In the landscape of American muscle cars and high-performance automotive engineering, the Chevrolet small-block engine line has long stood as a symbol of innovation, durability, and adrenaline-pumping power. Among its most notable developments in the early 21st century is the O Coyote engine, a testament to Ford Motor Company's commitment to pushing the boundaries of engine technology while blending classic performance with modern efficiency. Central to the conversation about high-performance V8s, the Coyote engine epitomizes a blend of advanced engineering, meticulous design, and in-depth industry understanding. As enthusiasts, mechanics, and automotive engineers alike seek comprehensive knowledge about this powerhouse, it's essential to explore its origins, technical specifications, variations, and its influence on the current and future automotive markets.
The Genesis and Evolution of the Coyote Engine

The Coyote engine first emerged as part of Ford’s commitment to revitalize its iconic V8 lineup in the early 2010s. Marked by its modular design, the original 5.0-liter version debuted in 2011 within the Mustang GT, transforming the muscle car landscape with notable advancements over its predecessor. Its name pays homage to the coyote, a native North American animal symbolizing resilience and adaptability—traits characteristic of this engine line. Beginning as an evolution of Ford’s modular V8 architecture, the Coyote was engineered from the ground up to meet rigorous performance standards, emissions regulations, and customer expectations.
This engine's strategic development drew heavily on Ford's decades-long experience in racing, particularly with the Ford GT program. The endeavor was to create an engine that combines the raw, visceral performance historically associated with American V8s while incorporating cutting-edge technology to improve fuel efficiency, reliability, and tuning potential. Over the years, the Coyote's architecture has undergone significant upgrades, marking its evolution from a simple powerplant to a versatile platform capable of handling both daily driving and competitive racing conditions. The engine's adaptability and continuous refinement underscore its foundational role in Ford's performance lineup.
Technical Foundations and Design Principles
At its core, the O Coyote engine exemplifies a modular design philosophy that emphasizes interchangeability and scalability across different vehicle applications. The latest iterations incorporate a host of technological innovations aimed at optimizing power delivery, efficiency, and durability.
Architecture and Displacement Variants
The original 5.0-liter V8 features a DOHC (Dual Overhead Camshaft) layout with four valves per cylinder. This setup allows for a broad, flat torque curve and high-revving capabilities. Subsequent variants include increased displacement versions, notably the 5.2-liter supercharged Voodoo from the GT350 and the 5.2-liter NA variant found in some Shelby models, each with specific design modifications tailored for their unique performance niches.
Key Components and Engineering Innovations
- Aluminum Cylinder Heads: Reduce overall engine weight while maintaining structural integrity.
- Double-Venturi Intake Manifold: Enhances airflow efficiency at high RPMs.
- Variable Valve Timing (VVT): Improves power and efficiency across a wider RPM range, introduced in 2018 models.
- Twin-Independent Variable Cam Timing (Ti-VCT): Offers precise control over intake and exhaust valve timing, maximizing performance and fuel economy.
- Forged Crankshaft and Pistons: Ensure resilience at high RPMs during aggressive driving or track use.
- Advanced Fuel Injection: Sequential multi-port injection system optimizes combustion and reduces emissions.
Performance Benchmarks and Specifications
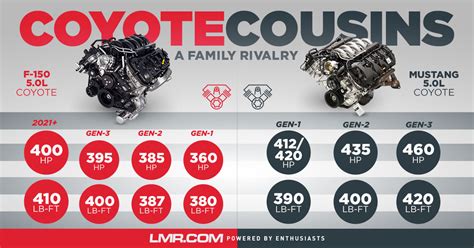
The Coyote engine’s performance metrics showcase a blend of power, efficiency, and reliability. For instance, the initial 5.0-liter variant produced approximately 412 horsepower and 390 lb-ft of torque, figures that have incrementally improved with technological updates and displacement enhancements.
| Relevance Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Peak Horsepower (2011-2014) | 412 HP at 6,500 RPM |
| Peak Torque | 390 lb-ft at 4,250 RPM |
| Redline | 7,000 RPM |
| Displacement Variants | 5.0L, 5.2L, 5.2L supercharged |
| Compression Ratio | 11.0:1 (most variants) |
| Fuel System | Sequential Multi-Port Fuel Injection |
Notably, these figures are subject to evolution with aftermarket tuning, forced induction, and ECU recalibration, which frequently push outputs beyond factory ratings. The compatibility of the architecture with various forced induction systems like superchargers and turbochargers underscores its flexibility.
Variants, Applications, and Market Position
The Coyote engine’s adaptability is evident in its deployment across multiple vehicle segments—from the Mustang to the F-150 series. Each application involves nuanced engineering considerations to optimize performance, durability, and compliance with safety and emissions standards.
Ford Mustang and Performance Models
The flagship 5.0-liter Coyote engine powers the Ford Mustang GT, serving as the benchmark for American muscle. Its integration with advanced transmission options, including six-speed manual and ten-speed automatic gearboxes, enables responsive power delivery suitable for both street and track use.
Pickup Trucks and Utility Vehicles
In the Ford F-150 lineup, the Coyote engine offers a balance of torque and fuel economy vital for towing and hauling. The engine’s design ensures longevity and efficiency under heavy loads, supported by features like high-pressure direct injection and intelligent variable valve timing.
Race and Custom Applications
High-performance racing teams leverage specially prepared Coyote engines, often employing proprietary tuning, forged internals, and forced induction components. Its robustness and modifiability have led to numerous victories in drag racing and road course events. The aftermarket industry has thrived on this platform, offering a wide range of performance parts and tuning solutions.
Limitations and Challenges

Despite its many strengths, the Coyote engine confronts certain limitations. The high-revving design, while advantageous for performance, demands meticulous maintenance and quality components to prevent issues such as valve train wear or piston failures under extreme conditions. Additionally, emissions regulations pose ongoing challenges, prompting continuous refinement in fuel management and exhaust systems.
Cost considerations also impact the aftermarket scene; high-performance parts for the Coyote can be expensive, sometimes exceeding the engine's value in heavily modified setups. Moreover, some enthusiasts argue that while the engine exhibits remarkable performance in naturally aspirated form, its full potential is unlocked with forced induction, which introduces reliability considerations and additional complexity.
Future Directions and Industry Implications
The Coyote engine line exemplifies the trend toward high-efficiency, high-performance powertrains that embed advanced technologies such as turbocharging and electrification. Ford’s ongoing investment hints at a future where turbocharged and hybrid variants of the Coyote might serve in diverse applications, including hybrid muscle cars and more sustainable performance vehicles.
Moreover, the engine's compatibility with emerging tuning methodologies, including direct-injection turbocharging, variable compression ratios, and lightweight materials, positions it at the forefront of automotive innovation. As the industry moves toward electrification, hybrid solutions rooted in traditional V8 architectures like the Coyote could offer transitional pathways that satisfy both performance and regulatory demands.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the Coyote Engine
The O Coyote engine embodies a blend of heritage, ingenuity, and adaptability. Its evolution over the past decade reflects a keen understanding of automotive engineering, consumer expectations, and industry trends. From its origins as a naturally aspirated powerhouse to its current iterations supporting forced induction and hybridization, the Coyote continues to influence high-performance automotive design profoundly.
For enthusiasts, tuners, and industry professionals, the engine remains a symbol of what modern engineering can accomplish when respecting tradition while embracing innovation. Its enduring relevance ensures the Coyote will be a cornerstone of performance motors for years to come, inspiring the next generation of powertrain technology and automotive excellence.
What are the main differences between the early and latest Coyote engine versions?
+Early versions of the Coyote, introduced in 2011, featured naturally aspirated 5.0-liter V8s with a focus on high-revving performance and durability. The latest iterations incorporate technologies like variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and improved intake systems. The most recent models also include stronger internals and optional supercharging, increasing power outputs beyond 600 horsepower with aftermarket tuning. Overall, advances have focused on improving efficiency, emissions compliance, and tuning potential without sacrificing core performance qualities.
How does the Coyote engine compare to other modern V8s in terms of reliability and performance?
+The Coyote engine is widely regarded for its balance of performance and reliability. Its forged internals and advanced manufacturing ensure durability under high-stress applications. Compared to competitors like the Chevrolet LS or Dodge’s HEMI engines, Coyote’s modular design allows for easier tuning and upgrades, making it a favorite among enthusiasts. However, like any high-performance engine, proper maintenance and quality parts are crucial to maximize longevity. Industry data shows that well-maintained Coyote engines often surpass 150,000 miles without significant issues, solidifying their reputation for dependability.
What modifications are most effective to increase the Coyote’s horsepower?
+Most effective modifications include adding a supercharger or turbocharger, upgrading the intake and exhaust systems, and tuning the ECU for optimized fuel and ignition maps. Strengthening internals with forged pistons and connecting rods allows for higher boost levels without risking internal failure. Additionally, optimizing the fuel system with larger injectors and an upgraded fuel pump supports increased power. Many tuners also recommend ECU remapping and camshaft upgrades to unlock additional horsepower, often pushing outputs well over 600 HP in fully tuned setups.
What are the maintenance considerations specific to the Coyote engine?
+Regular oil changes with high-quality synthetic oils are vital due to the high RPM operation. Valve train components, especially in highly tuned or forced induction setups, require close monitoring for wear. The timing chain system should be inspected periodically, and replacement intervals can vary—typically around 150,000 miles, depending on usage. Cooling system maintenance is also critical, as high-performance engines generate significant heat. Using OEM or racing-grade components ensures longevity, and professional tuning can prevent detonation and boost-related stress on internals.



