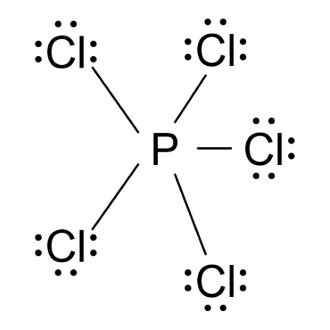
The PCL5 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry, representing the molecular structure of phosphorus pentachloride. To understand this structure, it's essential to have a solid grasp of Lewis structures and the principles of chemical bonding. Here, we'll delve into the world of PCL5, exploring its Lewis structure and providing 5 valuable tips for mastering this crucial concept.
Introduction to PCL5 and Lewis Structures
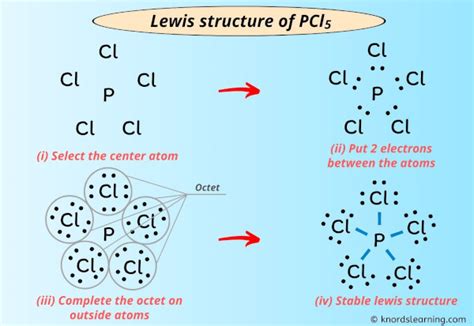
Phosphorus pentachloride, or PCL5, is a chemical compound consisting of one phosphorus atom bonded to five chlorine atoms. The Lewis structure is a visual representation of the molecule’s valence electrons, helping chemists understand the bonding and properties of the compound. The Lewis structure of PCL5 is crucial in understanding its reactivity, stability, and other chemical properties.
Key Points
- Understanding the Lewis structure of PCL5 is essential for predicting its chemical properties and reactivity.
- The PCL5 molecule has a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, with the phosphorus atom at the center.
- Mastering the rules for drawing Lewis structures is vital for accurately representing the molecular structure of PCL5.
- The VSEPR theory helps predict the shape of the PCL5 molecule based on its Lewis structure.
- Practicing drawing Lewis structures for various molecules, including PCL5, is key to developing a deep understanding of chemical bonding and molecular geometry.
Tip 1: Master the Rules for Drawing Lewis Structures
To draw the Lewis structure of PCL5, you need to follow a set of rules. First, determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule by adding the valence electrons of each atom. Phosphorus has 5 valence electrons, and each chlorine atom has 7, resulting in a total of 5 + 5*7 = 40 valence electrons. Next, draw the skeletal structure, connecting the atoms with single bonds, which accounts for 10 electrons. Then, distribute the remaining electrons around the atoms, following the octet rule, which states that each atom should have 8 electrons in its valence shell.
| Atom | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|
| Phosphorus (P) | 5 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 7 |
| Total Valence Electrons in PCL5 | 40 |

Tip 2: Understand the Molecular Geometry of PCL5
The molecular geometry of PCL5 is trigonal bipyramidal, with the phosphorus atom at the center. This geometry is predicted by the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory, which states that electron pairs around an atom arrange themselves to minimize repulsions. In PCL5, the phosphorus atom has 5 bonding pairs and no lone pairs, resulting in a trigonal bipyramidal shape. Understanding the molecular geometry is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of the compound.
Tip 3: Apply VSEPR Theory to Predict Molecular Shape
The VSEPR theory is a powerful tool for predicting the molecular shape of a compound based on its Lewis structure. For PCL5, the theory predicts a trigonal bipyramidal shape due to the arrangement of the 5 bonding pairs around the phosphorus atom. To apply the VSEPR theory, first, determine the number of electron pairs around the central atom, then use the theory’s predictions to determine the molecular shape. This theory is essential for understanding the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule and its implications for chemical properties.
Tip 4: Practice Drawing Lewis Structures for Various Molecules
Practicing drawing Lewis structures for different molecules, including PCL5, is vital for developing a deep understanding of chemical bonding and molecular geometry. By drawing Lewis structures, you can visualize the arrangement of valence electrons and predict the molecular shape and properties. Start with simple molecules and gradually move to more complex ones, ensuring you follow the rules for drawing Lewis structures and apply the VSEPR theory correctly.
Tip 5: Relate Lewis Structures to Chemical Properties and Reactivity
Understanding the Lewis structure of PCL5 and other molecules is not just about drawing diagrams; it’s about relating these structures to chemical properties and reactivity. The Lewis structure can help predict the polarity of the molecule, its reactivity towards other compounds, and its stability. For instance, the trigonal bipyramidal geometry of PCL5 and the presence of 5 bonding pairs without lone pairs around the phosphorus atom contribute to its high reactivity and ability to act as a Lewis acid.
What is the molecular geometry of PCL5?
+The molecular geometry of PCL5 is trigonal bipyramidal.
How do you draw the Lewis structure of PCL5?
+To draw the Lewis structure of PCL5, start by determining the total number of valence electrons, then draw the skeletal structure and distribute the remaining electrons to satisfy the octet rule for each atom.
What is the VSEPR theory, and how does it apply to PCL5?
+The VSEPR theory predicts the molecular shape of a compound based on the arrangement of its valence electrons. For PCL5, the theory predicts a trigonal bipyramidal shape due to the arrangement of the 5 bonding pairs around the phosphorus atom.
In conclusion, mastering the Lewis structure of PCL5 and understanding its implications for molecular geometry and chemical properties are crucial for any chemist. By following the tips outlined above and practicing the drawing of Lewis structures, you can develop a deep understanding of chemical bonding and molecular geometry, ultimately enhancing your ability to predict and explain the properties and reactivity of various chemical compounds.