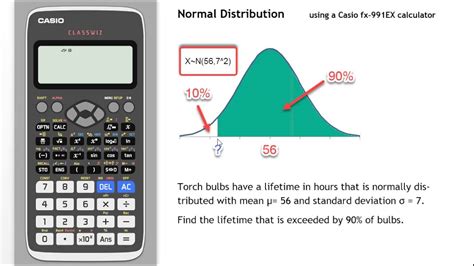
The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution, is a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis. It is a probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean. In various fields, including economics, engineering, and social sciences, understanding and calculating normal distribution is crucial for making informed decisions and predictions. Here are five tips for using a normal distribution calculator effectively, along with a deeper dive into the principles and applications of normal distribution.
Key Points
- Understanding the parameters of the normal distribution, including mean and standard deviation, is essential for accurate calculations.
- Choosing the right type of normal distribution calculator, whether for z-scores, probabilities, or inverse calculations, depends on the specific problem you're trying to solve.
- Interpreting the results correctly, considering the context of your data and the question being asked, is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
- Ensuring the data meets the assumptions of normality is important for the validity of the calculations and subsequent analyses.
- Practicing with real-world examples and datasets can help in mastering the use of normal distribution calculators and deepening your understanding of statistical concepts.
Understanding Normal Distribution Parameters
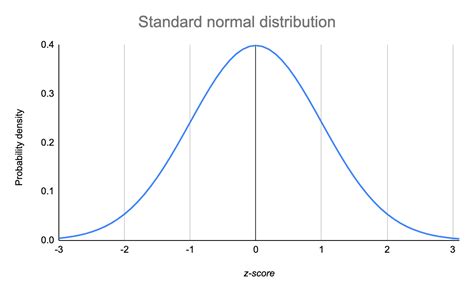
The normal distribution is characterized by two parameters: the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). The mean is the average value of the dataset, while the standard deviation measures the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Understanding these parameters is crucial because they define the shape and position of the normal distribution curve.
Calculating Z-Scores
A z-score indicates how many standard deviations an element is from the mean. A z-score is calculated using the formula: z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value of the element, μ is the mean of the dataset, and σ is the standard deviation. Z-scores are useful for comparing the relative positions of data points within a distribution. For instance, a z-score of 1 means that the data point is 1 standard deviation above the mean, and a z-score of -1 means it is 1 standard deviation below the mean.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean (μ) | The average value of the dataset. |
| Standard Deviation (σ) | A measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. |
| Z-Score | A measure of how many standard deviations an element is from the mean. |
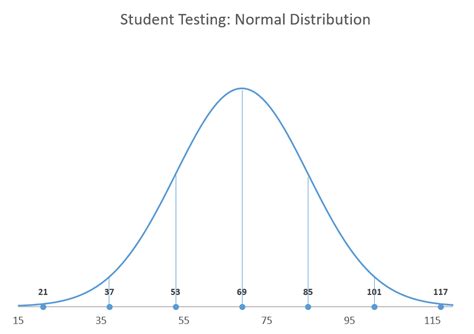
Choosing the Right Calculator
There are various types of normal distribution calculators available, each designed to solve specific problems. Some calculators are used to find the probability of a value given the mean and standard deviation (z-score to probability), while others are used to find the z-score given a probability (inverse normal distribution). The choice of calculator depends on the specific question being asked. For example, if you want to know the probability that a student will score above a certain threshold on a test, you would use a calculator that computes probabilities given z-scores.
Interpreting Results
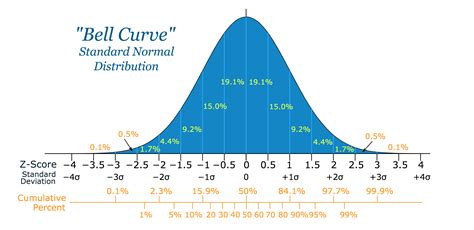
Once you have calculated the z-score or probability, it’s crucial to interpret the result correctly. For instance, if you find that a value has a z-score of 2, this means that the value is 2 standard deviations above the mean. In a normal distribution, about 95% of the values lie within 2 standard deviations of the mean, so a z-score of 2 indicates that the value is relatively rare. Understanding the implications of your calculations in the context of your data and research question is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Assumptions of Normality
Before applying normal distribution calculations, it’s important to check if your data meets the assumptions of normality. Normality assumptions include that the data should be continuous, the observations should be independent, and the data should be free from significant outliers. Violations of these assumptions can lead to incorrect conclusions. There are several tests and graphical methods, such as the Shapiro-Wilk test and Q-Q plots, that can be used to check for normality.
What is the primary use of a normal distribution calculator?
+The primary use of a normal distribution calculator is to find probabilities or z-scores given certain parameters of a normal distribution, facilitating statistical analysis and decision-making in various fields.
How do you ensure the accuracy of calculations with a normal distribution calculator?
+Ensuring the accuracy of calculations involves verifying the input values, choosing the correct type of calculation, and interpreting the results in the appropriate context, considering the assumptions of normality and the characteristics of the data.
What are some common applications of normal distribution in real-world scenarios?
+Normal distribution is applied in various fields such as finance for risk analysis, in engineering for quality control, in social sciences for understanding population behaviors, and in medicine for clinical trials and drug development, among others.
In conclusion, mastering the use of a normal distribution calculator is a valuable skill for anyone working with statistical data. By understanding the principles of normal distribution, choosing the right calculator for the task, interpreting results correctly, ensuring data meets the assumptions of normality, and practicing with real-world examples, individuals can leverage normal distribution calculations to make informed decisions and predictions in their respective fields.