The concept of perpendicular lines is a fundamental aspect of geometry and is crucial in various mathematical and real-world applications. Perpendicular lines are defined as lines that intersect at a right angle, which is 90 degrees. The equation of perpendicular lines is a mathematical representation that describes the relationship between the slopes of two lines that are perpendicular to each other.
To understand the equation of perpendicular lines, it is essential to first comprehend the concept of slope. The slope of a line is a measure of how steep it is and can be calculated using the formula: m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on the line. The slope of a line can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on its orientation.
The equation of a line in slope-intercept form is given by y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. This equation represents a line with a slope of m and a y-intercept of b.
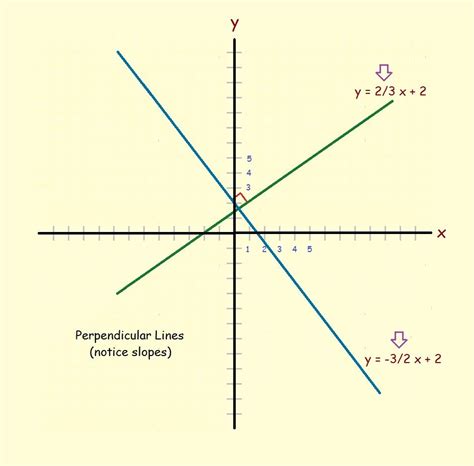
Now, let’s consider two lines that are perpendicular to each other. The slopes of these lines are related in a specific way. If the slope of the first line is m1, then the slope of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line, is given by m2 = -1/m1. This is known as the negative reciprocal rule.
For example, if the slope of the first line is 2, then the slope of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line, is -1⁄2. This means that if the equation of the first line is y = 2x + b, then the equation of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line, is y = (-1⁄2)x + c, where c is the y-intercept of the second line.
To find the equation of perpendicular lines, we can use the following steps:
- Find the slope of the first line using the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1).
- Use the negative reciprocal rule to find the slope of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line.
- Use the point-slope form of a line, y - y1 = m(x - x1), to find the equation of the second line.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
The equation of perpendicular lines has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields. In geometry, perpendicular lines are used to describe the relationships between different shapes and figures. In physics, perpendicular lines are used to describe the motion of objects and the forces that act upon them.
For instance, consider a particle moving in a two-dimensional space. The path of the particle can be described by a line, and the velocity of the particle can be represented by a vector. If the particle is moving at a constant speed, then the velocity vector is perpendicular to the position vector of the particle. This means that the equation of the path of the particle can be represented by a line that is perpendicular to the velocity vector.
In engineering, perpendicular lines are used to design and analyze structures, such as bridges, buildings, and roads. For example, the equation of a bridge’s arch can be represented by a line that is perpendicular to the horizontal axis, while the equation of the bridge’s support can be represented by a line that is perpendicular to the vertical axis.
Specific subtopic with natural language phrasing
One of the key concepts related to perpendicular lines is the idea of orthogonality. Two vectors are said to be orthogonal if they are perpendicular to each other. In mathematics, orthogonality is used to describe the relationships between different vectors and matrices. For instance, the dot product of two orthogonal vectors is zero, and the matrix product of two orthogonal matrices is the identity matrix.
To illustrate this concept, consider two vectors a = (1, 2) and b = (3, -1). The dot product of these vectors is given by a · b = (1)(3) + (2)(-1) = 1. Since the dot product is not zero, the vectors a and b are not orthogonal.
However, if we consider the vectors a = (1, 0) and b = (0, 1), then the dot product is given by a · b = (1)(0) + (0)(1) = 0. Since the dot product is zero, the vectors a and b are orthogonal.
| Vector | Dot Product |
|---|---|
| a = (1, 2) | a · b = 1 |
| b = (3, -1) | a · b = 1 |
| a = (1, 0) | a · b = 0 |
| b = (0, 1) | a · b = 0 |
Key Points
- The equation of perpendicular lines is a mathematical representation that describes the relationship between the slopes of two lines that are perpendicular to each other.
- The negative reciprocal rule states that if the slope of the first line is m1, then the slope of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line, is given by m2 = -1/m1.
- The equation of a line in slope-intercept form is given by y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- Perpendicular lines have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields.
- The concept of orthogonality is crucial in understanding the relationships between different vectors and matrices.
In conclusion, the equation of perpendicular lines is a fundamental concept in mathematics and has numerous applications in various fields. The negative reciprocal rule provides a straightforward way to find the slope of a line that is perpendicular to a given line. By understanding the concept of orthogonality and the equation of perpendicular lines, we can better analyze and describe the relationships between different vectors and matrices.
What is the equation of perpendicular lines?
+The equation of perpendicular lines is a mathematical representation that describes the relationship between the slopes of two lines that are perpendicular to each other. If the slope of the first line is m1, then the slope of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line, is given by m2 = -1/m1.
What is the negative reciprocal rule?
+The negative reciprocal rule states that if the slope of the first line is m1, then the slope of the second line, which is perpendicular to the first line, is given by m2 = -1/m1.
What are the applications of perpendicular lines?
+Perpendicular lines have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other fields. They are used to describe the relationships between different shapes and figures, the motion of objects, and the forces that act upon them.
Meta description: “The equation of perpendicular lines is a mathematical representation that describes the relationship between the slopes of two lines that are perpendicular to each other. Learn more about the negative reciprocal rule, orthogonality, and the applications of perpendicular lines.”