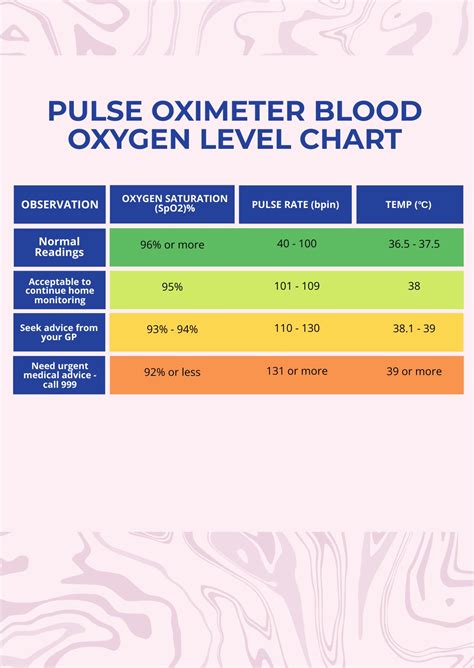
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method used to monitor the oxygen saturation of a patient's blood, as well as their heart rate. The device used to perform this measurement is called a pulse oximeter, and it provides valuable information about the patient's oxygenation status. One of the key components of pulse oximetry is the oximeter readings chart, which helps healthcare professionals interpret the results and make informed decisions about patient care.
Understanding Oximeter Readings
Oximeter readings are typically expressed as a percentage, with values ranging from 0% to 100%. The readings are calculated by measuring the changes in light absorption in oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin. A normal oximeter reading is typically considered to be between 95% and 100%, although this can vary slightly depending on the individual and the specific device being used. Readings below 90% may indicate hypoxemia, or low oxygen levels in the blood, which can be a cause for concern and may require medical attention.
Interpreting Oximeter Readings
When interpreting oximeter readings, it’s essential to consider the patient’s overall clinical condition and medical history. For example, a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may have a lower normal range due to their condition. Additionally, factors such as altitude, anemia, and carbon monoxide poisoning can affect oximeter readings. The following chart provides a general guide for interpreting oximeter readings:
| Oximeter Reading (%) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 95-100% | Normal oxygen saturation |
| 90-94% | Mild hypoxemia |
| 80-89% | Moderate hypoxemia |
| 70-79% | Severe hypoxemia |
| < 70% | Life-threatening hypoxemia |
Key Points
- Oximeter readings are used to monitor oxygen saturation and heart rate in patients.
- A normal oximeter reading is typically between 95% and 100%.
- Readings below 90% may indicate hypoxemia, which can be a cause for concern.
- Interpreting oximeter readings requires consideration of the patient's overall clinical condition and medical history.
- Oximeter readings should be used in conjunction with other clinical assessments to get a comprehensive understanding of the patient's condition.
Clinical Applications of Oximeter Readings
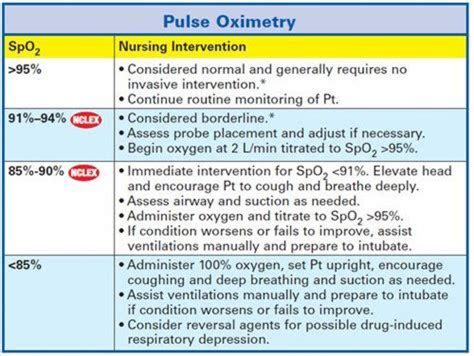
Oximeter readings have a wide range of clinical applications, from monitoring patients during surgery to assessing oxygenation status in patients with respiratory or cardiac conditions. In the emergency department, oximeter readings can help quickly identify patients who require immediate oxygen therapy or other interventions. In critical care settings, continuous oximeter monitoring can provide real-time information about the patient’s oxygenation status, allowing for prompt adjustments to treatment.
Pediatric and Neonatal Considerations
In pediatric and neonatal patients, oximeter readings can be particularly useful for monitoring oxygenation status, especially in premature infants or those with respiratory distress syndrome. However, it’s essential to consider the specific challenges and limitations of using pulse oximetry in these populations, such as the potential for inaccurate readings due to poor perfusion or movement.
When using oximeter readings in pediatric and neonatal patients, it's crucial to choose a device specifically designed for this population and to follow established guidelines for monitoring and interpretation. The following chart provides a general guide for interpreting oximeter readings in pediatric and neonatal patients:
| Age Group | Normal Oximeter Reading (%) |
|---|---|
| Newborn (0-24 hours) | 85-95% |
| Neonate (24 hours-1 week) | 90-95% |
| Infant (1 week-1 year) | 95-100% |
| Child (1-12 years) | 95-100% |
Advances in Oximeter Technology
Recent advances in oximeter technology have led to the development of more accurate and reliable devices, including those that can measure other parameters such as carbon monoxide and methemoglobin levels. Additionally, the use of wireless and mobile oximeter devices has increased, allowing for greater flexibility and convenience in monitoring patients. However, it’s essential to carefully evaluate the accuracy and reliability of these devices, as well as their potential limitations and challenges.
What is a normal oximeter reading?
+A normal oximeter reading is typically considered to be between 95% and 100%.
What does a low oximeter reading indicate?
+A low oximeter reading may indicate hypoxemia, or low oxygen levels in the blood, which can be a cause for concern and may require medical attention.
How are oximeter readings used in clinical practice?
+Oximeter readings are used to monitor oxygen saturation and heart rate in patients, and to guide clinical decision-making in a wide range of settings, from emergency departments to critical care units.
In conclusion, oximeter readings are a valuable tool for monitoring oxygen saturation and heart rate in patients, and can provide critical information for guiding clinical decision-making. By understanding how to interpret oximeter readings and considering the potential limitations and challenges associated with their use, healthcare professionals can provide better care for their patients and improve outcomes.