggesting alternative therapies.
What are the primary causes of night sweats during the menstrual cycle?
+The primary causes include hormonal fluctuations, particularly the drop in estrogen levels, and can be exacerbated by lifestyle factors such as stress, certain foods, and environmental temperature.
How can lifestyle modifications help in reducing night sweats?
+Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, dietary changes to include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B6, and ensuring a cool sleeping environment can help reduce the frequency and severity of night sweats.
When should I consult a healthcare provider about my night sweats?
+You should consult a healthcare provider if your night sweats are severe, disrupt your daily life, or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms. A healthcare provider can offer personalized advice and treatment options based on your specific situation.
In conclusion, night sweats during a woman’s period, while distressing, can often be managed through a combination of lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, and, in some cases, medical interventions. Understanding the causes and being proactive about seeking advice can significantly improve comfort and quality of life. By acknowledging the complex interplay between hormonal fluctuations, lifestyle factors, and individual variability, women can work towards finding effective solutions to this common, yet often disruptive, symptom of the menstrual cycle.