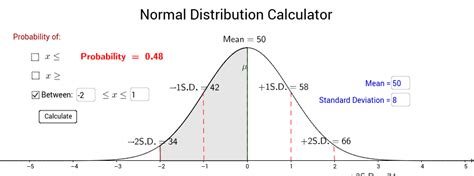
The normal probability calculator is a statistical tool used to calculate the probability of a value or range of values within a normal distribution. The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution or bell curve, is a probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, indicating that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean. In this article, we will explore five ways a normal probability calculator can be utilized, highlighting its importance in statistical analysis and decision-making processes.
Understanding the Normal Distribution
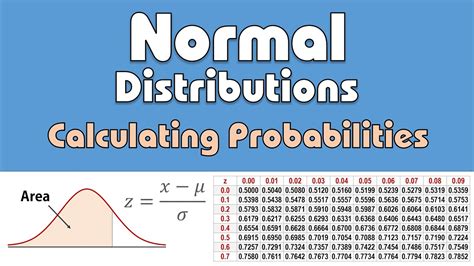
Before diving into the ways to use a normal probability calculator, it’s essential to understand the basics of the normal distribution. The normal distribution is characterized by its mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ). The mean is the central tendency of the distribution, while the standard deviation measures the amount of variation or dispersion from the mean. A small standard deviation indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean, while a large standard deviation indicates that the data points are spread out over a wider range of values.
Calculating Z-Scores
A key concept in using a normal probability calculator is the calculation of Z-scores. A Z-score tells us how many standard deviations away from the mean our value of interest is. The formula for calculating a Z-score is Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value of interest, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation. For example, if we have a mean of 80 and a standard deviation of 10, and we want to find the Z-score for a value of 90, we would calculate Z = (90 - 80) / 10 = 1. This means that the value 90 is one standard deviation above the mean.
| Value | Mean (μ) | Standard Deviation (σ) | Z-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 80 | 10 | 1 |
| 70 | 80 | 10 | -1 |
5 Ways to Use a Normal Probability Calculator

A normal probability calculator can be utilized in various ways to facilitate statistical analysis and decision-making. Here are five key ways to use this calculator:
1. Finding the Probability of a Single Value
One of the primary uses of a normal probability calculator is to find the probability of a single value occurring within a normal distribution. This involves calculating the Z-score for the given value and then using a standard normal distribution table (Z-table) or a calculator to find the corresponding probability. For instance, if we want to find the probability of a value greater than 90 in a distribution with a mean of 80 and a standard deviation of 10, we first calculate the Z-score (Z = 1) and then look up this Z-score in the Z-table to find the probability.
2. Calculating the Probability of a Range of Values
Another important use of a normal probability calculator is to calculate the probability of a range of values. This can be done by finding the Z-scores for the lower and upper bounds of the range and then using the Z-table to find the probabilities corresponding to these Z-scores. The probability of the range is then found by subtracting the probability of the lower bound from the probability of the upper bound. For example, to find the probability of values between 70 and 90, we calculate the Z-scores for 70 and 90, look up these Z-scores in the Z-table, and then subtract the probability of the Z-score for 70 from the probability of the Z-score for 90.
3. Determining Percentiles
A normal probability calculator can also be used to determine percentiles within a normal distribution. Percentiles are values below which a certain percentage of the data falls. To find a percentile, we use the inverse of the normal distribution (also known as the quantile function) to calculate the value corresponding to a given percentage. This involves finding the Z-score that corresponds to the desired percentile and then converting this Z-score back into the original scale using the formula X = μ + (Z * σ).
4. Comparing Distributions
Comparing different normal distributions is another application of a normal probability calculator. By calculating and comparing the Z-scores for different values across distributions, we can assess how likely it is for a value to occur in one distribution versus another. This comparison can be useful in a variety of contexts, such as comparing the performance of different groups or assessing the likelihood of different outcomes under varying conditions.
5. Making Predictions
Finally, a normal probability calculator can be used to make predictions about future outcomes based on historical data that follows a normal distribution. By understanding the probability of certain values or ranges of values, decision-makers can predict the likelihood of achieving specific targets or encountering particular challenges. This predictive capability is invaluable in fields such as business, finance, and engineering, where forecasting and risk assessment are critical components of strategic planning.
Key Points
- The normal probability calculator is a versatile tool for statistical analysis, offering insights into the probability of values and ranges within a normal distribution.
- Understanding the normal distribution, including its mean and standard deviation, is crucial for effective use of the calculator.
- Calculating Z-scores is a fundamental step in using the normal probability calculator, as it allows for the conversion of values into a standard scale that can be looked up in a Z-table.
- The calculator can be used for a variety of purposes, including finding the probability of single values, ranges of values, determining percentiles, comparing distributions, and making predictions.
- Applying the insights gained from a normal probability calculator can enhance decision-making in numerous fields by providing a quantitative basis for assessing probabilities and predicting outcomes.
In conclusion, the normal probability calculator is an indispensable tool for anyone working with data that follows a normal distribution. Its ability to calculate probabilities, determine percentiles, compare distributions, and make predictions based on historical data makes it a powerful instrument for statistical analysis and decision-making. As demonstrated, understanding how to use this calculator effectively requires a grasp of the normal distribution, Z-scores, and how to interpret the results in a meaningful context.
What is the primary function of a normal probability calculator?
+The primary function of a normal probability calculator is to calculate the probability of a value or range of values within a normal distribution. This is achieved by calculating the Z-score for the given value and then looking up this Z-score in a standard normal distribution table (Z-table) or using a calculator to find the corresponding probability.
How do you calculate the Z-score for a given value in a normal distribution?
+The Z-score for a given value X in a normal distribution with mean μ and standard deviation σ is calculated using the formula Z = (X - μ) / σ. This formula standardizes the value X to a Z-score, which can then be used to find the probability of the value occurring within the distribution.
What are some common applications of a normal probability calculator?
+A normal probability calculator has several common applications, including finding the probability of single values or ranges of values, determining percentiles, comparing different normal distributions, and making predictions about future outcomes based on historical data. These applications are valuable in various fields such as business, finance, engineering, and social sciences.