Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. The condition can affect anyone, regardless of age, and its severity can vary from mild to severe. Understanding the visual aspects of eczema is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Visual Identification of Eczema

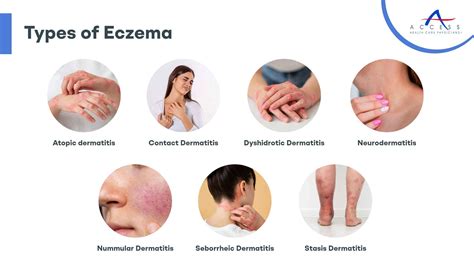
The appearance of eczema can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s skin type. Common visual characteristics include redness, inflammation, and dryness of the skin. In severe cases, the skin may crack and bleed, leading to increased risk of infection. Eczema can appear anywhere on the body, but it most commonly affects the hands, feet, face, and behind the knees.
Eczema Symptoms and Appearance
Symptoms of eczema can include intense itching, burning sensations, and sensitivity to touch. The skin may appear thickened, scaly, or crusty due to chronic scratching and rubbing. In some cases, eczema can lead to the formation of small, raised bumps or blisters that may ooze and crust over. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, as the appearance of eczema can be similar to other skin conditions.
| Eczema Type | Description | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Most common type, often linked to allergies and asthma | Red, itchy, and scaly patches, commonly on hands, feet, face, and behind the knees |
| Contact Dermatitis | Caused by skin contact with an allergen or irritant | Red, itchy, and blistered skin at the site of contact |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp | Flaky, itchy, and red patches, often accompanied by dandruff |
Key Points
- Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with varying severity and appearance.
- Common visual characteristics include redness, inflammation, dryness, and thickening of the skin.
- The condition can appear anywhere on the body but most commonly affects hands, feet, face, and behind the knees.
- Symptoms include intense itching, burning sensations, and sensitivity to touch.
- A healthcare professional's diagnosis is necessary due to the similarity in appearance to other skin conditions.
Treatment and Management of Eczema
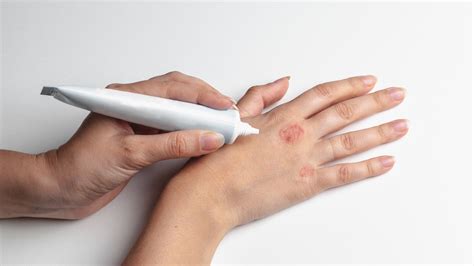
Treatment for eczema focuses on relieving symptoms, preventing future outbreaks, and improving the quality of life for those affected. Topical corticosteroids and moisturizers are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and keep the skin hydrated. In severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy may be recommended. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers, maintaining good skin care, and managing stress, are also essential components of eczema management.
Complications and Prevention
Untreated or poorly managed eczema can lead to complications, including skin infections, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. Preventive measures include avoiding known allergens or irritants, keeping the skin moisturized, and practicing good hygiene to reduce the risk of infection. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with eczema.
What does eczema look like?
+Eczema can appear as red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin, often affecting the hands, feet, face, and behind the knees. Its appearance can vary depending on the severity and the individual’s skin type.
How is eczema diagnosed?
+Eczema is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and sometimes additional tests to rule out other skin conditions. A healthcare professional’s evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Can eczema be treated?
+Yes, eczema can be treated with topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, and in severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and maintaining good skin care, are also crucial for managing the condition.



