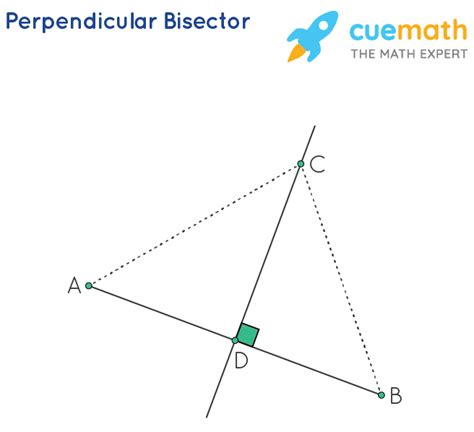
The Bisector Theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry, providing a powerful tool for solving problems related to triangles and angles. At its core, the theorem states that in a triangle, an angle bisector divides the opposite side into segments that are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides. This concept has far-reaching implications and applications in various fields of mathematics and science. In this article, we will delve into the workings of the Bisector Theorem, exploring its underlying principles, applications, and the significant role it plays in geometric analysis.
Key Points
- The Bisector Theorem is based on the principle that the ratio of the lengths of the two segments of the opposite side is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle.
- It applies to all types of triangles, including acute, right, and obtuse triangles, making it a versatile tool in geometric calculations.
- The theorem is essential in finding unknown side lengths or angle measures in triangles when certain conditions are met.
- Its applications extend beyond basic geometry, influencing areas such as trigonometry, calculus, and even engineering and architecture.
- Understanding the Bisector Theorem enhances problem-solving skills in mathematics, particularly in geometric and trigonometric contexts.
Principle of the Bisector Theorem
The Bisector Theorem can be mathematically expressed as follows: In triangle ABC, if AD is the bisector of angle A, then BD/DC = AB/AC. This principle underscores the proportional relationship between the segments created by the angle bisector and the lengths of the triangle’s sides. This relationship is pivotal in solving problems that involve finding lengths of segments or the entire sides of triangles based on given conditions.
Application in Solving Triangle Problems
A key application of the Bisector Theorem is in solving triangle problems where an angle bisector and certain side lengths are known. By applying the theorem, one can calculate the lengths of unknown segments or sides, given that the ratio of the other sides is known. This is particularly useful in problems where direct measurement or calculation of all sides is not feasible, and an angle bisector provides a critical piece of information.
| Triangle Type | Application of Bisector Theorem |
|---|---|
| Right Triangle | Used in conjunction with Pythagorean theorem for solving problems involving right triangles. |
| Obtuse Triangle | Essential in finding lengths of segments in obtuse triangles where direct calculation might be complex. |
| Acute Triangle | Facilitates the calculation of unknown sides or segments in acute triangles with known angle bisectors. |

Extensions and Applications Beyond Basic Geometry

Beyond its application in basic geometric problems, the Bisector Theorem has implications in more advanced mathematical disciplines. In trigonometry, for instance, the theorem can be related to the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines, providing alternative methods for solving triangle problems. In calculus, the concept of proportional segments can be generalized to understand rates of change and accumulation, further highlighting the theorem’s significance in the broader mathematical landscape.
Impact on Engineering and Architecture
The Bisector Theorem also has practical applications in fields like engineering and architecture. In the design of structures, understanding the proportional relationships between different parts of a triangle can be crucial for ensuring stability and balance. For example, in the construction of bridges or buildings, applying the principles of the Bisector Theorem can help in the calculation of stresses and loads, contributing to safer and more efficient designs.
In conclusion, the Bisector Theorem is a fundamental geometric principle with wide-ranging applications in mathematics, science, and engineering. Its ability to relate angle bisectors with side lengths in triangles provides a powerful tool for problem-solving, making it an indispensable part of geometric analysis. As we continue to explore and apply geometric principles, the Bisector Theorem stands out as a cornerstone of mathematical reasoning, facilitating advancements in various fields and inspiring new generations of mathematicians, scientists, and engineers.
What is the primary application of the Bisector Theorem in geometry?
+The primary application of the Bisector Theorem is in solving problems related to triangles, particularly in finding unknown side lengths or segment lengths based on the given angle bisector and side lengths.
How does the Bisector Theorem relate to other geometric principles?
+The Bisector Theorem is interconnected with other geometric principles such as the Pythagorean theorem, the Law of Sines, and the Law of Cosines, providing alternative methods for solving geometric problems.
What are the practical applications of the Bisector Theorem beyond mathematics?
+Beyond mathematics, the Bisector Theorem has practical applications in engineering and architecture, particularly in the design and construction of structures where understanding proportional relationships is crucial for stability and efficiency.