The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, used to organize and display the known elements. One of the key features of the periodic table is the arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, which is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom. The periodic table charges refer to the ions that are formed when an element gains or loses electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. In this article, we will explore the concept of periodic table charges, their types, and their significance in chemistry.
Understanding Periodic Table Charges

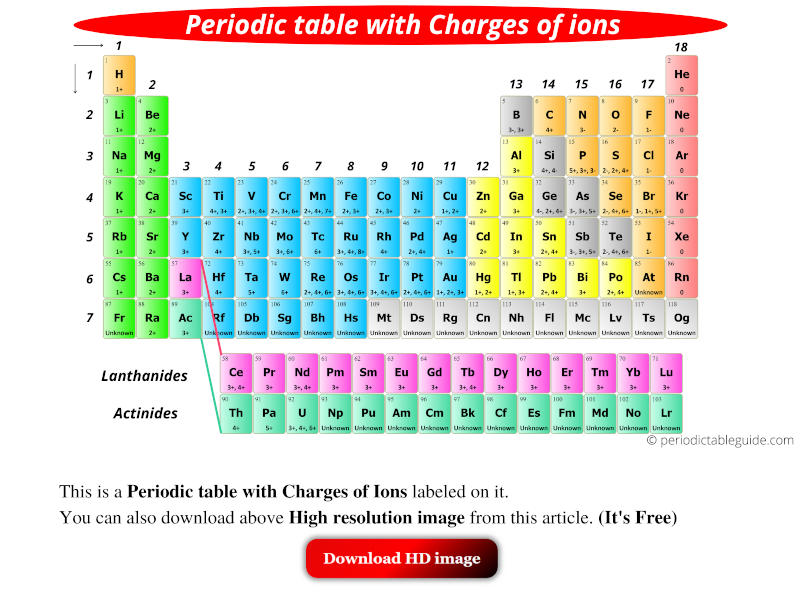
Periodic table charges are the result of the gain or loss of electrons by an atom, which leads to the formation of ions. Ions are atoms or molecules that have a net positive or negative charge due to the gain or loss of electrons. The charge on an ion is determined by the number of electrons gained or lost, and it is denoted by a superscript (+) or (-) symbol. For example, a sodium ion (Na+) has a +1 charge, while a chloride ion (Cl-) has a -1 charge.
Types of Periodic Table Charges
There are two main types of periodic table charges: positive and negative. Positive charges are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons, resulting in a deficiency of electrons. Negative charges, on the other hand, are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons, resulting in an excess of electrons. The type of charge on an ion depends on the element’s position in the periodic table and its electron configuration.
| Element | Charge |
|---|---|
| Sodium (Na) | +1 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | -1 |
| Calcium (Ca) | +2 |
| Oxygen (O) | -2 |
Key Factors Influencing Periodic Table Charges
The periodic table charges are influenced by several factors, including the element’s atomic number, electron configuration, and position in the periodic table. The atomic number of an element determines the number of protons in its nucleus, which in turn affects the number of electrons it can hold. The electron configuration of an element, which describes the arrangement of electrons in its orbitals, also plays a crucial role in determining its charge.
Electron Configuration and Periodic Table Charges
The electron configuration of an element is a critical factor in determining its charge. Elements in the same group (vertical column) of the periodic table have similar electron configurations and tend to form ions with the same charge. For example, all the elements in group 1 (alkali metals) have a +1 charge, while all the elements in group 17 (halogens) have a -1 charge.
Key Points
- The periodic table charges are the result of the gain or loss of electrons by an atom.
- There are two main types of periodic table charges: positive and negative.
- The type of charge on an ion depends on the element's position in the periodic table and its electron configuration.
- The atomic number and electron configuration of an element influence its charge.
- Understanding periodic table charges is crucial in predicting the chemical properties and behavior of elements.
Significance of Periodic Table Charges in Chemistry
The periodic table charges have significant implications in chemistry, as they determine the chemical properties and behavior of elements. The charge on an ion affects its reactivity, solubility, and interactions with other elements. For example, ions with opposite charges tend to form ionic bonds, while ions with the same charge tend to repel each other.
Applications of Periodic Table Charges
The periodic table charges have numerous applications in chemistry, including the prediction of chemical reactions, the synthesis of compounds, and the understanding of biological processes. By analyzing the charge on an ion, chemists can predict its reactivity and interactions with other elements, which is essential in the development of new materials, pharmaceuticals, and technologies.
What is the significance of periodic table charges in chemistry?
+The periodic table charges determine the chemical properties and behavior of elements, including their reactivity, solubility, and interactions with other elements.
How do the atomic number and electron configuration influence the charge on an ion?
+The atomic number determines the number of protons in the nucleus, which affects the number of electrons an element can hold. The electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an element's orbitals, which influences the charge on an ion.
What are the applications of periodic table charges in chemistry?
+The periodic table charges have numerous applications in chemistry, including the prediction of chemical reactions, the synthesis of compounds, and the understanding of biological processes.
Meta Description: Learn about periodic table charges, including their types, significance, and applications in chemistry. Understand how the atomic number and electron configuration influence the charge on an ion and explore the implications of periodic table charges in chemical reactions and biological processes. (150 characters)