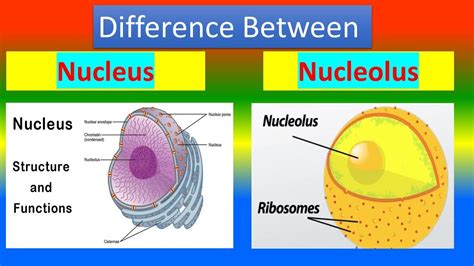
The cell nucleus and nucleolus are two of the most critical components of eukaryotic cells, playing pivotal roles in the regulation of cellular activities. While both terms are often used in the context of cell biology, they refer to distinct entities with different functions and characteristics. Understanding the differences between the nucleus and nucleolus is essential for comprehending the intricacies of cellular biology. Here, we delve into the distinctions and explore five key facts that highlight the unique aspects of each.
Introduction to the Nucleus and Nucleolus
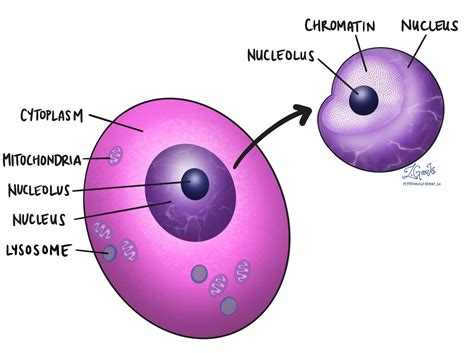
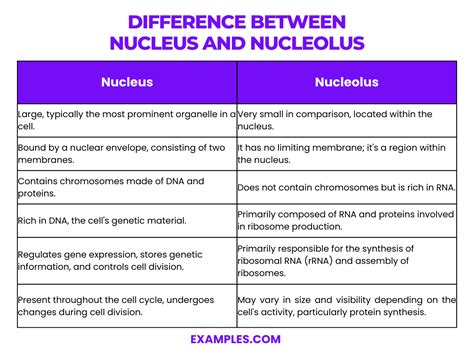
The nucleus is the control center of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. It is a membrane-bound organelle that regulates cellular activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Within the nucleus, there is a smaller region known as the nucleolus, which is involved in the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and the assembly of ribosomes. The nucleolus is not membrane-bound and appears as a dense region within the nucleus.
Key Points
- The nucleus is the primary site for DNA storage and transcription in eukaryotic cells.
- The nucleolus is responsible for ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosome assembly.
- The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope, whereas the nucleolus lacks a membrane.
- Both the nucleus and nucleolus play critical roles in cell growth, division, and response to environmental changes.
- Alterations in the structure or function of the nucleus or nucleolus can lead to various diseases, including cancer.
Functionality and Structure
One of the primary distinctions between the nucleus and nucleolus lies in their functions. The nucleus acts as the cell’s genetic library, housing the DNA that encodes the cell’s genetic blueprint. It is the site where DNA replication and transcription occur, processes that are essential for the transmission of genetic information and the synthesis of proteins. In contrast, the nucleolus is specialized for the production of ribosomal components. It transcribes rRNA genes, and the transcripts are then processed and assembled into ribosomal subunits within the nucleolus.
| Component | Function | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Stores genetic material, regulates cellular activities | Membrane-bound organelle |
| Nucleolus | Synthesizes rRNA, assembles ribosomes | Non-membrane-bound region within the nucleus |
Biological Significance
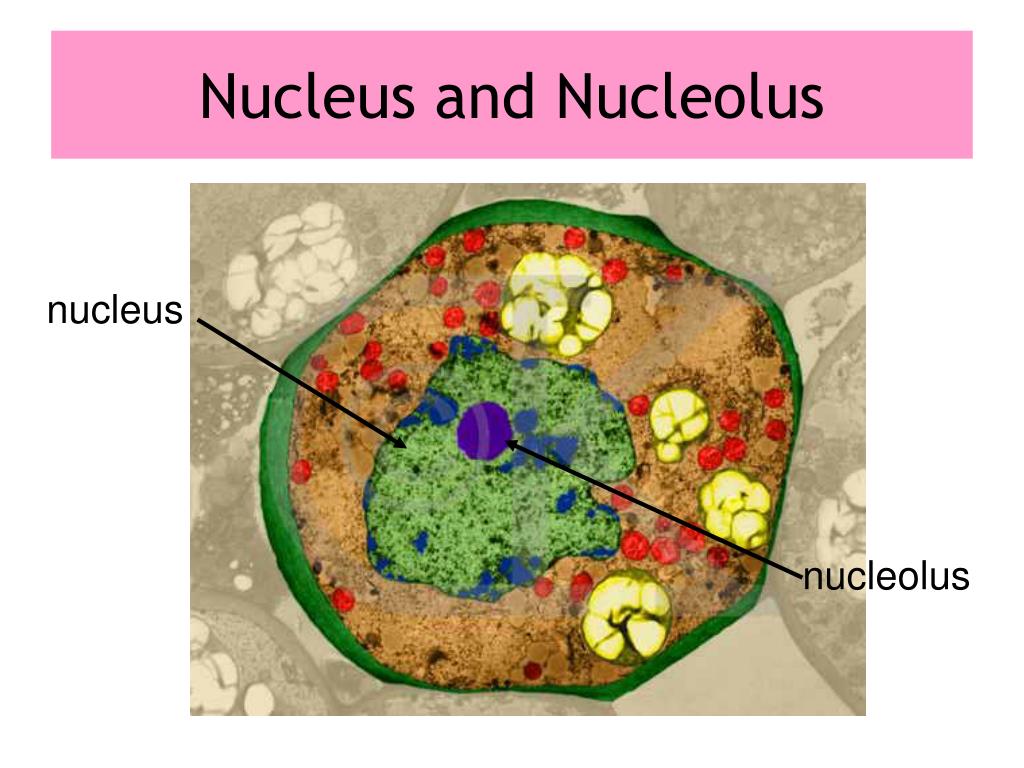
The biological significance of the nucleus and nucleolus cannot be overstated. The nucleus, by housing the cell’s genome, is central to the cell’s ability to replicate, grow, and differentiate. The nucleolus, through its role in ribosome biogenesis, is essential for protein synthesis, which is a critical component of cellular metabolism and function. Alterations in either the nucleus or nucleolus can have profound effects on cellular and organismal health, leading to conditions such as cancer, where uncontrolled cell growth and division are hallmarks of the disease.
Disease Implications
Dysfunction or alterations in the structure of the nucleus or nucleolus can have significant implications for cellular health. For instance, mutations in genes that encode proteins involved in the maintenance of nuclear structure or function can lead to diseases characterized by premature aging or increased susceptibility to cancer. Similarly, alterations in nucleolar function can impact ribosome biogenesis, leading to disorders known as ribosomopathies, which affect various tissues and organs.
In conclusion, the nucleus and nucleolus are critical components of eukaryotic cells, each with unique roles and structures. The nucleus serves as the cell's genetic control center, while the nucleolus is specialized for ribosome synthesis. Understanding the distinctions between these two entities is essential for appreciating the complex biology of eukaryotic cells and the implications of their dysfunction in disease.
What is the primary function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
+The primary function of the nucleus is to store the cell’s genetic material and regulate cellular activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
What role does the nucleolus play in cellular biology?
+The nucleolus is responsible for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and the assembly of ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis.
How do alterations in the nucleus or nucleolus affect cellular health?
+Alterations in the nucleus or nucleolus can lead to various diseases, including cancer and ribosomopathies, by disrupting normal cellular functions such as DNA replication, transcription, and protein synthesis.