At the heart of life on Earth lies the intricate balance between two fundamental biological processes: photosynthesis and cellular respiration. These processes are not only essential for the survival of nearly all living organisms but also play a critical role in shaping our planet's environment. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of organic compounds, such as glucose, is often seen as the precursor to life as we know it. On the other hand, cellular respiration, the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP, is crucial for the metabolic activities of all living cells. Understanding the interplay between these two processes is vital for grasping the basics of biology and ecology.
Key Points
- Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
- Cellular respiration is the process of breaking down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP.
- Both processes are interdependent and essential for life on Earth.
- Photosynthesis occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts in plant cells.
- Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
- The equation for photosynthesis is 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2.
- The equation for cellular respiration is C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP (energy).
Photosynthesis: Harnessing Light Energy
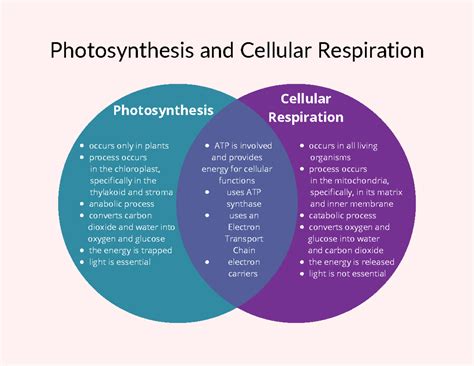
Photosynthesis is a complex process that involves the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using sunlight as an energy source. This process occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts, which are present in plant cells. Chloroplasts contain pigments such as chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy and initiates a series of reactions that ultimately lead to the production of glucose. The overall equation for photosynthesis is 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2. This process not only provides energy and organic compounds for plants but also produces oxygen as a byproduct, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
The Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions are the first stage of photosynthesis and occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast. During this stage, light energy is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll and converted into ATP and NADPH. The light-dependent reactions involve the transfer of electrons from water to a special molecule called an electron acceptor, resulting in the formation of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane. This gradient is then used to produce ATP through the process of chemiosmosis.
The Light-Independent Reactions
The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma of the chloroplast and do not require light directly. During this stage, CO2 is fixed into organic molecules using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions. The Calvin cycle involves a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that ultimately lead to the production of glucose.
Cellular Respiration: Breaking Down Glucose for Energy
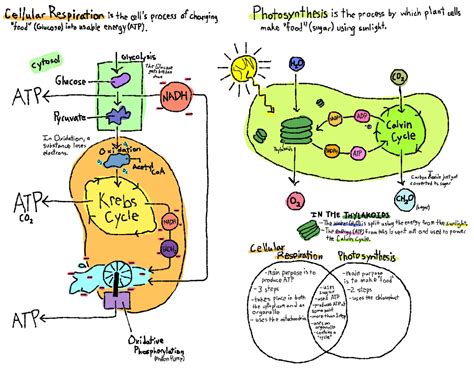
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and involves the breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy that is then used to produce ATP. The overall equation for cellular respiration is C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP (energy). Cellular respiration is essential for the metabolic activities of all living cells and is the primary source of energy for most organisms.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytosol of the cell. During this stage, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, meaning it does not require oxygen, and is the only stage of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
The Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, occurs in the mitochondria and involves the breakdown of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which then enters the citric acid cycle. The citric acid cycle produces ATP, NADH, and FADH2 as byproducts. The electrons from NADH and FADH2 are then passed through a series of electron transport chains in the mitochondrial inner membrane, resulting in the production of a proton gradient. This gradient is then used to produce ATP through the process of chemiosmosis, a process known as oxidative phosphorylation.
| Process | Location | Energy Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | Cytosol | 2 ATP, 2 NADH |
| Citric Acid Cycle | Mitochondria | 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 |
| Oxidative Phosphorylation | Mitochondria | 32-34 ATP |

Interplay Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interdependent processes that are crucial for life on Earth. Photosynthesis provides the organic compounds and oxygen necessary for cellular respiration, while cellular respiration produces the carbon dioxide and water necessary for photosynthesis. The balance between these two processes is essential for maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystem and ensuring the survival of nearly all living organisms.
What is the primary difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
+The primary difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is the direction of energy flow. Photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, while cellular respiration involves the breakdown of chemical energy to produce ATP.
Where do photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur in the cell?
+Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, while cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
What is the overall equation for photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
+The overall equation for photosynthesis is 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2. The overall equation for cellular respiration is C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP (energy).
In conclusion, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two interconnected processes that are essential for life on Earth. Understanding the intricacies of these processes and their interplay is crucial for grasping the basics of biology and ecology. By recognizing the importance of these processes, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of our ecosystem and work towards preserving it for future generations.



