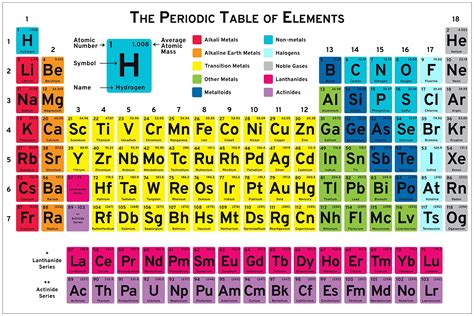
The Periodic Table of Elements is a fundamental tool in chemistry, providing a comprehensive and organized framework for understanding the properties and relationships of the elements. The table is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
History and Development of the Periodic Table

The development of the Periodic Table is a story that spans centuries, with contributions from many scientists and researchers. The earliest attempts to classify the elements date back to the early 19th century, when chemists such as John Newlands and Julius Lothar Meyer developed early versions of the table. However, it was not until the work of Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 19th century that the modern Periodic Table began to take shape. Mendeleev’s table was based on the periodic law, which states that the properties of the elements recur periodically when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight.
Structure of the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table is typically arranged in a rectangular format, with the elements listed in order of increasing atomic number. The table is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. The elements in each group exhibit similar chemical properties, due to the similar arrangement of electrons in their outermost energy level. The periods are divided into blocks, which are based on the type of orbital that is being filled with electrons.
| Block | Period | Group |
|---|---|---|
| s-block | 1-2 | 1-2 |
| p-block | 2-7 | 13-18 |
| d-block | 4-7 | 3-12 |
| f-block | 6-7 | lanthanides and actinides |

Key Features of the Periodic Table

The Periodic Table has several key features that make it a useful tool for chemists and other scientists. These include:
- Periodic trends: The table shows how the properties of the elements change as you move across a period or down a group. For example, the elements in group 1 (the alkali metals) are all highly reactive and tend to lose one electron to form a positive ion.
- Blocks: The table is divided into blocks, which are based on the type of orbital that is being filled with electrons. The s-block elements, for example, are in the first two groups of the table and have a pair of electrons in the outermost energy level.
- Groups and families: The elements in each group exhibit similar chemical properties, due to the similar arrangement of electrons in their outermost energy level. The groups are sometimes referred to as families, and the elements within a family are said to be homologous.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The Periodic Table has many applications in chemistry and other fields. Some of the most significant applications include:
- Prediction of properties: The table can be used to predict the properties of elements, such as their reactivity, electronegativity, and ionization energy.
- Understanding chemical reactions: The table provides a framework for understanding the chemical reactions that occur between elements, including the formation of compounds and the transfer of electrons.
- Materials science: The table is used in materials science to understand the properties of materials and to design new materials with specific properties.
Key Points
- The Periodic Table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, providing a comprehensive and organized framework for understanding the properties and relationships of the elements.
- The table is arranged in a rectangular format, with the elements listed in order of increasing atomic number.
- The elements in each group exhibit similar chemical properties, due to the similar arrangement of electrons in their outermost energy level.
- The table has many applications in chemistry and other fields, including the prediction of properties, understanding chemical reactions, and materials science.
- The Periodic Table is a powerful tool for predicting the properties of elements and understanding the relationships between them.
What is the Periodic Table of Elements?
+The Periodic Table of Elements is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Who developed the Periodic Table?
+The development of the Periodic Table is a story that spans centuries, with contributions from many scientists and researchers. The modern Periodic Table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 19th century.
What are the key features of the Periodic Table?
+The key features of the Periodic Table include periodic trends, blocks, groups, and families. The table shows how the properties of the elements change as you move across a period or down a group.
In conclusion, the Periodic Table of Elements is a fundamental tool in chemistry, providing a comprehensive and organized framework for understanding the properties and relationships of the elements. The table has many applications in chemistry and other fields, and its development is a testament to the power of human ingenuity and scientific inquiry.