The Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7) are two widely used tools in the healthcare industry for assessing depression and anxiety, respectively. These questionnaires are designed to be simple, efficient, and effective in identifying individuals who may be experiencing symptoms of these mental health conditions. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of these tools, exploring their development, application, and the insights they provide into mental health assessment and management.
Understanding the PHQ-9 and GAD-7
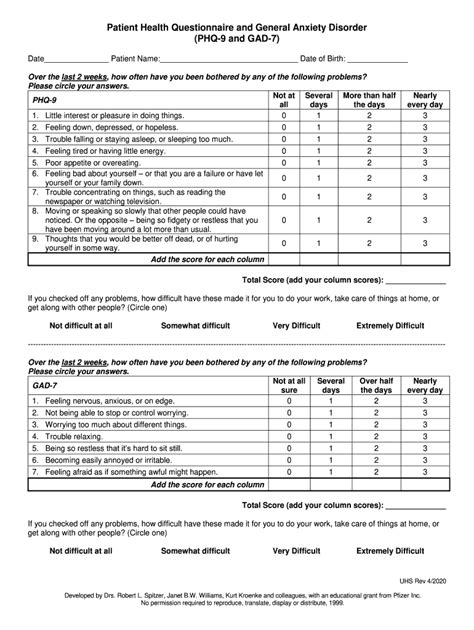
The PHQ-9 is a 9-item questionnaire that assesses the frequency of depressive symptoms over the past two weeks. It covers a range of symptoms, including mood, interest in activities, sleep, appetite, energy, concentration, and thoughts of self-harm. Each item is scored on a scale from 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms. The total score ranges from 0 to 27, with scores of 5, 10, 15, and 20 representing mild, moderate, moderately severe, and severe depression, respectively.
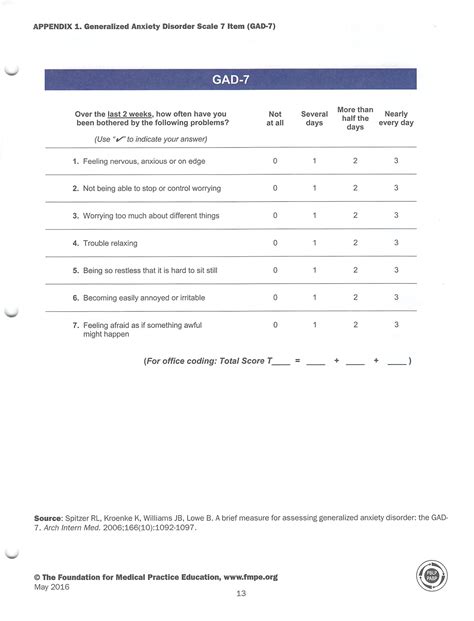
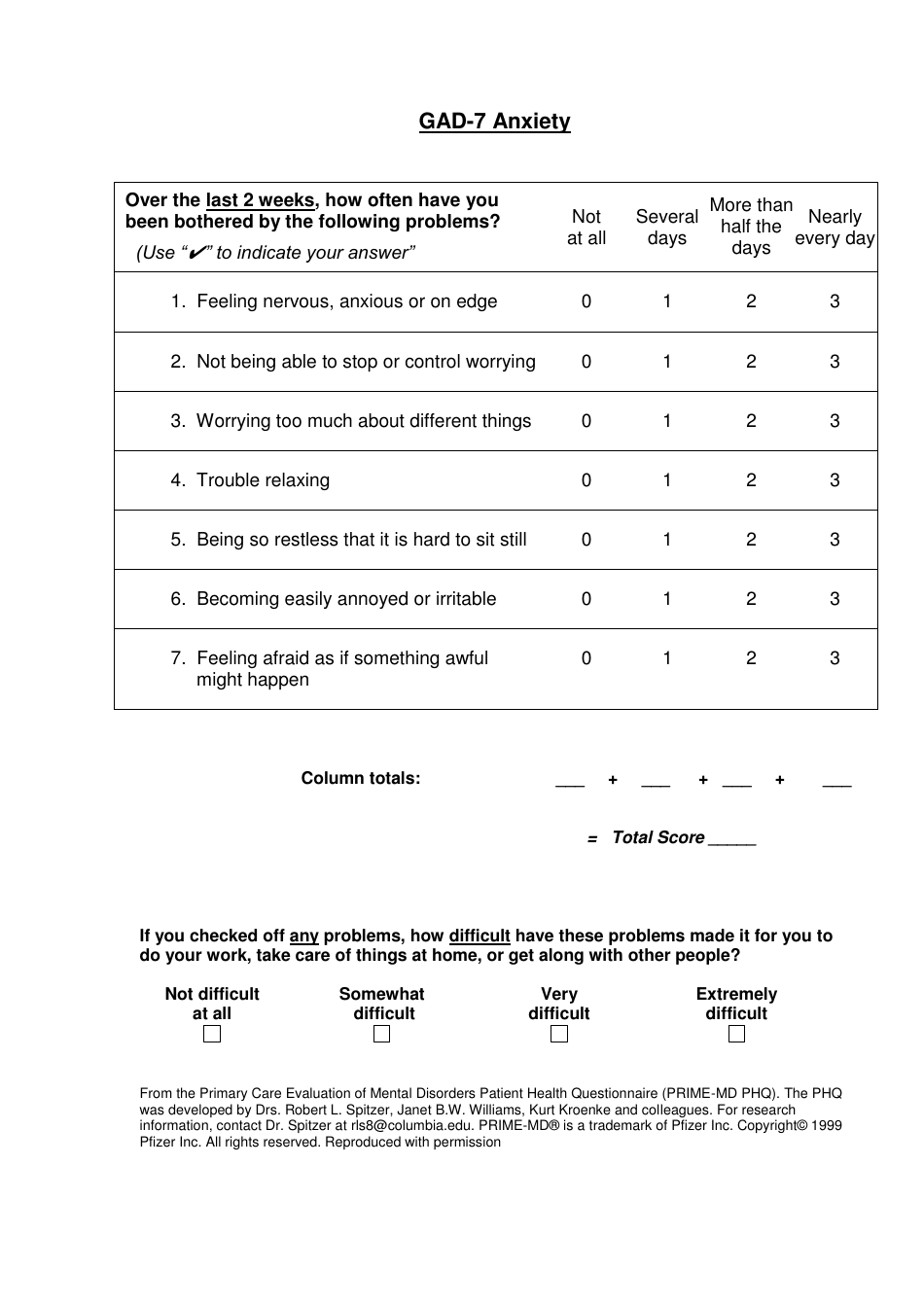
The GAD-7, on the other hand, is a 7-item questionnaire that evaluates the severity of anxiety symptoms over the past two weeks. It assesses feelings of nervousness, worry, fear, and restlessness, among other symptoms. Like the PHQ-9, each item is scored from 0 to 3, with the total score ranging from 0 to 21. Scores of 5, 10, and 15 indicate mild, moderate, and severe anxiety levels.
Application and Interpretation
Both the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are designed for use in primary care settings and can be administered by healthcare professionals or self-reported by patients. Their simplicity and brevity make them valuable tools for initial screenings and for monitoring the progression of symptoms over time. However, it’s essential to remember that while these questionnaires can indicate the presence and severity of depressive and anxiety symptoms, they should not be used as the sole basis for diagnosis. A comprehensive clinical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
| Scale | Items | Score Range | Severity Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHQ-9 | 9 | 0-27 | Mild (5-9), Moderate (10-14), Moderately Severe (15-19), Severe (20-27) |
| GAD-7 | 7 | 0-21 | Mild (5-9), Moderate (10-14), Severe (15-21) |
7 Tips for Effective Use of PHQ-9 and GAD-7
1. Regular Administration: Regular use of these tools can help in early detection and monitoring of depression and anxiety symptoms.
2. Comprehensive Clinical Evaluation: While the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are valuable screening tools, they should be used as part of a comprehensive clinical evaluation that includes a thorough patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic interviews.
3. Patient Education: Educating patients about these questionnaires and their purpose can improve compliance and reduce anxiety related to the screening process.
4. Monitoring Progress: Regularly administering the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 can help track the effectiveness of treatments and guide adjustments to care plans.
5. Multi-Disciplinary Approach: Collaboration between healthcare professionals from different disciplines can enhance the accuracy of assessments and the effectiveness of interventions.
6. Cultural Sensitivity: Recognizing the cultural nuances of patients’ experiences and perceptions of mental health can improve the validity and usefulness of these screening tools.
7. Continuity of Care: Ensuring continuity of care and follow-up appointments can help in managing mental health conditions effectively and preventing relapse.
Key Points
- The PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are valuable tools for assessing depression and anxiety but should be used as part of a comprehensive clinical evaluation.
- Regular administration can help in early detection and monitoring of symptoms.
- Patient education and a multi-disciplinary approach can enhance the effectiveness of these tools.
- Cultural sensitivity and continuity of care are crucial for accurate assessments and effective management of mental health conditions.
- These questionnaires can be used to monitor treatment response and guide adjustments to care plans.
In conclusion, the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 are indispensable tools in the assessment and management of depression and anxiety. By understanding their application, interpretation, and limitations, healthcare providers can utilize these questionnaires effectively to improve patient outcomes. Continuous education, cultural sensitivity, and a patient-centered approach are key to leveraging these tools in the pursuit of better mental health care.
What is the primary use of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 in clinical settings?
+The primary use of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 is for the screening and monitoring of depressive and anxiety symptoms, respectively. They help healthcare professionals in identifying individuals who may benefit from a more detailed evaluation and treatment.
How often should the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 be administered to monitor treatment response?
+The frequency of administration depends on the clinical context and the patient’s response to treatment. Generally, these questionnaires can be administered at intervals of 2-4 weeks to monitor changes in symptoms and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Can the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 be used in patients with limited literacy or those who prefer not to self-report?
+Yes, the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 can be administered by a healthcare provider in an interview format for patients with limited literacy or those who prefer not to self-report. This approach ensures that all patients can benefit from these screening tools regardless of their literacy level or preference.