Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the structure of molecules. In NMR spectroscopy, the sample is dissolved in a solvent, and the solvent can sometimes give rise to peaks in the NMR spectrum. These peaks are known as solvent peaks and can be a source of interference, making it challenging to interpret the spectrum. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to NMR solvent peaks, including their origin, types, and how to avoid or minimize them.
Introduction to NMR Solvent Peaks

NMR solvent peaks arise from the nuclei of the solvent molecules, which are present in large excess compared to the sample molecules. The most common solvents used in NMR spectroscopy are deuterated solvents, such as deuterium oxide (D2O), deuterated chloroform (CDCl3), and deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO-d6). These solvents are used because they provide a lock signal, which helps to stabilize the magnetic field and improve the resolution of the spectrum. However, the solvent molecules can also give rise to peaks in the spectrum, which can overlap with the peaks of the sample molecules.
Types of NMR Solvent Peaks
There are several types of NMR solvent peaks, including:
- Deuterium solvent peaks: These peaks arise from the deuterium nuclei in the solvent molecules. They are typically observed in the ¹H NMR spectrum and can be minimized by using a deuterium lock signal.
- Proton solvent peaks: These peaks arise from the proton nuclei in the solvent molecules. They are typically observed in the ¹H NMR spectrum and can be minimized by using a proton-decoupled solvent or by applying a solvent suppression technique.
- Carbon solvent peaks: These peaks arise from the carbon nuclei in the solvent molecules. They are typically observed in the ¹³C NMR spectrum and can be minimized by using a carbon-decoupled solvent or by applying a solvent suppression technique.
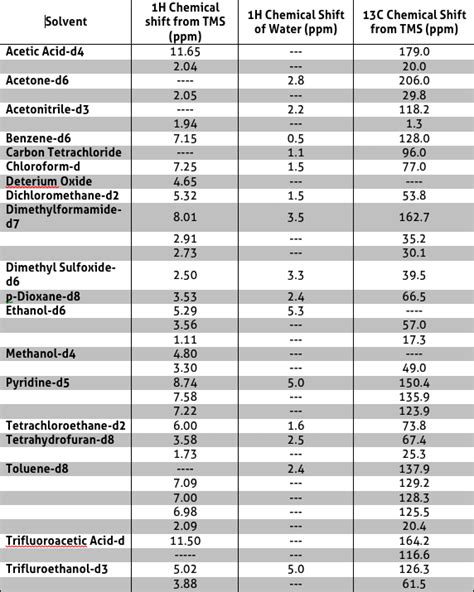
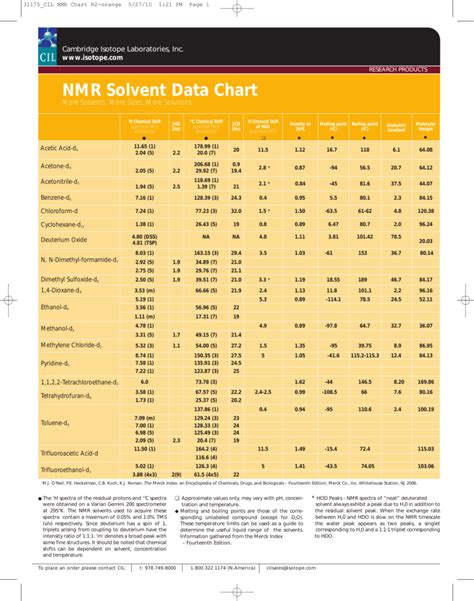
| Solvent | ¹H NMR Peak (ppm) | ¹³C NMR Peak (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| CDCl3 | 7.26 | 77.0 |
| DMSO-d6 | 2.50 | 39.5 |
| D2O | 4.79 | - |
Minimizing NMR Solvent Peaks
There are several techniques that can be used to minimize NMR solvent peaks, including:
- Solvent suppression techniques: These techniques, such as presaturation or gradient-based methods, can be used to suppress the solvent peaks in the spectrum.
- Deuterium lock signal: Using a deuterium lock signal can help to stabilize the magnetic field and minimize the deuterium solvent peaks.
- Proton-decoupled solvent: Using a proton-decoupled solvent, such as CDCl3, can help to minimize the proton solvent peaks.
- Carbon-decoupled solvent: Using a carbon-decoupled solvent, such as DMSO-d6, can help to minimize the carbon solvent peaks.
Practical Applications of NMR Solvent Peaks
NMR solvent peaks have several practical applications, including:
- Quantification of sample concentration: By measuring the intensity of the solvent peaks, researchers can quantify the concentration of the sample molecules.
- Validation of NMR spectra: Solvent peaks can be used as a reference to validate the accuracy of NMR spectra.
- Optimization of NMR experiments: By understanding the origin and types of solvent peaks, researchers can optimize NMR experiments to minimize interference and improve the quality of the spectra.
Key Points
- NMR solvent peaks arise from the nuclei of the solvent molecules and can interfere with the interpretation of the spectrum.
- There are several types of NMR solvent peaks, including deuterium, proton, and carbon solvent peaks.
- Techniques such as solvent suppression, deuterium lock signal, and proton-decoupled or carbon-decoupled solvents can be used to minimize NMR solvent peaks.
- NMR solvent peaks have practical applications, including quantification of sample concentration, validation of NMR spectra, and optimization of NMR experiments.
- Understanding the origin and types of solvent peaks is essential for accurate and reliable results in NMR spectroscopy.
In conclusion, NMR solvent peaks are an essential aspect of NMR spectroscopy, and understanding their origin and types is crucial for accurate and reliable results. By using techniques such as solvent suppression, deuterium lock signal, and proton-decoupled or carbon-decoupled solvents, researchers can minimize NMR solvent peaks and optimize NMR experiments. The practical applications of NMR solvent peaks, including quantification of sample concentration, validation of NMR spectra, and optimization of NMR experiments, make them a valuable tool in the field of NMR spectroscopy.
What are NMR solvent peaks?
+NMR solvent peaks are peaks in the NMR spectrum that arise from the nuclei of the solvent molecules.
How can NMR solvent peaks be minimized?
+NMR solvent peaks can be minimized using techniques such as solvent suppression, deuterium lock signal, and proton-decoupled or carbon-decoupled solvents.
What are the practical applications of NMR solvent peaks?
+NMR solvent peaks have practical applications, including quantification of sample concentration, validation of NMR spectra, and optimization of NMR experiments.