The common cold is a viral infection that affects the upper respiratory system, including the nose, throat, and lungs. It is a highly contagious illness that can be caused by over 200 different viruses, with the rhinovirus being the most common culprit. The progression of a cold can be divided into several distinct phases, each with its own set of symptoms and characteristics.
Phase 1: Incubation (1-3 days)
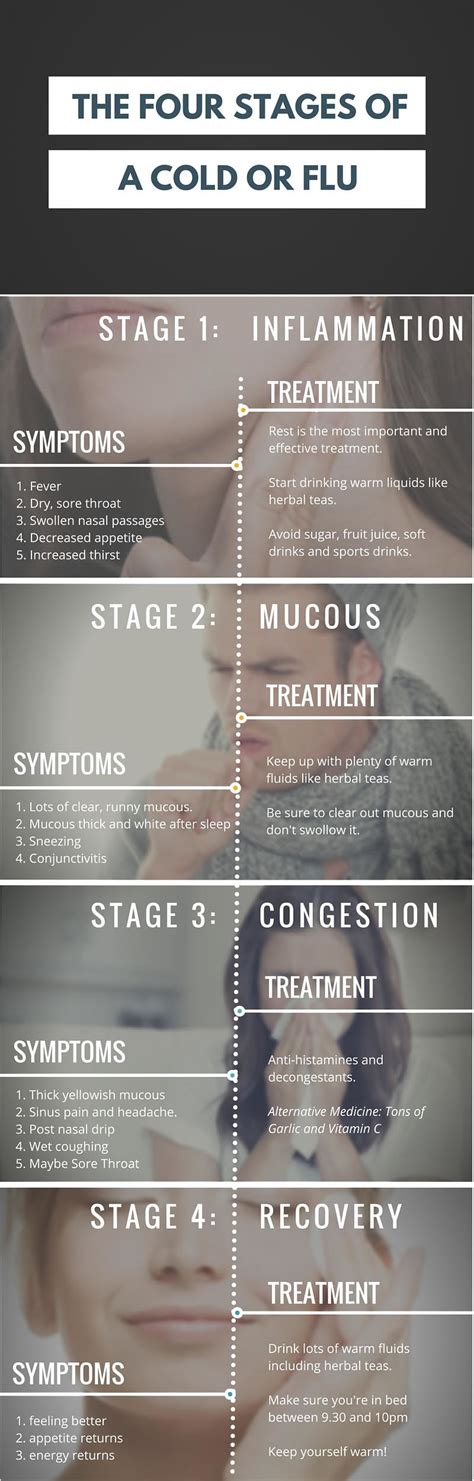
The incubation phase of a cold is the period of time between exposure to the virus and the onset of symptoms. During this phase, the virus is multiplying and spreading throughout the body, but the individual may not yet be experiencing any noticeable symptoms. The incubation period for a cold can range from 1-3 days, depending on the specific virus and the individual’s immune system.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the average incubation period for a cold is around 2 days. During this time, the individual may be contagious, even if they are not yet showing symptoms. This is why it's so important to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others, to help prevent the spread of the virus.
Key Factors Influencing Incubation Period
Several factors can influence the length of the incubation period, including the type of virus, the individual’s immune system, and their overall health. For example, people with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly or those with chronic illnesses, may experience a longer incubation period.| Virus Type | Incubation Period |
|---|---|
| Rhinovirus | 1-3 days |
| Coronavirus | 2-5 days |
| Adenovirus | 2-14 days |
Phase 2: Onset (1-3 days)
The onset phase of a cold is characterized by the sudden appearance of symptoms, such as a runny nose, sneezing, and a sore throat. During this phase, the virus is actively replicating and causing inflammation in the body. The onset phase can last anywhere from 1-3 days, during which time the individual may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Runny nose and congestion
- Sneezing and coughing
- Sore throat and hoarseness
- Fatigue and headaches
- Loss of appetite and mild fever
According to a study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases, the most common symptoms of a cold during the onset phase are a runny nose and sneezing, which occur in over 90% of cases. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the specific virus.
Managing Symptoms During Onset
There are several ways to manage symptoms during the onset phase, including:Rest and hydration: Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated can help to reduce the severity of symptoms and support the immune system. Over-the-counter medications: Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and decongestants, can help to alleviate symptoms such as headaches and congestion. Steam inhalation: Steam inhalation can help to loosen mucus and reduce congestion.
Key Points
- The incubation period for a cold can range from 1-3 days, depending on the specific virus and individual factors.
- The onset phase is characterized by the sudden appearance of symptoms, such as a runny nose and sneezing.
- Managing symptoms during the onset phase can help to reduce the severity of the cold and support the immune system.
- Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can help to alleviate symptoms.
- Steam inhalation can help to loosen mucus and reduce congestion.
Phase 3: Peak (3-5 days)
The peak phase of a cold is the period of time when symptoms are at their worst. During this phase, the virus has reached its maximum level of replication, and the body’s immune system is working to fight off the infection. The peak phase can last anywhere from 3-5 days, during which time the individual may experience:Serious congestion and sinus pressure, which can lead to headaches and facial pain. A persistent cough, which can be dry and hacking or produce mucus. Fatigue and weakness, which can make it difficult to perform daily activities. Loss of appetite, which can lead to dehydration and malnutrition.
Supporting the Immune System During Peak
There are several ways to support the immune system during the peak phase, including:Nutrition and hydration: Eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated can help to support the immune system and reduce the severity of symptoms. Rest and relaxation: Getting plenty of rest and engaging in relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help to reduce stress and support the immune system. Supplements and vitamins: Certain supplements and vitamins, such as vitamin C and zinc, can help to support the immune system and reduce the severity of symptoms.
What are the most common symptoms of a cold during the peak phase?
+The most common symptoms of a cold during the peak phase include serious congestion and sinus pressure, a persistent cough, fatigue and weakness, and loss of appetite.
How can I support my immune system during the peak phase of a cold?
+Supporting your immune system during the peak phase of a cold can be achieved by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting plenty of rest, and engaging in relaxation techniques. Certain supplements and vitamins, such as vitamin C and zinc, can also help to support the immune system.
How long does the peak phase of a cold typically last?
+The peak phase of a cold typically lasts anywhere from 3-5 days, during which time symptoms are at their worst.
Phase 4: Recovery (5-7 days)
The recovery phase of a cold is the period of time when symptoms begin to subside, and the body starts to recover from the infection. During this phase, the immune system has successfully fought off the virus, and the individual may start to feel better. The recovery phase can last anywhere from 5-7 days, during which time the individual may experience:Mild residual symptoms, such as a runny nose and cough. Fatigue and weakness, which can linger for several days. Loss of appetite, which can take time to recover from. A gradual return to normal activities and routines.
Preventing Future Illness During Recovery
There are several ways to prevent future illness during the recovery phase, including:Practicing good hygiene: Washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others can help to prevent the spread of the virus. Getting plenty of rest: Getting plenty of rest and avoiding overexertion can help to support the immune system and reduce the risk of future illness. Eating a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated can help to support the immune system and reduce the risk of future illness.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about the different phases of a cold, from incubation to recovery, and how to manage symptoms and support your immune system during each phase.”