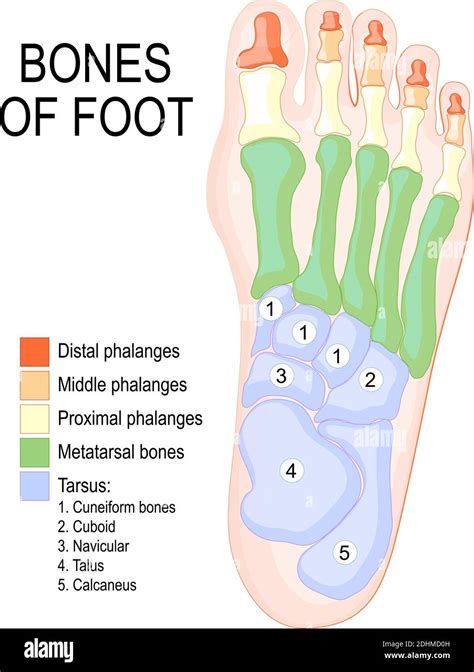
The human foot is a complex and fascinating anatomical structure, comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Understanding the different parts of the foot is essential for maintaining proper foot health, preventing injuries, and addressing various foot-related conditions. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the foot, exploring its various components, their functions, and the importance of proper foot care.
Key Points
- The foot is divided into three main sections: the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot.
- The forefoot contains the toes and the metatarsal bones, which play a crucial role in balance and mobility.
- The midfoot is composed of the cuneiform, cuboid, and navicular bones, which provide arch support and stability.
- The hindfoot is made up of the calcaneus and talus bones, which form the ankle joint and facilitate movement.
- Proper foot care is essential for preventing injuries, reducing the risk of foot-related conditions, and maintaining overall foot health.
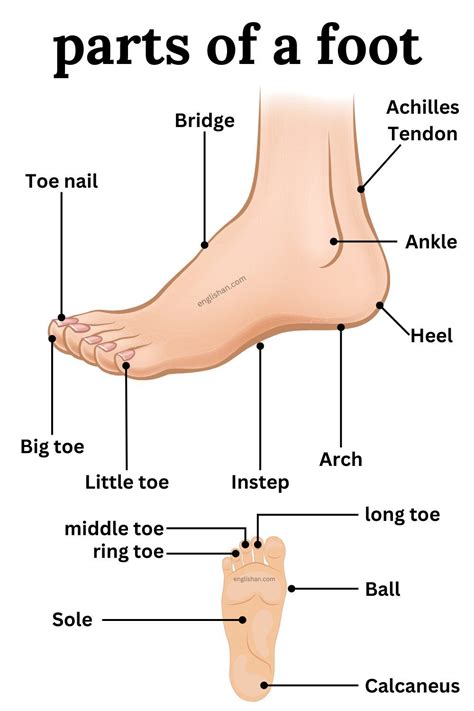
Forefoot Anatomy
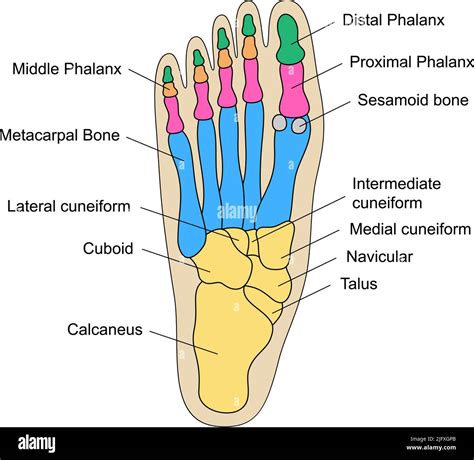
The forefoot, also known as the anterior portion of the foot, comprises the toes and the metatarsal bones. The toes are made up of phalanges, which are small bones that form the toe joints. The metatarsal bones, on the other hand, are long, thin bones that connect the toes to the rest of the foot. The forefoot plays a vital role in balance, mobility, and weight distribution, making it a critical component of the foot’s overall anatomy.
Toes and Phalanges
The toes are made up of three phalanges: the proximal, intermediate, and distal phalanges. The proximal phalanx is the base of the toe, while the intermediate phalanx is the middle section, and the distal phalanx is the tip of the toe. The toes are connected by joints, which allow for flexibility and movement. The toes also contain tendons, ligaments, and muscles, which work together to facilitate toe movement and maintain balance.
| Bone | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Phalanges | Toes | Form toe joints, facilitate movement |
| Metatarsal bones | Forefoot | Connect toes to rest of foot, provide support |
| Cuneiform bones | Midfoot | Provide arch support, stability |
| Cuboid bone | Midfoot | Facilitate movement, provide support |
| Navicular bone | Midfoot | Provide arch support, stability |
Midfoot Anatomy
The midfoot, also known as the medial portion of the foot, is composed of the cuneiform, cuboid, and navicular bones. These bones work together to provide arch support and stability, facilitating movement and weight distribution. The midfoot is a critical component of the foot’s overall anatomy, as it plays a vital role in maintaining proper foot alignment and preventing injuries.
Cuneiform, Cuboid, and Navicular Bones
The cuneiform bones are wedge-shaped bones that form the arch of the foot. The cuboid bone is a cube-shaped bone that facilitates movement and provides support. The navicular bone is a boat-shaped bone that provides arch support and stability. These bones work together to maintain proper foot alignment and prevent injuries.
Hindfoot Anatomy
The hindfoot, also known as the posterior portion of the foot, is made up of the calcaneus and talus bones. The calcaneus bone is the heel bone, which forms the heel of the foot. The talus bone is a small, cube-shaped bone that connects the calcaneus bone to the rest of the foot. The hindfoot plays a vital role in facilitating movement and maintaining proper foot alignment.
Calcaneus and Talus Bones
The calcaneus bone is the largest bone in the foot, forming the heel of the foot. The talus bone is a small, cube-shaped bone that connects the calcaneus bone to the rest of the foot. These bones work together to facilitate movement and maintain proper foot alignment.
What are the most common foot-related conditions?
+Some of the most common foot-related conditions include plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, and bunions. These conditions can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor foot care, improper footwear, and overuse.
How can I prevent foot injuries?
+Preventing foot injuries requires a combination of proper foot care, proper footwear, and regular exercise. It's essential to wear shoes that fit properly, stretch regularly, and avoid overuse.
What are the benefits of proper foot care?
+Proper foot care can help prevent injuries, reduce the risk of foot-related conditions, and maintain overall foot health. It's essential to practice good foot hygiene, wear proper footwear, and seek medical attention if you experience any foot-related issues.
In conclusion, understanding the different parts of the foot is essential for maintaining proper foot health, preventing injuries, and addressing various foot-related conditions. By recognizing the importance of proper foot care and taking steps to maintain good foot hygiene, individuals can reduce their risk of foot-related issues and enjoy overall better health.
Meta Description: Learn about the different parts of the foot, including the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot, and discover the importance of proper foot care for maintaining overall foot health. (149 characters)



