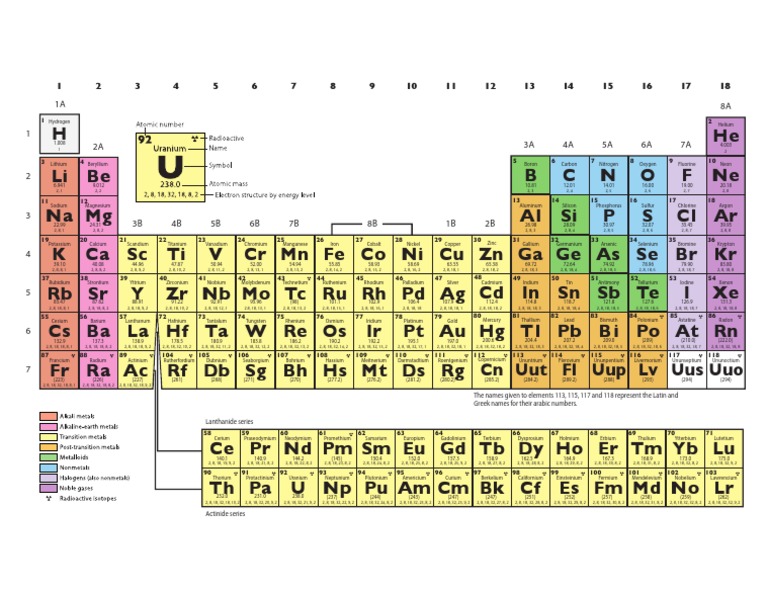
The Periodic Table of Elements is a fundamental tool in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, used to organize and display the known elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. The periodic table is a dynamic and continually updated resource, with new elements being added as they are discovered and characterized.
Understanding the Periodic Table
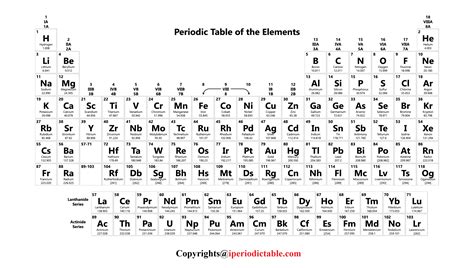
The periodic table is structured to reflect the periodic trends of the elements, which are the patterns that emerge when elements are arranged by their atomic number. These trends include variations in atomic radius, electronegativity, and the tendency to lose or gain electrons to form ions. The table is divided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, with metals being on the left side and center of the table, nonmetals on the right side, and metalloids along the metal-nonmetal dividing line.
Main Elements Groups
The elements can be broadly categorized into several groups based on their properties and electron configurations. These include the alkali metals (Group 1), alkaline earth metals (Group 2), halogens (Group 17), noble gases (Group 18), and the transition metals, which occupy the d-block of the periodic table. Each group has distinct properties; for example, the alkali metals are highly reactive and readily lose one electron to form a positive ion, while the noble gases are unreactive due to their full outer energy level.
| Group Number | Group Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alkali Metals | Highly reactive, readily lose one electron |
| 2 | Alkaline Earth Metals | Less reactive than alkali metals, lose two electrons |
| 17 | Halogens | Highly reactive, readily gain one electron |
| 18 | Noble Gases | Unreactive, full outer energy level |
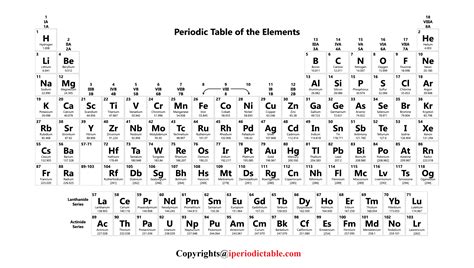
Periodic Table Layout
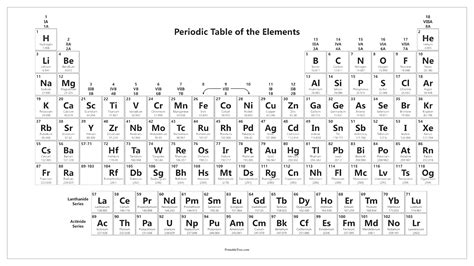
The standard periodic table layout is designed to maximize the recognition of periodic trends. The horizontal rows are called periods, and the vertical columns are called groups or families. Elements in the same group exhibit similar chemical behavior due to the same number of electrons in their outer shell, which determines their chemical properties. The periods are less straightforward in terms of trends, as the properties of elements can vary significantly across a period due to changes in electron configuration and nuclear charge.
Blocks of the Periodic Table
The periodic table can also be divided into blocks based on the orbital type of the outermost energy level that is being filled. The s-block includes the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, the p-block includes the nonmetals and metalloids, and the d-block includes the transition metals. The f-block, situated at the bottom of the periodic table, contains the lanthanides and actinides, also known as the inner transition metals, which exhibit unique properties due to the filling of the f orbitals.
Key Points
- The periodic table organizes elements by atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
- Elements are grouped into periods (rows) and groups (columns) based on their electron configuration.
- The table reflects periodic trends, including variations in atomic radius, electronegativity, and ionization energy.
- Understanding the periodic table is essential for predicting chemical behavior and properties of elements and compounds.
- The layout and structure of the periodic table facilitate the identification of relationships between elements and their properties.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table has numerous applications in chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering. It is used to predict the properties of elements and compounds, to understand chemical reactions, and to design new materials with specific properties. The periodic table is also a tool for discovering new elements and for understanding the geochemical distribution of elements in the Earth’s crust.
Education and Research
In educational settings, the periodic table serves as a fundamental teaching tool, helping students understand the basics of chemistry and the relationships between different elements. In research, scientists use the periodic table to identify gaps in the current understanding of elements and to predict the existence of new, undiscovered elements with unique properties.
| Periodic Table Applications | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Prediction of Chemical Properties |
| 2 | Understanding of Chemical Reactions |
| 3 | Design of New Materials |
| 4 | Discovery of New Elements |
| 5 | Geochemical Distribution Studies |
What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry?
+The periodic table is significant because it organizes elements in a way that reveals periodic trends in their properties, making it easier to predict chemical behavior and understand the structure of matter.
How are elements grouped in the periodic table?
+Elements are grouped into periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns) based on their atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
What are the main applications of the periodic table?
+The periodic table is used in predicting chemical properties, understanding chemical reactions, designing new materials, discovering new elements, and studying geochemical distributions.
Meta Description: Discover the organization, trends, and applications of the periodic table, a fundamental tool in chemistry and physics that organizes elements based on their atomic number and recurring chemical properties.
The periodic table is an indispensable resource for anyone interested in chemistry, physics, and related sciences, offering insights into the structure, properties, and reactions of elements. Its layout, based on the atomic number and electron configuration of elements, allows for the prediction of chemical behavior and the identification of relationships between elements. The table’s structure and the periodic trends it displays have far-reaching implications for the understanding of matter at the atomic and molecular levels, facilitating advancements in various fields of science and technology.