The overall ionic equation is a fundamental concept in chemistry, particularly in the realm of chemical reactions. It represents a concise way to express the reaction between ions in a solution, highlighting the reactants and products involved. Understanding how to write and balance overall ionic equations is crucial for identifying the species that actually participate in a chemical reaction, as opposed to spectator ions that do not change during the reaction.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance

To delve into the realm of overall ionic equations, it’s essential to first grasp the basics of chemical reactions and the behavior of ions in solution. Ionic compounds, which are composed of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions), dissociate into their constituent ions when dissolved in water. These ions can then react with other ions or molecules to form new compounds. The overall ionic equation provides a simplified representation of these reactions, focusing on the ions that undergo a change.
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
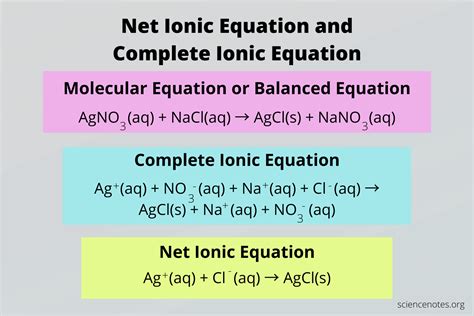
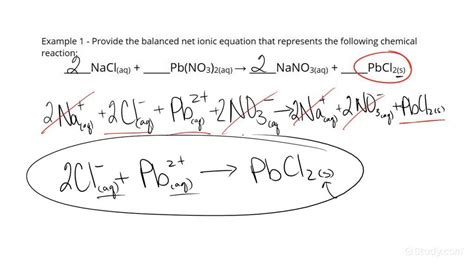
Writing an overall ionic equation involves several steps, starting with identifying the reactants and products. For instance, consider the reaction between sodium chloride (NaCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) in aqueous solutions. The first step is to write the balanced molecular equation, which includes all the reactants and products. Then, one must identify the ions present in each compound and write the total ionic equation, showing all the ions. Finally, by canceling out the spectator ions (ions that appear on both sides of the equation unchanged), one can derive the net ionic equation, also known as the overall ionic equation.
| Reaction Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Molecular Equation | Write the balanced equation with molecular formulas. |
| 2. Total Ionic Equation | Show all ions in their dissociated form. |
| 3. Net Ionic Equation | Cancel spectator ions to get the overall ionic equation. |
Key Points
- The overall ionic equation focuses on the ions that undergo a change during a chemical reaction.
- It is derived from the total ionic equation by canceling out spectator ions.
- Understanding the behavior of ions in solution is crucial for writing accurate overall ionic equations.
- The process involves identifying reactants and products, writing the molecular and total ionic equations, and then simplifying to the net ionic equation.
- Recognizing spectator ions is key to simplifying the equation and understanding the reaction's chemical changes.
Advanced Concepts and Applications

Beyond the basic steps, it’s essential to understand the conditions under which certain reactions occur. For example, the solubility of compounds can affect the availability of ions for reaction. The overall ionic equation can provide insights into these aspects by showing which ions are involved in the reaction. Furthermore, in the context of acid-base chemistry, overall ionic equations can help illustrate the donation and acceptance of protons (H+ ions), which is fundamental to understanding acid-base reactions.
Practical Applications and Examples
In practical terms, overall ionic equations are indispensable in various chemical processes, including the manufacture of chemicals, water treatment, and the study of biological systems. For instance, understanding the ionic reactions involved in the formation of precipitates is crucial in analytical chemistry for the detection and quantification of ions. Moreover, in environmental chemistry, the overall ionic equation can help predict the behavior of pollutants in aquatic systems, guiding remediation strategies.
| Field of Application | Role of Overall Ionic Equations |
|---|---|
| Chemical Manufacturing | Predicting reaction outcomes and optimizing processes. |
| Water Treatment | Understanding ion removal and water purification mechanisms. |
| Biological Systems | Elucidating the role of ions in physiological processes. |
What is the primary purpose of writing an overall ionic equation?
+The primary purpose is to clearly show which ions are involved in a chemical reaction, excluding spectator ions, to provide a simplified and informative representation of the reaction.
How do you identify spectator ions in an ionic equation?
+Spectator ions are those that appear on both sides of the total ionic equation unchanged. They can be identified by comparing the reactants and products and canceling out any ions that are common to both sides.
What is the significance of overall ionic equations in environmental chemistry?
+Overall ionic equations are significant in environmental chemistry as they help in understanding and predicting the behavior of pollutants in aquatic systems, which is crucial for developing effective water treatment and pollution remediation strategies.
In conclusion, the overall ionic equation is a powerful tool in chemistry, offering insights into the fundamental processes of chemical reactions. By mastering the art of writing and interpreting these equations, chemists can better understand complex reactions, predict outcomes, and apply this knowledge in a wide range of fields, from chemical manufacturing to environmental science. The expertise in deriving and applying overall ionic equations not only reflects a deep understanding of chemical principles but also demonstrates the ability to analyze, simplify, and predict the behavior of ions in solution, which is essential for advancing knowledge and solving real-world problems.