The English language is replete with complexities, and one of the most intriguing aspects is the verb "fall" and its past tense, "fell." Understanding the correct usage of these terms is crucial for effective communication. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of "fall" and "fell," exploring their meanings, usage, and the historical context that has shaped their development.
Introduction to Fall and Fell
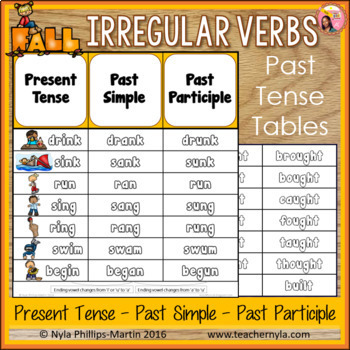
The verb “fall” is a fundamental part of the English language, used to describe the act of dropping or coming down from a higher position to a lower one. It can also be used figuratively to describe a decline or decrease in something. The past tense of “fall” is “fell,” which is used to describe an action that occurred in the past. For example, “I fell down the stairs yesterday” indicates that the action of falling happened at a specific point in the past.
Key Points
- The verb "fall" is used in the present tense to describe the act of dropping or coming down.
- The past tense of "fall" is "fell," used for past actions.
- The past participle of "fall" is "fallen," which is used with "has" or "had" to form the present or past perfect tense.
- Understanding the correct usage of "fall," "fell," and "fallen" is essential for clear and effective communication.
- Historical context and evolutionary developments have influenced the grammatical structure and usage of these terms.
Historical Context of Fall and Fell
The verb “fall” has its roots in Old English, where it was spelled “feallan.” Over time, the spelling and pronunciation have evolved, but the core meaning has remained relatively consistent. The past tense “fell” has been in use since Middle English, demonstrating a clear distinction between the present and past actions. This historical context is crucial for understanding the development of English grammar and the specific usage of “fall” and “fell.”
| Verb Form | Past Tense | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| Fall | Fell | Fallen |
| Rise | Rose | Risen |
| Go | Gone |

Practical Applications and Examples

In everyday conversation, the correct usage of “fall” and “fell” can significantly impact the clarity of the message. For example, “If I fall, I will get hurt” versus “I fell down the stairs and got hurt.” The first sentence is in the present tense, discussing a potential future action, while the second sentence is in the past tense, describing an action that has already occurred.
Common Mistakes and Clarifications
One common mistake is the confusion between “fell” and “felt.” While “fell” is the past tense of “fall,” “felt” is the past tense of “feel.” For instance, “I felt sad when I fell” correctly uses both past tenses in a single sentence. Understanding these distinctions is vital for effective communication and to avoid confusion.
What is the difference between "fall," "fell," and "fallen"?
+"Fall" is the present tense, "fell" is the past tense, and "fallen" is the past participle used for the present or past perfect tense.
How do I use "fell" correctly in a sentence?
+"Fell" is used to describe an action that occurred in the past. For example, "I fell down the stairs yesterday" or "She fell asleep during the movie."
What is the historical context of "fall" and "fell"?
+The verb "fall" originates from Old English "feallan," with "fell" emerging in Middle English as the past tense, reflecting the evolution of the English language over time.
In conclusion, the correct usage of “fall,” “fell,” and “fallen” is not merely a matter of grammar but also of effectively conveying meaning. By understanding the historical context, grammatical rules, and practical applications of these terms, individuals can improve their communication skills and avoid common mistakes. Whether in writing or speech, the distinction between these verb forms is essential for clarity and precision, reflecting the complexity and beauty of the English language.