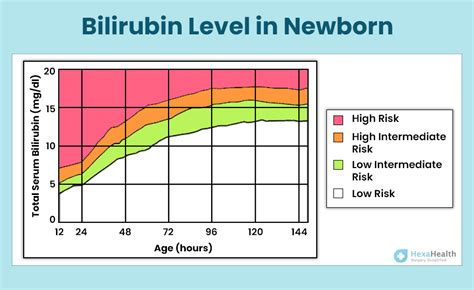
Understanding bilirubin levels in infants is crucial for their health and well-being. Bilirubin is a yellow compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in red blood cells. In infants, especially those who are newly born, the liver might not be mature enough to process bilirubin as efficiently as it should, leading to its accumulation in the blood. This condition is known as jaundice and is characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
Normal Bilirubin Levels in Infants
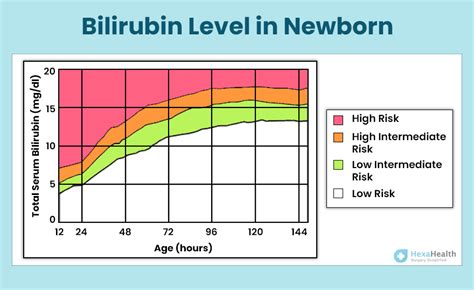
The normal bilirubin level in infants can vary depending on several factors, including the age of the infant in hours or days, whether the infant is premature or full-term, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions. Generally, bilirubin levels are considered normal if they are below certain thresholds that are established based on these factors. For newborns, bilirubin levels typically peak around the 3rd to 5th day of life and then gradually decrease. High levels of bilirubin can be dangerous and may require treatment to prevent serious complications such as kernicterus, a type of brain damage caused by high bilirubin levels.
Interpretation of Bilirubin Levels
Interpreting bilirubin levels in infants requires careful consideration of the clinical context. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) provides guidelines for the management of neonatal jaundice, which include the use of bilirubin level thresholds to determine the need for phototherapy or other treatments. These guidelines take into account the age of the infant, the gestational age at birth, and the presence of risk factors for severe jaundice. For example, premature infants or those with hemolytic disease of the newborn may require more aggressive management of bilirubin levels due to their increased risk of complications.
Key Points
- Normal bilirubin levels in infants vary based on age and other factors.
- High bilirubin levels can lead to jaundice and potentially serious complications.
- Guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics help determine the need for treatment based on bilirubin levels and clinical context.
- Phototherapy is a common treatment for high bilirubin levels, using light to help break down bilirubin in the skin.
- Monitoring and managing bilirubin levels is crucial in the first few days of life to prevent complications.
Table 1 below provides a general outline of bilirubin levels in infants at different ages, though it's essential to refer to the most current clinical guidelines and consult with healthcare professionals for specific advice.
| Age (Hours) | Bilirubin Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| 0-24 | < 5 |
| 24-48 | < 8 |
| 48-72 | < 12 |
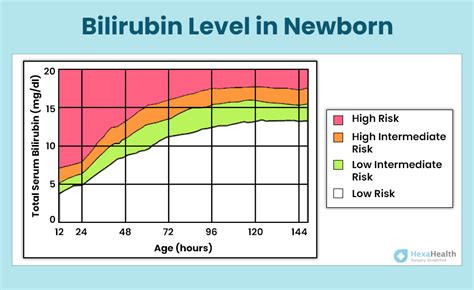
Management and Treatment
The management of high bilirubin levels in infants typically involves phototherapy, where the infant is placed under a special light that helps to break down bilirubin in the skin, making it easier for the liver to process. In more severe cases, exchange transfusion may be necessary to quickly reduce bilirubin levels. Breastfeeding is also encouraged as it can help in the excretion of bilirubin. The decision to start treatment depends on the bilirubin level, the age of the infant, and the presence of any risk factors for complications.
Complications of High Bilirubin Levels
High bilirubin levels can lead to serious complications if not managed properly. Kernicterus, a condition characterized by brain damage due to high bilirubin levels, is a significant concern. Early recognition and treatment of high bilirubin levels are critical to preventing such complications. Parents and caregivers should be aware of the signs of jaundice and seek medical attention if they notice any yellowing of the skin or eyes in their infant.
What are the signs of jaundice in infants?
+The signs of jaundice in infants include a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes. It's also important to look for other signs such as lethargy, poor feeding, or dark urine.
How is jaundice treated in newborns?
+Treatment for jaundice in newborns typically involves phototherapy. In more severe cases, exchange transfusion may be necessary. Breastfeeding and ensuring adequate hydration are also important.
Can high bilirubin levels cause long-term problems?
+Yes, very high bilirubin levels can cause long-term problems, including kernicterus, which is a type of brain damage. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent such complications.
In conclusion, understanding and managing bilirubin levels in infants is a critical aspect of neonatal care. By recognizing the signs of jaundice, understanding the risks associated with high bilirubin levels, and following established guidelines for treatment, healthcare providers and parents can work together to ensure the best possible outcomes for newborns.