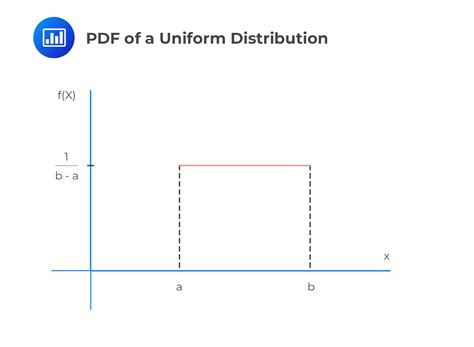
The Uniform Distribution is a fundamental concept in probability theory and statistics, playing a crucial role in understanding and modeling random phenomena. At its core, the Uniform Distribution, also known as the Rectangular Distribution, is a continuous probability distribution where every possible outcome within a certain range has an equal likelihood of occurring. This distribution is characterized by its probability density function (PDF), which is essential for calculating probabilities and understanding the behavior of random variables that follow this distribution.
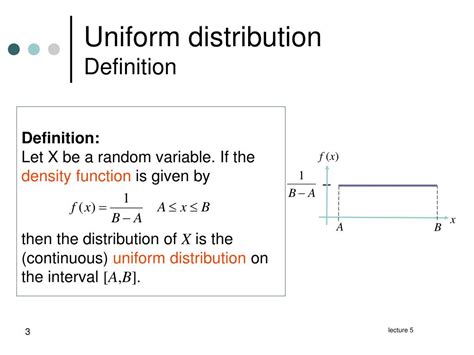
To delve into the Uniform Distribution PDF, it's essential to first establish the parameters that define it. The Uniform Distribution is typically denoted as U(a, b), where 'a' and 'b' are the minimum and maximum values of the range, respectively. The PDF of a Uniform Distribution, denoted as f(x), is given by the formula:
f(x) = 1 / (b - a) for a ≤ x ≤ b
and
f(x) = 0 for x < a or x > b
This formula indicates that for any value of x within the range [a, b], the probability density is constant and equal to 1 / (b - a), and for any value of x outside this range, the probability density is 0.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
The Uniform Distribution PDF is not only straightforward to understand but also has significant implications in statistical analysis and modeling. One of its key applications is in the simulation of random events, where the outcome is equally likely to be any value within a specified range. For instance, rolling a fair die can be modeled using a discrete uniform distribution, but for continuous intervals, the Uniform Distribution PDF provides a powerful tool for analyzing and predicting outcomes.
Moreover, the Uniform Distribution serves as a foundational element in more complex statistical distributions and models. It is often used as a prior distribution in Bayesian inference, where the lack of prior knowledge about a parameter can be represented by a uniform distribution over a reasonable range of values. This versatility and the simplicity of its PDF make the Uniform Distribution an indispensable component of statistical theory and practice.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
A critical aspect of working with the Uniform Distribution PDF is understanding its properties, such as the mean, variance, and standard deviation. The mean (μ) of a Uniform Distribution U(a, b) is given by (a + b) / 2, which intuitively makes sense as the midpoint of the range. The variance (σ^2) is (b - a)^2 / 12, reflecting the spread of the distribution. These parameters are essential for further statistical analysis and for comparing the Uniform Distribution with other distributions.
| Parameter | Formula |
|---|---|
| Mean (μ) | (a + b) / 2 |
| Variance (σ^2) | (b - a)^2 / 12 |
| Standard Deviation (σ) | √((b - a)^2 / 12) |

Key Points
- The Uniform Distribution is a continuous probability distribution where every outcome in a range [a, b] has an equal probability.
- The PDF of the Uniform Distribution is given by f(x) = 1 / (b - a) for a ≤ x ≤ b and 0 otherwise.
- The distribution is characterized by its mean (μ) = (a + b) / 2 and variance (σ^2) = (b - a)^2 / 12.
- It has significant applications in statistical modeling, simulation, and as a prior in Bayesian inference.
- Understanding the Uniform Distribution PDF is essential for working with statistical distributions and models.
In practice, the Uniform Distribution PDF is applied in various fields, including engineering, economics, and computer science. For instance, in reliability engineering, it can be used to model the time to failure of a component when the failure rate is constant over a period. In economics, it can help in modeling certain types of demand where the probability of purchase is evenly distributed across different price points.
Moreover, the Uniform Distribution plays a critical role in statistical inference, particularly in hypothesis testing and confidence interval construction. Its properties make it an ideal distribution for modeling random variables in situations where there is no prior knowledge about the distribution of the variable, except that it falls within a certain range.
Applications and Implications
Beyond its theoretical significance, the Uniform Distribution has numerous practical applications. In simulation studies, generating random numbers from a Uniform Distribution is a common approach to modeling real-world phenomena. This is because many programming languages and statistical software packages provide built-in functions for generating uniform random variables, which can then be transformed to follow other distributions if needed.
Additionally, the Uniform Distribution is used in the field of finance for modeling stock prices, interest rates, and other financial metrics when there is a belief that the variable of interest is equally likely to be anywhere within a certain range. This approach, while simplistic, can provide valuable insights into potential future outcomes and help in risk assessment and management.
What is the Uniform Distribution used for in statistics?
+The Uniform Distribution is used in statistics for modeling random variables that have an equal probability of occurring within a specified range. It's applied in simulation studies, as a prior in Bayesian inference, and in various fields such as engineering and economics.
How do you calculate the mean of a Uniform Distribution?
+The mean (μ) of a Uniform Distribution U(a, b) is calculated as (a + b) / 2, which is the midpoint of the range [a, b].
What are some real-world applications of the Uniform Distribution?
+The Uniform Distribution has applications in reliability engineering, economics, computer science, and finance. It's used for modeling time to failure, demand, simulation studies, and for generating random numbers, among other applications.
In conclusion, the Uniform Distribution PDF is a fundamental concept in statistics and probability theory, offering a simple yet powerful tool for modeling and analyzing random phenomena. Its applications span across various disciplines, from engineering and economics to finance and computer science. Understanding the Uniform Distribution and its properties is essential for any statistician or data analyst aiming to apply statistical models effectively in real-world scenarios.