Odynophagia and dysphagia are two terms often used in the medical field to describe difficulties related to swallowing. While they are related, these terms have distinct meanings and implications for patient care. Understanding the differences between odynophagia and dysphagia is crucial for healthcare professionals to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, causes, symptoms, and management strategies for both conditions, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Key Points
- Odynophagia refers specifically to painful swallowing, which can be caused by various factors including infections, injuries, or conditions affecting the esophagus.
- Dysphagia is a broader term that encompasses difficulties in swallowing, which can range from mild discomfort to complete inability to swallow, and can be due to a wide array of causes.
- Accurate diagnosis is key to managing both conditions, often involving a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies, and endoscopic examinations.
- Treatment approaches vary significantly depending on the underlying cause, ranging from dietary adjustments and medication to surgical interventions.
- Early recognition and intervention are critical to prevent complications such as malnutrition, dehydration, and respiratory issues.
- Interdisciplinary care, including input from gastroenterologists, otolaryngologists, and speech-language pathologists, is often necessary for comprehensive management.
Understanding Odynophagia
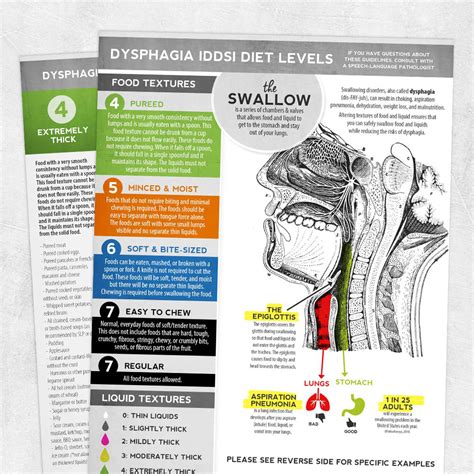
Odynophagia, or painful swallowing, is a symptom that indicates an underlying issue with the esophagus or the process of swallowing. This condition can stem from various causes, including esophageal infections (esophagitis), inflammation, or physical obstruction. The pain experienced during swallowing can vary in intensity and may be sharp, burning, or a dull ache, depending on the cause. For instance, esophageal candidiasis, a fungal infection, can cause severe odynophagia, especially in immunocompromised patients.
Causes and Symptoms of Odynophagia
The causes of odynophagia can be categorized into infectious, inflammatory, and mechanical factors. Infectious causes include viral, bacterial, or fungal infections of the esophagus. Inflammatory conditions such as eosinophilic esophagitis can also lead to painful swallowing. Mechanical factors might involve obstruction due to tumors, strictures, or foreign bodies. Symptoms can include pain upon swallowing, difficulty initiating swallows, and in severe cases, avoidance of eating or drinking due to the associated pain.
| Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Esophageal Infections | Painful swallowing, fever, difficulty eating |
| Inflammatory Conditions | Dysphagia, food impaction, chest pain |
| Mechanical Obstruction | Progressive dysphagia, regurgitation, weight loss |
Understanding Dysphagia
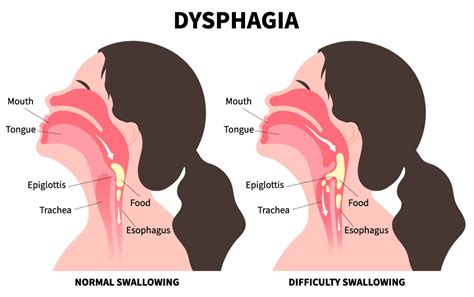
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is a more general term that can encompass a wide range of swallowing disorders. It can affect any part of the swallowing process, from the mouth to the esophagus, and can result from various neurological, structural, or functional issues. Dysphagia can manifest as trouble initiating swallows, feeling like food is stuck in the throat or chest, or coughing and choking while eating or drinking.
Causes and Symptoms of Dysphagia
The causes of dysphagia are diverse and can be categorized into oropharyngeal (related to the mouth and throat) and esophageal dysphagia. Oropharyngeal dysphagia might stem from neurological conditions such as stroke or Parkinson’s disease, while esophageal dysphagia could be due to structural issues like esophageal strictures or achalasia, a motility disorder. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include difficulty swallowing solids, liquids, or both, and symptoms like coughing, choking, or regurgitation.
Esophageal manometry and 24-hour pH monitoring are diagnostic tools that can help identify motility and acid reflux issues contributing to dysphagia. Treatment plans are highly individualized and may involve dietary modifications, swallowing exercises, medication to manage symptoms, or in some cases, surgical intervention to address underlying structural issues.
What are the primary differences between odynophagia and dysphagia?
+Odynophagia specifically refers to painful swallowing, while dysphagia is a broader term that encompasses any difficulty in swallowing, which can range from mild discomfort to severe inability to swallow.
How are odynophagia and dysphagia diagnosed?
+Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies like barium swallow or endoscopy, and in some cases, manometry or pH monitoring to evaluate esophageal function.
What are the potential complications of untreated odynophagia and dysphagia?
+Potential complications include malnutrition, dehydration, respiratory infections due to aspiration, and in severe cases, esophageal perforation or obstruction requiring emergency intervention.
In conclusion, while both odynophagia and dysphagia relate to difficulties with swallowing, they represent different aspects of this complex process. Odynophagia focuses on the pain associated with swallowing, whereas dysphagia encompasses a broader range of swallowing difficulties. Understanding these distinctions is essential for healthcare providers to offer precise diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and comprehensive management are critical in addressing these conditions and preventing potential complications.



