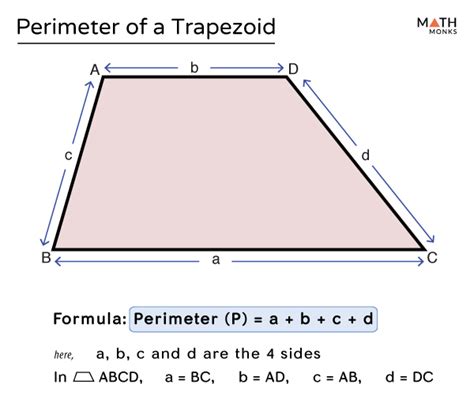
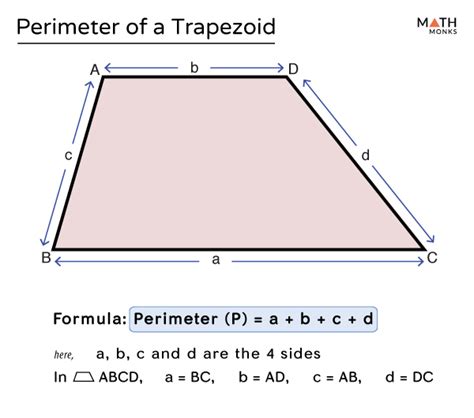
The trapezoid, a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides, is a fundamental shape in geometry. Calculating its perimeter is essential in various mathematical and real-world applications. The perimeter of a trapezoid can be determined by adding the lengths of all its sides. Here, we'll delve into the specifics of calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid, exploring key concepts, formulas, and practical examples to enhance understanding and application.
Understanding Trapezoid Basics
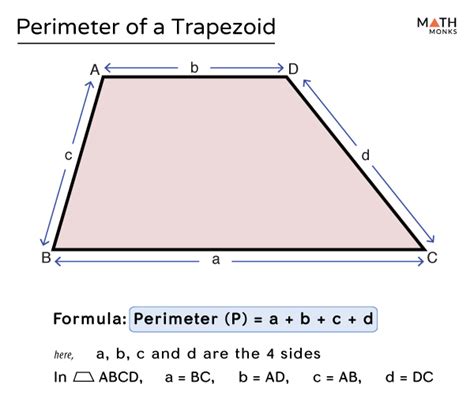
A trapezoid is characterized by its two parallel sides, known as the bases, and its two non-parallel sides, referred to as the legs. The bases are typically denoted as a and b, while the legs are denoted as c and d. The height of the trapezoid, which is the perpendicular distance between the bases, is crucial for calculating the area but not directly for the perimeter. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a trapezoid is P = a + b + c + d.
Calculating Perimeter with Given Side Lengths
To calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid, you simply add the lengths of all four sides. For instance, if the lengths of the sides of a trapezoid are given as a = 5 cm, b = 7 cm, c = 4 cm, and d = 6 cm, the perimeter would be P = 5 + 7 + 4 + 6 = 22 cm. This straightforward calculation is fundamental to understanding and working with trapezoids in geometry and real-world applications.
| Side | Length (cm) |
|---|---|
| Base $a$ | 5 |
| Base $b$ | 7 |
| Leg $c$ | 4 |
| Leg $d$ | 6 |
| Perimeter $P$ | 22 |
Practical Applications and Variations
The calculation of a trapezoid’s perimeter has numerous practical applications, from architecture to engineering. For instance, in the design of a building’s facade, understanding the perimeter of trapezoidal elements can be crucial for estimating material costs and structural integrity. Moreover, in land surveying, calculating the perimeter of trapezoidal plots of land is essential for property valuation and boundary disputes.
Tips for Calculating Trapezoid Perimeter
Here are five key tips to keep in mind when calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid:
- Ensure Unit Consistency: All measurements should be in the same units to ensure an accurate calculation.
- Accurate Measurement: The lengths of the sides must be measured accurately, as small errors can lead to significant discrepancies in the final perimeter calculation.
- Understanding the Formula: Familiarize yourself with the perimeter formula $P = a + b + c + d$ to ensure you're adding all the sides correctly.
- Real-World Applications: Recognize the practical applications of trapezoid perimeter calculations, such as in construction, engineering, and design, to appreciate the relevance of this geometric concept.
- Double-Check Calculations: Always double-check your calculations, especially in critical applications, to avoid errors that could have significant consequences.
Key Points
- The perimeter of a trapezoid is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides.
- Ensure all measurements are in the same units for accuracy.
- The formula for the perimeter is $P = a + b + c + d$.
- Accurate measurement and calculation are crucial for practical applications.
- Double-checking calculations is essential, especially in critical applications.
In conclusion, calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid involves a straightforward application of the formula $P = a + b + c + d$. However, accuracy, unit consistency, and understanding of the formula are critical for obtaining the correct perimeter. By following the tips outlined and appreciating the practical significance of trapezoid perimeter calculations, individuals can enhance their geometric understanding and apply it effectively in various contexts.
What is the formula for the perimeter of a trapezoid?
+The formula for the perimeter (P) of a trapezoid is P = a + b + c + d, where a and b are the lengths of the bases, and c and d are the lengths of the legs.
Why is it important to ensure all measurements are in the same units?
+Ensuring all measurements are in the same units is crucial for accuracy in the final calculation. Mixing units can lead to errors and incorrect results.
What are some practical applications of calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid?
+Practical applications include architecture, engineering, design, and land surveying, where understanding the perimeter of trapezoidal shapes is essential for material estimation, structural integrity, and property valuation.