I’ll help you create a blog post about Pennsylvania State University Cost. I’ll use the WebSearch tool to gather current information to ensure accuracy. Based on the search results, I’ll craft an HTML-formatted blog post about Pennsylvania State University Cost:
Navigating the financial landscape of higher education can be challenging, and understanding the Pennsylvania State University Cost is crucial for prospective students and their families. As of the 2026 academic year, Penn State offers a comprehensive breakdown of expenses that goes beyond simple tuition rates, providing students with a transparent view of their potential investment in education.
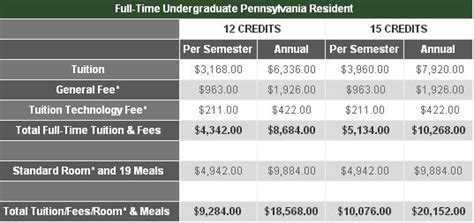
Tuition Breakdown by Residency and Program

The cost of attending Penn State varies significantly depending on several key factors:
- Residency status (Pennsylvania resident vs. non-resident)
- Specific academic program
- Campus location
- Credit load
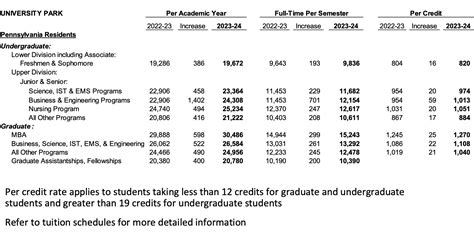
Non-Pennsylvania Resident Undergraduate Tuition Rates (2026-2027)
Here's a detailed look at the per academic year tuition for non-Pennsylvania residents:
- Freshman & Sophomore (Lower Division): $44,574
- Science, IST & EMS Programs: $49,616
- Business & Engineering Programs: $52,656
- Nursing Program: $52,656
- All Other Programs: $46,812
Complete Cost of Attendance Considerations

The total cost of attendance extends beyond tuition and includes several additional expenses. Penn State breaks down these costs per semester for different living scenarios:
| Expense Category | On Campus (per semester) | Off Campus (per semester) |
|---|---|---|
| Food | $3,170 | $3,170 |
| Housing | $4,503 | $5,968 |
| Books & Supplies | $645 | $645 |
| Transportation | $1,122 | $1,122 |
| Miscellaneous | $1,556 | $1,556 |

Financial Aid and Support

Penn State is committed to making education accessible through various financial aid options:
- Need-blind admissions process
- Scholarships based on academic excellence
- Grants for students with financial need
- Work-study programs
- Federal student loans
💡 Note: Students are encouraged to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) to explore their financial aid opportunities.
Long-Term Investment Perspective

While the costs might seem substantial, the total estimated four-year baccalaureate tuition and fees for non-Pennsylvania residents can range from $189,457 to $201,854, depending on the specific program. This investment potentially translates into significant career opportunities and earning potential.
How often do Penn State tuition rates change?

+
Penn State’s Board of Trustees sets tuition rates annually, typically in July. Historically, rates have increased by approximately 2-4% for Pennsylvania residents and 4% for non-residents.
Are there differences in tuition rates across Penn State campuses?

+
Yes, tuition rates vary between University Park and Commonwealth Campuses. Commonwealth Campuses generally have lower tuition rates compared to the main University Park campus.
What additional costs should students budget for?
+
Beyond tuition, students should budget for books, supplies, transportation, personal expenses, housing, and food. The total cost of attendance includes these additional expenses.
