Parallel processing, a fundamental concept in computer science, has revolutionized the way we approach complex computational tasks. By dividing tasks into smaller sub-tasks and processing them simultaneously, parallel processing enables computers to perform calculations at unprecedented speeds. This technology has far-reaching implications, from scientific simulations to artificial intelligence, and is a crucial component of modern computing. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of parallel processing, exploring its core principles, architectures, and applications.
Key Points
- Parallel processing divides tasks into smaller sub-tasks for simultaneous execution, significantly improving computational speed.
- There are several parallel processing architectures, including symmetric multiprocessing, asymmetric multiprocessing, and distributed processing.
- Parallel algorithms are designed to optimize task distribution, minimize communication overhead, and ensure data consistency.
- Applications of parallel processing include scientific simulations, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Programming models, such as MPI and OpenMP, provide a framework for developing parallel applications.
Introduction to Parallel Processing
Parallel processing is a technique that allows computers to execute multiple instructions or tasks concurrently, leveraging multiple processing units, such as cores or processors. This approach enables computers to tackle complex problems that would be impractical or impossible to solve using traditional sequential processing methods. By harnessing the power of parallel processing, researchers and developers can accelerate scientific discoveries, optimize business processes, and create innovative products.
Types of Parallel Processing Architectures
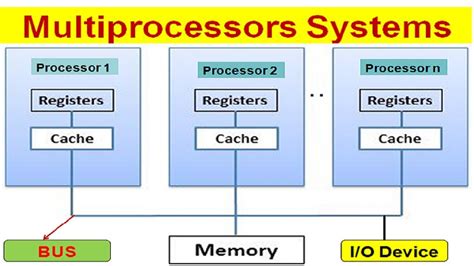
There are several parallel processing architectures, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) architectures, for example, feature multiple processors sharing a common memory space, allowing for efficient communication and data exchange. Asymmetric multiprocessing (ASMP) architectures, on the other hand, use multiple processors with separate memory spaces, requiring more complex communication protocols. Distributed processing architectures, which comprise multiple computers or nodes connected via a network, offer a scalable and flexible solution for large-scale computations.
| Architecture | Description |
|---|---|
| Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) | Multiple processors sharing a common memory space |
| Asymmetric Multiprocessing (ASMP) | Multiple processors with separate memory spaces |
| Distributed Processing | Multiple computers or nodes connected via a network |

Parallel Algorithms and Programming Models
Parallel algorithms are designed to optimize task distribution, minimize communication overhead, and ensure data consistency. These algorithms can be categorized into several types, including data parallelism, task parallelism, and pipeline parallelism. Programming models, such as Message Passing Interface (MPI) and OpenMP, provide a framework for developing parallel applications, allowing developers to create efficient and scalable code.
Applications of Parallel Processing
Parallel processing has a wide range of applications, from scientific simulations to artificial intelligence and machine learning. In scientific simulations, parallel processing enables researchers to model complex phenomena, such as climate patterns or molecular interactions, with unprecedented accuracy. In data analytics, parallel processing facilitates the rapid processing of large datasets, allowing businesses to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. In artificial intelligence and machine learning, parallel processing accelerates the training of neural networks, enabling the development of more sophisticated AI models.
What is the primary benefit of parallel processing?
+The primary benefit of parallel processing is the significant improvement in computational speed, enabling computers to tackle complex problems that would be impractical or impossible to solve using traditional sequential processing methods.
What are the different types of parallel processing architectures?
+There are several parallel processing architectures, including symmetric multiprocessing (SMP), asymmetric multiprocessing (ASMP), and distributed processing.
What are some applications of parallel processing?
+Parallel processing has a wide range of applications, including scientific simulations, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
In conclusion, parallel processing is a powerful technology that has revolutionized the way we approach complex computational tasks. By understanding the core principles, architectures, and applications of parallel processing, developers and researchers can harness its power to accelerate scientific discoveries, optimize business processes, and create innovative products. As the demand for high-performance computing continues to grow, parallel processing will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of computing.
Meta Description: Discover the power of parallel processing and how it can accelerate complex computational tasks. Learn about parallel processing architectures, algorithms, and applications, and explore the benefits of this technology for scientific simulations, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. (149 characters)