The NO2 molecule, also known as nitrogen dioxide, is a crucial compound in atmospheric chemistry and a significant pollutant. Understanding its Lewis structure is essential for grasping its chemical properties and reactivity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of NO2, exploring its Lewis structure, bonding, and implications for its behavior.
Key Points
- The NO2 molecule consists of one nitrogen atom and two oxygen atoms.
- The central nitrogen atom shares two pairs of electrons with each oxygen atom, forming a double bond with one oxygen and a single bond with the other.
- The NO2 molecule has a bent or V-shape due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
- The Lewis structure of NO2 is essential for understanding its chemical properties, such as its reactivity and polarity.
- NO2 plays a significant role in atmospheric chemistry, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Lewis Structure
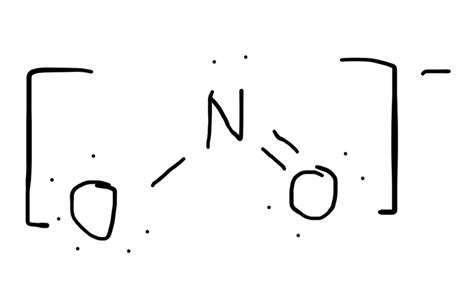
To construct the Lewis structure of NO2, we start by determining the total number of valence electrons. Nitrogen has five valence electrons, and each oxygen atom has six. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in NO2 is 5 (N) + 2 * 6 (O) = 17. We then draw the skeleton structure, placing the nitrogen atom in the center and the two oxygen atoms on either side. Next, we connect the atoms with single bonds, which accounts for four electrons. The remaining 13 electrons are distributed around the atoms to satisfy the octet rule, resulting in a double bond between the nitrogen and one oxygen atom, and a single bond between the nitrogen and the other oxygen atom.
Bonding in NO2
The NO2 molecule exhibits a mix of single and double bonds between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms. The double bond is characterized by a shorter bond length and higher bond energy compared to the single bond. The presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom also influences the molecular geometry, resulting in a bent or V-shape. This unique arrangement of electrons and bonds contributes to the molecule’s polarity and reactivity.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Bond Order |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 5 | 2 (double bond) and 1 (single bond) |
| Oxygen (O1) | 6 | 2 (double bond) |
| Oxygen (O2) | 6 | 1 (single bond) |

Implications of the NO2 Lewis Structure

The Lewis structure of NO2 has significant implications for its chemical properties and behavior. The molecule’s polarity and reactivity make it a key player in atmospheric chemistry, contributing to the formation of ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter. Understanding the NO2 Lewis structure is essential for developing strategies to mitigate its harmful effects on human health and the environment. Furthermore, the NO2 molecule serves as a model system for studying the chemistry of nitrogen oxides, which are crucial components of combustion processes and atmospheric reactions.
Atmospheric Chemistry and Air Quality
NO2 is a primary pollutant emitted by fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, and vehicle emissions. In the atmosphere, NO2 can react with other pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and ozone (O3), to form ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter. These secondary pollutants can have severe impacts on human health, including respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and even premature death. Therefore, understanding the NO2 Lewis structure and its chemical properties is crucial for developing effective strategies to reduce NO2 emissions and mitigate its harmful effects on air quality and human health.
What is the significance of the NO2 Lewis structure in atmospheric chemistry?
+The NO2 Lewis structure is essential for understanding its chemical properties and reactivity, which influence its role in atmospheric chemistry and air quality. The molecule's polarity and reactivity make it a key contributor to the formation of ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter.
How does the NO2 molecule's bent shape affect its chemical properties?
+The NO2 molecule's bent shape, resulting from the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, contributes to its polarity and reactivity. The bent shape allows the molecule to participate in various reactions, influencing its chemical properties and behavior in atmospheric chemistry.
What are the primary sources of NO2 emissions?
+The primary sources of NO2 emissions include fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, and vehicle emissions. These sources release NO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to its harmful effects on air quality and human health.
In conclusion, the NO2 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in understanding the chemical properties and behavior of nitrogen dioxide. By examining the molecule’s bonding, polarity, and reactivity, we can gain insights into its role in atmospheric chemistry and air quality. As we continue to explore the complexities of NO2 chemistry, we can develop effective strategies to mitigate its harmful effects and improve our understanding of this crucial pollutant.