The art of converting percentages to letter grades is a nuanced process, often dependent on the specific grading scale employed by an educational institution or instructor. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a general understanding of the most commonly used grading scales can provide a solid foundation for conversion. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of percentage to letter grade conversion, exploring the various scales, their applications, and the implications for students and educators alike.
Key Points
- Understanding the most commonly used grading scales is essential for accurate percentage to letter grade conversion.
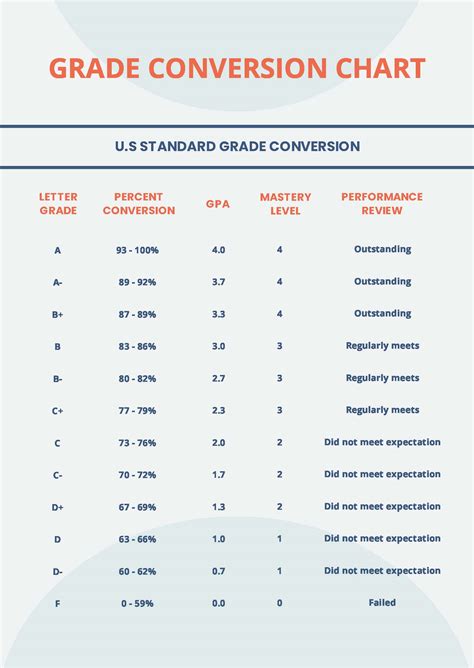
- The standard grading scale, often used in the United States, assigns letter grades based on the following percentages: A (90-100%), B (80-89%), C (70-79%), D (60-69%), and F (below 60%).
- Alternative grading scales, such as the plus/minus system, can provide a more nuanced evaluation of student performance.
- Grading scales can vary significantly between institutions and instructors, emphasizing the importance of clear communication and understanding.
- Percentage to letter grade conversion tools and calculators can facilitate the process, but it is essential to verify their accuracy and relevance to the specific grading scale being used.
Standard Grading Scale
The standard grading scale, widely used in the United States, is a straightforward system that assigns letter grades based on the following percentages: A (90-100%), B (80-89%), C (70-79%), D (60-69%), and F (below 60%). This scale provides a clear and concise framework for evaluating student performance, allowing for easy comparison and communication between educators and students.
Plus/Minus System
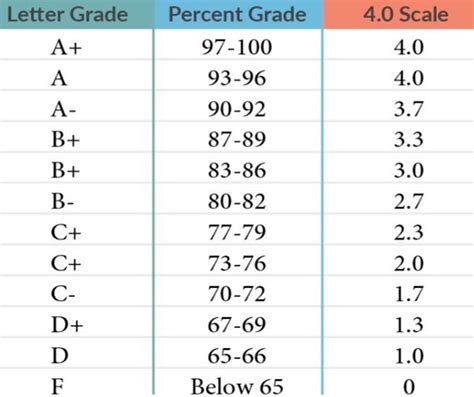
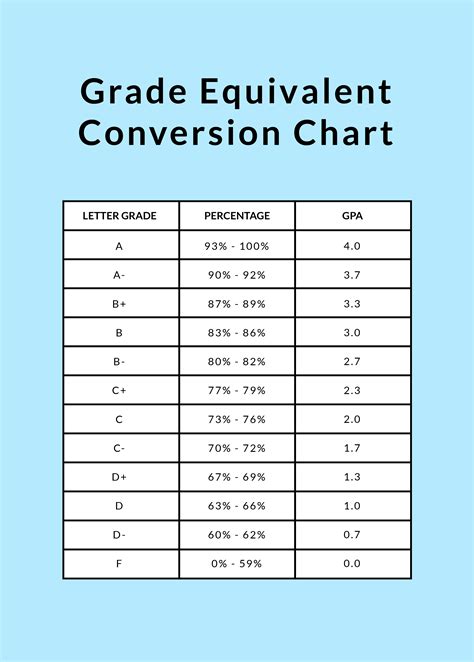
A variation of the standard grading scale is the plus/minus system, which further differentiates between letter grades by adding a plus or minus designation. For example, an A- might correspond to a percentage range of 90-92%, while an A+ might represent a range of 97-100%. This system provides a more nuanced evaluation of student performance, allowing for a more detailed assessment of academic achievement.
| Letter Grade | Percentage Range (Standard Scale) | Percentage Range (Plus/Minus Scale) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 90-100% | 93-100% (A), 90-92% (A-) |
| B | 80-89% | 87-92% (B+), 83-86% (B), 80-82% (B-) |
| C | 70-79% | 77-82% (C+), 73-76% (C), 70-72% (C-) |
| D | 60-69% | 67-69% (D+), 63-66% (D), 60-62% (D-) |
| F | below 60% | below 60% |
Implications and Considerations
The conversion of percentages to letter grades has significant implications for students, educators, and institutions. A deep understanding of the grading scale being used is crucial for accurate evaluation and communication. Furthermore, the use of alternative grading scales, such as the plus/minus system, can provide a more nuanced assessment of student performance, but may also introduce additional complexity and variability.
Percentage to Letter Grade Conversion Tools
Various online tools and calculators are available to facilitate the conversion of percentages to letter grades. However, it is essential to verify the accuracy and relevance of these tools to the specific grading scale being used. A thorough understanding of the underlying grading scale and its application is necessary to ensure accurate and reliable conversions.
What is the most commonly used grading scale in the United States?
+The standard grading scale, which assigns letter grades based on the following percentages: A (90-100%), B (80-89%), C (70-79%), D (60-69%), and F (below 60%).
How does the plus/minus system differ from the standard grading scale?
+The plus/minus system further differentiates between letter grades by adding a plus or minus designation, providing a more nuanced evaluation of student performance.
Why is it essential to clearly communicate the grading scale being used?
+Clear communication of the grading scale ensures that students understand the expectations and criteria for evaluation, promoting a more effective learning environment and alleviating confusion.
In conclusion, the conversion of percentages to letter grades is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of the underlying grading scale and its application. By recognizing the importance of clear communication, nuance, and accuracy, educators and students can work together to create a more effective and equitable learning environment.