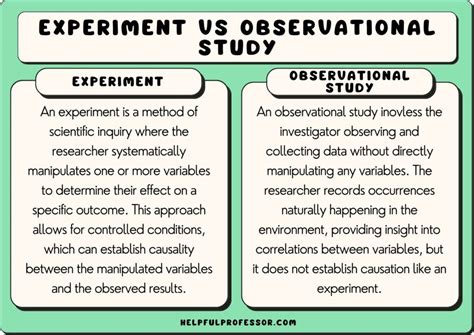
When it comes to conducting research in various fields such as medicine, psychology, and social sciences, researchers often find themselves at a crossroads, deciding between two fundamental study designs: observational and experimental. The primary distinction between these two lies in the level of control the researcher has over the variables being studied and the manner in which data is collected. Understanding the differences, advantages, and limitations of observational and experimental studies is crucial for designing, interpreting, and applying research findings effectively.
Key Points
- Observational studies involve observing participants without intervening, allowing for the collection of data in natural settings.
- Experimental studies involve manipulating one or more independent variables and measuring their effect on the dependent variable, offering high internal validity.
- The choice between observational and experimental studies depends on the research question, ethical considerations, and the degree of control needed over study variables.
- Both study types have their strengths and weaknesses, including issues related to validity, reliability, and generalizability.
- Combining insights from both observational and experimental studies can provide a more comprehensive understanding of research topics.
Observational Studies
Observational studies are characterized by the researcher’s role as an observer, where participants are not subjected to any intervention by the researcher. Instead, the researcher observes and records the behaviors, outcomes, or exposures as they naturally occur. This type of study design is often used to identify associations, correlations, or risk factors between variables. Observational studies can be further categorized into descriptive (case series, case reports), analytical (case-control, cohort), and cross-sectional studies, each serving different purposes and offering unique insights into the research question at hand.
Advantages of Observational Studies
One of the significant advantages of observational studies is their ability to be conducted in real-world settings, which enhances their external validity. They can also be less expensive and time-consuming compared to experimental studies, as they often utilize existing data or observe naturally occurring phenomena. Moreover, observational studies can explore a wide range of research questions, including those related to rare diseases or outcomes that are difficult to replicate in an experimental setting.
Limitations of Observational Studies
Despite their advantages, observational studies have several limitations. A primary concern is the potential for bias and confounding variables, which can lead to incorrect conclusions about the relationships between variables. Additionally, observational studies often lack control over extraneous variables, which can affect the outcome measures. This lack of control limits the ability to establish causality between variables, a critical aspect of understanding the underlying mechanisms of a phenomenon.
Experimental Studies
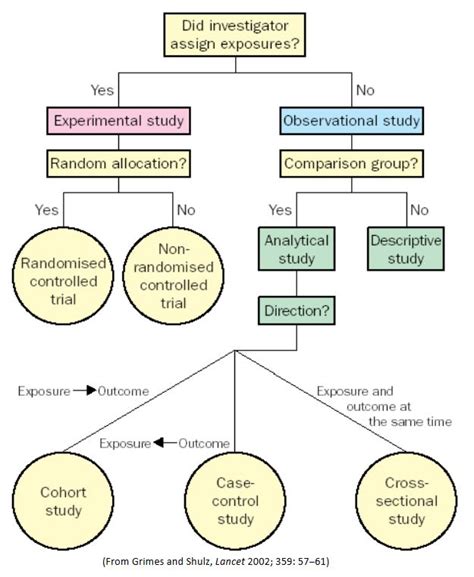
Experimental studies, on the other hand, involve the manipulation of one or more independent variables and the measurement of their effect on a dependent variable. This design allows researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables with a high degree of internal validity. Experimental studies can be conducted in controlled environments, such as laboratories, or in real-world settings, and they often involve the random assignment of participants to treatment or control groups to minimize bias.
Advantages of Experimental Studies
The primary advantage of experimental studies is their ability to establish causality between variables. By controlling for extraneous variables and manipulating the independent variable, researchers can determine whether changes in the dependent variable are due to the experimental manipulation. Experimental studies also allow for the testing of hypotheses and theories under controlled conditions, which is essential for advancing knowledge in various fields.
Limitations of Experimental Studies
However, experimental studies have their own set of limitations. They can be time-consuming, expensive, and sometimes unethical, especially when involving human subjects. The artificial nature of experimental settings can also limit the generalizability of the findings to real-world situations. Furthermore, experimental studies may not be feasible for researching certain topics, such as the effects of long-term exposure to a particular risk factor, due to ethical and practical constraints.
| Study Type | Internal Validity | External Validity | Ethical Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observational | Lower | Higher | Varying |
| Experimental | Higher | Lower | Significant |

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, both observational and experimental studies play critical roles in advancing our understanding of various phenomena. While observational studies offer insights into real-world associations and correlations, experimental studies provide the means to establish causality and test hypotheses under controlled conditions. The future of research lies in the strategic combination of these study designs, leveraging their respective strengths to address complex questions and inform evidence-based practices. By understanding the nuances of observational and experimental studies, researchers can design more effective studies, policymakers can make more informed decisions, and ultimately, society can benefit from the application of research findings to real-world problems.
What is the primary difference between observational and experimental studies?
+The primary difference lies in the level of control the researcher has over the variables being studied and the manner in which data is collected. Observational studies involve observing participants without intervening, while experimental studies involve manipulating one or more independent variables and measuring their effect on the dependent variable.
Which study design is better for establishing causality?
+Experimental studies are better suited for establishing causality between variables due to their ability to control for extraneous variables and manipulate the independent variable.
What are the ethical considerations in choosing between observational and experimental studies?
+Researchers must consider the potential risks and benefits to participants, the feasibility of the study, and the ethical implications of intervening or not intervening in the phenomenon being studied. Experimental studies, in particular, require careful consideration of ethical principles to ensure the protection of human subjects.