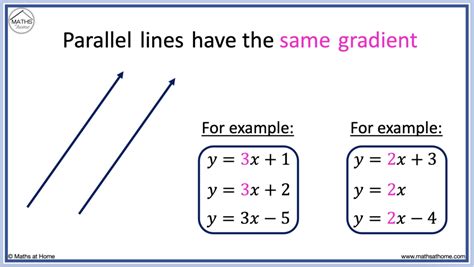
The concept of parallel lines is a fundamental aspect of geometry, and understanding how to work with their equations is crucial for various mathematical and real-world applications. Parallel lines are lines that lie in the same plane and never intersect, maintaining a constant distance between them. The equation of a line can be expressed in various forms, including slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), point-slope form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)), and standard form (Ax + By = C), where m represents the slope of the line, and b is the y-intercept.
When dealing with parallel lines, it's essential to recognize that they share the same slope (m) but have different y-intercepts (b). This means that if we have two parallel lines, their equations will be of the form y = mx + b1 and y = mx + b2, where m is the same for both lines, but b1 and b2 are different. This understanding is critical for identifying and working with parallel lines in various geometric and algebraic contexts.
Key Points
- Parallel lines have the same slope (m) but different y-intercepts (b).
- The equation of a line can be expressed in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), point-slope form (y - y1 = m(x - x1)), or standard form (Ax + By = C).
- Identifying parallel lines involves recognizing that they have the same slope but different y-intercepts.
- Working with parallel lines requires understanding their equations and how to manipulate them to solve problems.
- Applications of parallel lines include geometry, graphing, and real-world problems involving distances and relationships between lines.
Understanding Parallel Line Equations
To work effectively with parallel lines, it’s crucial to understand how to write and manipulate their equations. The slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) is particularly useful for identifying parallel lines, as it clearly shows the slope (m) and the y-intercept (b). By comparing the slopes and y-intercepts of two lines, we can determine if they are parallel. For instance, if we have two lines with equations y = 2x + 3 and y = 2x - 4, we can see that they have the same slope (m = 2) but different y-intercepts (b = 3 and b = -4), indicating that they are parallel.
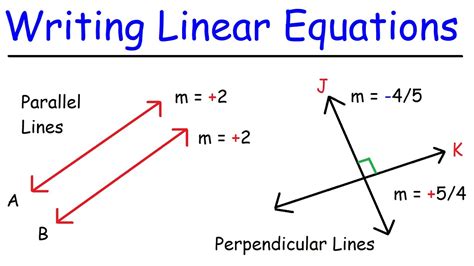
Writing Equations of Parallel Lines
Writing the equation of a line parallel to a given line involves maintaining the same slope and changing the y-intercept. For example, if we want to find the equation of a line parallel to y = 3x - 2, we keep the slope (m = 3) and change the y-intercept. If the new y-intercept is 5, the equation of the parallel line would be y = 3x + 5. This process demonstrates how to generate equations of parallel lines by adjusting the y-intercept while keeping the slope constant.
| Slope (m) | Y-Intercept (b) | Equation of the Line |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | y = 2x + 3 |
| 2 | -4 | y = 2x - 4 |
| 3 | -2 | y = 3x - 2 |
| 3 | 5 | y = 3x + 5 |
Applications of Parallel Lines
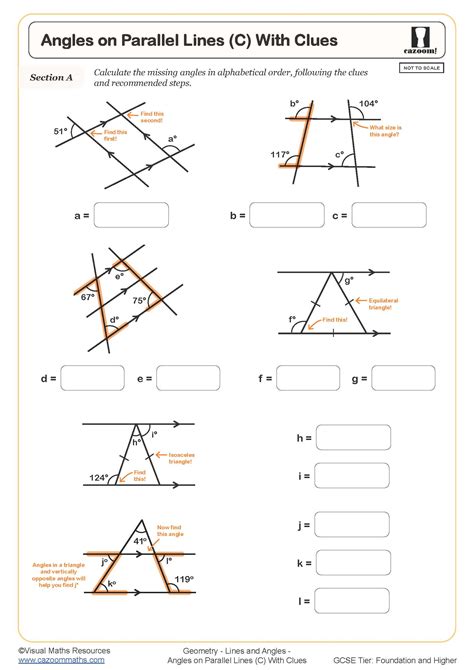
Parallel lines have numerous applications in geometry, graphing, and real-world problems. In geometry, understanding parallel lines is essential for solving problems involving angles, distances, and shapes. In graphing, recognizing parallel lines helps in understanding the behavior of functions and their relationships. Real-world applications include designing structures, understanding spatial relationships, and solving problems in physics and engineering that involve distances and forces between objects.
Geometry and Graphing
In geometry, parallel lines are used to define angles, including corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles. These angles are equal when formed by a transversal intersecting two parallel lines, which is a fundamental property used in solving geometric problems. In graphing, parallel lines can represent functions that have the same rate of change (slope) but start at different points (y-intercepts), illustrating how changes in the y-intercept affect the graph without altering its slope.
Furthermore, the concept of parallel lines is critical in understanding and working with other geometric figures, such as parallelograms and rectangles, where opposite sides are parallel. This understanding extends to more complex figures and spatial relationships, demonstrating the breadth of application of parallel lines in geometric and spatial reasoning.
What is the primary characteristic of parallel lines in terms of their equations?
+Parallel lines have the same slope (m) but different y-intercepts (b) in their equations.
How do you write the equation of a line parallel to a given line?
+To write the equation of a line parallel to a given line, you maintain the same slope (m) as the given line and change the y-intercept (b) to a new value.
What are some applications of parallel lines in real-world problems?
+Parallel lines have applications in designing structures, understanding spatial relationships, and solving problems in physics and engineering that involve distances and forces between objects.
In conclusion, understanding parallel lines and their equations is a fundamental aspect of geometry and algebra, with applications extending into various real-world problems. By recognizing the key characteristics of parallel lines, including their shared slope and different y-intercepts, individuals can better solve problems, understand geometric and spatial relationships, and apply these concepts in practical scenarios. The ability to write, manipulate, and apply the equations of parallel lines is a crucial skill that demonstrates a deep understanding of geometric principles and their applications.