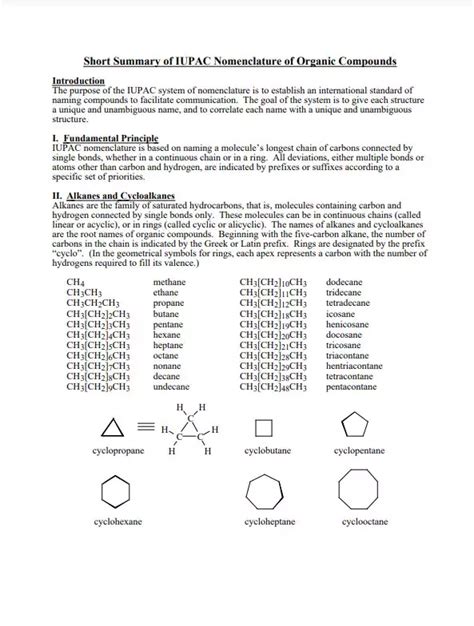
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) naming conventions are a set of rules used to generate unique and consistent names for chemical compounds. These conventions are essential in chemistry, as they provide a standardized way of communicating complex chemical information. Mastering IUPAC naming can seem daunting at first, but with practice and a few key tips, it can become second nature. In this article, we will delve into five essential IUPAC naming tips that will help you navigate the world of chemical nomenclature with confidence.
Key Points
- Understanding the basics of IUPAC naming, including parent compounds and substituents.
- Learning the prefixes and suffixes used in IUPAC names.
- Applying the rules for numbering the carbon chain in a molecule.
- Recognizing and naming functional groups and substituents.
- Practicing with complex molecules to reinforce understanding of IUPAC naming rules.
Tip 1: Mastering the Basics of IUPAC Naming

The foundation of IUPAC naming lies in identifying the parent compound and any substituents. The parent compound is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms, which determines the base name of the compound. Substituents are groups attached to the parent chain, and they are named using specific prefixes. For example, a methyl group (CH3) is named using the prefix “methyl-”. Understanding the hierarchy of substituents and how they are named is crucial for generating correct IUPAC names.
IUPAC Naming Hierarchy
The IUPAC naming hierarchy dictates that the parent compound is named first, followed by the substituents in alphabetical order. When there are multiple substituents of the same type, they are indicated by prefixes such as “di-” for two, “tri-” for three, and so on. This hierarchical approach ensures that IUPAC names are unique and unambiguous.
| Prefix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| mono- | one |
| di- | two |
| tri- | three |
| tetra- | four |
| penta- | five |
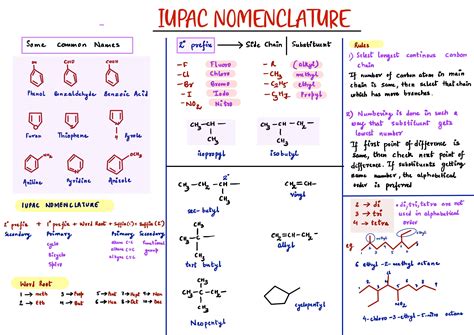
Tip 2: Learning Prefixes and Suffixes
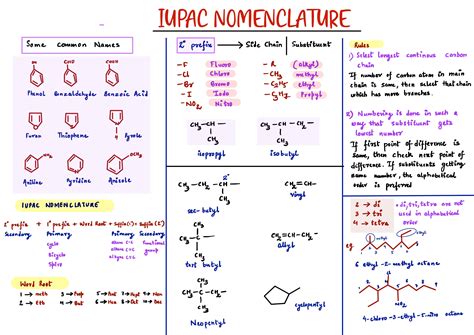
IUPAC names are constructed using a combination of prefixes, roots, and suffixes. Prefixes indicate the type and number of substituents, roots indicate the size of the parent chain, and suffixes indicate the type of functional group present. For example, the suffix “-ane” indicates an alkane (a saturated hydrocarbon), while the suffix “-ene” indicates an alkene (an unsaturated hydrocarbon with one or more double bonds). Familiarizing yourself with these prefixes and suffixes is essential for decoding and constructing IUPAC names.
Common IUPAC Suffixes
Some common IUPAC suffixes include “-ol” for alcohols, “-al” for aldehydes, and “-oic acid” for carboxylic acids. Understanding the meaning of these suffixes can help you quickly identify the functional group present in a molecule and construct the correct IUPAC name.
Example: The compound CH3CH2CH2OH would be named using the suffix "-ol" to indicate the alcohol functional group, resulting in the name "propan-1-ol".
Tip 3: Numbering the Carbon Chain
Correctly numbering the carbon chain is crucial in IUPAC naming. The chain should be numbered to give the lowest possible numbers to the substituents. If there are multiple substituents, the chain should be numbered to give the lowest number to the substituent that comes first alphabetically. This rule ensures consistency and clarity in IUPAC names.
Numbering the Chain with Multiple Substituents
When there are multiple substituents, it’s essential to prioritize them correctly. Functional groups generally take precedence over alkyl groups, and when there are multiple functional groups, they are prioritized based on their suffix in the IUPAC naming hierarchy.
Example: In the compound CH3CH2CH2COOH, the carboxylic acid group takes precedence over the alkyl groups, resulting in the name "propanoic acid".
Tip 4: Recognizing and Naming Functional Groups and Substituents
Functional groups and substituents are crucial components of IUPAC names. Recognizing these groups and knowing how to name them is essential for constructing correct IUPAC names. Functional groups such as alcohols, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids have specific suffixes, while substituents like methyl and ethyl groups have specific prefixes.
Common Functional Groups and Their Suffixes
Some common functional groups and their suffixes include the alcohol (-ol), aldehyde (-al), and carboxylic acid (-oic acid) groups. Understanding these suffixes and how to apply them is vital for accurate IUPAC naming.
| Functional Group | Suffix |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | -ol |
| Aldehyde | -al |
| Carboxylic Acid | -oic acid |
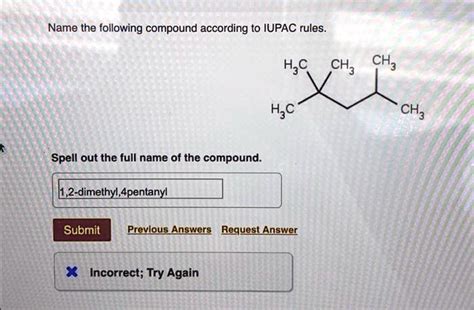
Tip 5: Practicing with Complex Molecules
Once you have a grasp of the basics, it’s essential to practice with more complex molecules. This includes molecules with multiple substituents, functional groups, and branches. Practicing with these complex molecules will help reinforce your understanding of IUPAC naming rules and improve your ability to construct correct names.
Real-World Applications of IUPAC Naming
IUPAC naming is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world applications in chemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. Being able to accurately name and identify chemical compounds is crucial for research, development, and communication in these fields.
In conclusion, mastering IUPAC naming requires a combination of understanding the basics, learning prefixes and suffixes, correctly numbering the carbon chain, recognizing and naming functional groups and substituents, and practicing with complex molecules. By following these tips and practicing regularly, you can become proficient in IUPAC naming and enhance your understanding and communication of chemical information.
What is the purpose of IUPAC naming in chemistry?
+The purpose of IUPAC naming is to provide a standardized system for naming chemical compounds, ensuring clarity, consistency, and uniqueness in chemical communication.
How do I determine the parent compound in IUPAC naming?
+The parent compound is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule. It determines the base name of the compound and is essential for constructing the IUPAC name.
What is the difference between a prefix and a suffix in IUPAC naming?
+A prefix indicates the type and number of substituents, while a suffix indicates the type of functional group present in the molecule. Both are crucial components of IUPAC names.