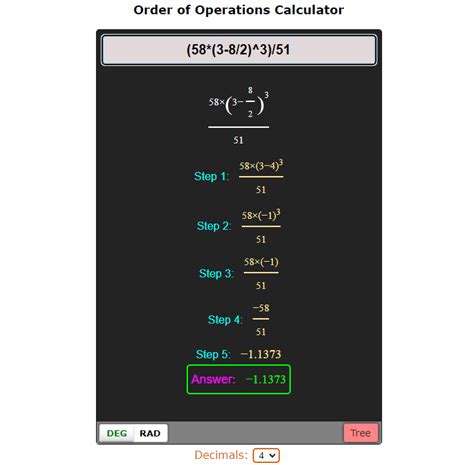
The calculator order of operations is a fundamental concept in mathematics that ensures calculations are performed in a consistent and accurate manner. It is a set of rules that dictates the order in which mathematical operations should be carried out when there are multiple operations involved in an expression. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the calculator order of operations, its importance, and how to apply it in various mathematical contexts.
Key Points
- The calculator order of operations is often remembered using the acronym PEMDAS, which stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, and Addition and Subtraction.
- This order of operations is crucial in ensuring that mathematical expressions are evaluated consistently and accurately.
- Understanding the calculator order of operations is essential for solving complex mathematical problems and for working with mathematical models in various fields such as science, engineering, and economics.
- The order of operations applies to both manual calculations and those performed using calculators or computers.
- It is important to follow the order of operations carefully to avoid errors in calculation and to ensure that the results obtained are accurate and reliable.
Introduction to the Calculator Order of Operations
The calculator order of operations is based on a simple acronym: PEMDAS. Each letter in this acronym represents the first letter of a word that corresponds to a specific mathematical operation. The order in which these operations are performed is as follows: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, and Addition and Subtraction. By following this order, one can ensure that mathematical expressions are evaluated correctly and consistently.
Understanding PEMDAS
Let’s break down the PEMDAS acronym to understand each component and how it applies to mathematical expressions:
- Parentheses: Evaluate expressions inside parentheses first. This means that any calculations within parentheses should be performed before moving on to the next step.
- Exponents: Evaluate any exponential expressions next (for example, 2^3). This step comes after evaluating expressions within parentheses because exponents can affect the outcome of the calculations within the parentheses.
- Multiplication and Division: Evaluate multiplication and division operations from left to right. This means that if an expression contains both multiplication and division, the operation that appears first from the left should be performed first.
- Addition and Subtraction: Finally, evaluate any addition and subtraction operations from left to right. Similar to multiplication and division, if both addition and subtraction are present in an expression, the operation that appears first from the left should be performed first.
| Operation | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Parentheses | 2 * (3 + 4) | Evaluate the expression inside the parentheses first: 3 + 4 = 7, then multiply by 2: 2 * 7 = 14 |
| Exponents | 2^3 * 4 | Evaluate the exponent first: 2^3 = 8, then multiply by 4: 8 * 4 = 32 |
| Multiplication and Division | 12 / 3 * 2 | Evaluate from left to right: first division, 12 / 3 = 4, then multiplication, 4 * 2 = 8 |
| Addition and Subtraction | 10 + 5 - 3 | Evaluate from left to right: first addition, 10 + 5 = 15, then subtraction, 15 - 3 = 12 |

Applying the Calculator Order of Operations in Real-World Scenarios

The calculator order of operations is not limited to simple arithmetic expressions. It applies to all mathematical operations, including those involving variables, fractions, and decimals. In real-world scenarios, such as science, engineering, economics, and computer programming, understanding and applying the order of operations is essential for solving complex problems and making accurate predictions or calculations.
Example Applications
Consider a scenario in physics where the trajectory of a projectile is being calculated. The equation for the trajectory might involve several mathematical operations, including exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction. Applying the calculator order of operations ensures that the calculations are performed in the correct order, resulting in an accurate prediction of the projectile’s path.
In economics, when calculating the cost of producing a certain quantity of goods, the formula might involve several operations, including multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction. The order of operations helps ensure that the calculations are performed correctly, leading to an accurate determination of the production costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the calculator order of operations is a foundational concept in mathematics that ensures calculations are performed accurately and consistently. By following the PEMDAS acronym and understanding the logical sequence of mathematical operations, individuals can solve complex mathematical problems with confidence. Whether in academic settings, professional environments, or everyday applications, mastering the calculator order of operations is essential for anyone who works with numbers and mathematical models.
What is the purpose of the calculator order of operations?
+The purpose of the calculator order of operations is to ensure that mathematical expressions are evaluated consistently and accurately, by providing a standardized sequence of operations to follow when there are multiple operations in an expression.
How does the calculator order of operations apply to real-world scenarios?
+The calculator order of operations applies to all mathematical operations, including those in real-world scenarios such as science, engineering, economics, and computer programming, where accurate calculations are crucial for making predictions, solving problems, and making informed decisions.
Why is it important to follow the order of operations carefully?
+Following the order of operations carefully is important because it ensures that mathematical expressions are evaluated accurately and consistently, avoiding errors in calculation that could lead to incorrect results or conclusions.