The pH of lemon juice is a topic of interest in various fields, including culinary arts, food science, and chemistry. Lemon juice, extracted from the fruit of the lemon tree (Citrus limon), is a common ingredient in many recipes and beverages. Its acidic nature is well-known, but the exact pH level can vary depending on several factors, such as the ripeness of the lemons, the method of extraction, and the concentration of the juice.
Natural Acidity of Lemon Juice
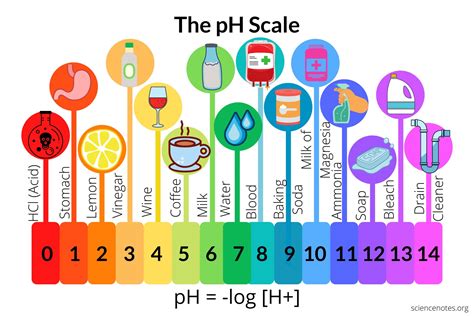
Lemon juice is characterized by its high concentration of citric acid, which is responsible for its distinctive sour taste. Citric acid is a weak organic acid that donates a proton (H+ ion) in aqueous solutions, thereby decreasing the pH. The pH of freshly squeezed lemon juice typically ranges from 2.0 to 2.5, with an average pH of around 2.2. This acidity is significant, as it not only affects the taste and texture of food products but also influences the stability and safety of certain foods by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
Factors Influencing the pH of Lemon Juice
Several factors can influence the pH of lemon juice. For instance, the pH can vary slightly depending on the variety of lemon, the ripeness of the fruit, and the conditions under which the lemons are grown. Environmental factors such as climate, soil quality, and irrigation practices can also impact the acidity level of the lemons. Furthermore, the method of juice extraction and any subsequent processing or dilution can alter the final pH of the lemon juice. For example, commercial lemon juices may have a slightly different pH compared to freshly squeezed juice due to pasteurization, concentration, or the addition of preservatives.
| Factor | Effect on pH |
|---|---|
| Ripeness of Lemons | Slightly increases pH as lemons ripen |
| Extraction Method | Manual vs. mechanical pressing can affect pH due to varying levels of oxygen exposure |
| Concentration | Dilution decreases acidity, thus increasing pH |
| Pasteurization | May slightly decrease pH due to thermal degradation of certain compounds |

Key Points
- The pH of lemon juice typically ranges from 2.0 to 2.5, with an average of around 2.2.
- Citric acid is the primary component responsible for the acidity of lemon juice.
- Factors such as lemon variety, ripeness, extraction method, and processing can influence the pH of lemon juice.
- The acidity of lemon juice is important for both flavor and food safety considerations.
- Understanding the pH of lemon juice is essential for its effective use in culinary and industrial applications.
Applications and Considerations

The pH of lemon juice has significant implications for its use in various applications. In cooking, the acidity of lemon juice can help to brighten flavors, preserve colors, and tenderize certain foods. In food manufacturing, the pH level must be carefully controlled to ensure the stability and safety of products, particularly those that are acidic in nature. Furthermore, the pH of lemon juice can affect its interaction with other ingredients, influencing the overall texture, taste, and appearance of the final product.
Technical Specifications and pH Control
In industrial settings, controlling the pH of lemon juice is critical for achieving consistent product quality. This can involve adjusting the concentration of the juice, blending it with other ingredients to achieve a desired pH range, or using buffering agents to stabilize the pH. Technical specifications for lemon juice products often include pH ranges as part of the quality control measures to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
For instance, in the production of lemonade or other citrus-based beverages, the pH of the lemon juice used can significantly affect the final taste and stability of the product. A pH that is too low can result in an overly acidic taste, while a pH that is too high may lead to spoilage or an unappealing flavor profile. Therefore, manufacturers must carefully manage the pH levels during production to achieve the desired product characteristics.
What is the typical pH range of freshly squeezed lemon juice?
+The typical pH range of freshly squeezed lemon juice is between 2.0 and 2.5.
How does the ripeness of lemons affect the pH of lemon juice?
+The ripeness of lemons can slightly affect the pH of lemon juice, with riper lemons potentially having a slightly higher pH due to changes in citric acid concentration.
Why is controlling the pH of lemon juice important in food manufacturing?
+Controlling the pH of lemon juice is important in food manufacturing because it affects the taste, stability, and safety of the final product. Incorrect pH levels can lead to spoilage, off-flavors, or textures that are undesirable to consumers.
In conclusion, the pH of lemon juice is a critical parameter that influences its use and applications in various industries. Understanding the factors that affect the pH of lemon juice and how to control it is essential for achieving desired product qualities and ensuring consumer safety. Whether in culinary arts, food science, or chemistry, recognizing the significance of lemon juice acidity can lead to more effective and innovative uses of this versatile ingredient.