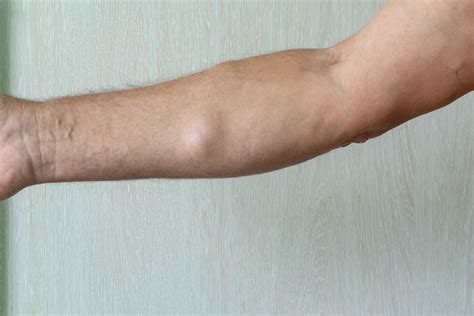
Lipomas are benign tumors composed of fat tissue that can appear almost anywhere on the body. They are typically soft, movable, and painless, although in some cases, they can cause discomfort or pain if they press on surrounding nerves or tissues. The appearance of lipomas can vary, but they are often described as dome-shaped and can range in size from small (about the size of a pea) to quite large (several centimeters in diameter). Here, we will explore various aspects of lipomas, including their appearance, types, diagnosis, and treatment options, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking to understand more about these common growths.
Key Points
- Lipomas are benign growths primarily made of fat cells.
- They can occur almost anywhere on the body but are most common on the neck, shoulders, and back.
- The diagnosis is often based on clinical examination, with imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI used for confirmation in some cases.
- Treatment options include observation for small, asymptomatic lipomas and surgical removal for larger or symptomatic ones.
- Lipomas are generally not harmful and do not increase the risk of cancer, but rare types like liposarcomas are malignant and require immediate medical attention.
Understanding Lipomas
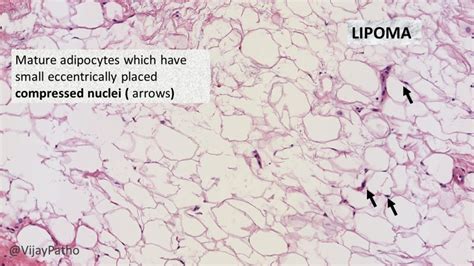
Lipomas are among the most common types of soft tissue tumors. They tend to develop just under the skin, but they can also occur in deeper tissues. The exact cause of lipomas is not well understood, but they seem to be associated with genetic factors, as they can run in families. Furthermore, alterations in the genetic material of the fat cells are thought to contribute to their development. Pictures of lipomas can show a variety of appearances, from small, barely noticeable bumps to larger masses that can be quite conspicuous.
Types of Lipomas
While the classic presentation of a lipoma is a soft, movable mass under the skin, there are several types of lipomas that can vary in their characteristics and locations. These include:
- Subcutaneous lipomas, which occur just beneath the skin and are the most common type.
- Deep lipomas, which develop in deeper tissues, such as within muscles or beneath fasciae.
- Intramuscular lipomas, which are located within the muscle itself.
- Interscapular lipoma, occurring between the shoulder blades.
- Cervical lipoma, found in the neck area.
Each type of lipoma may have a slightly different appearance, and understanding these variations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
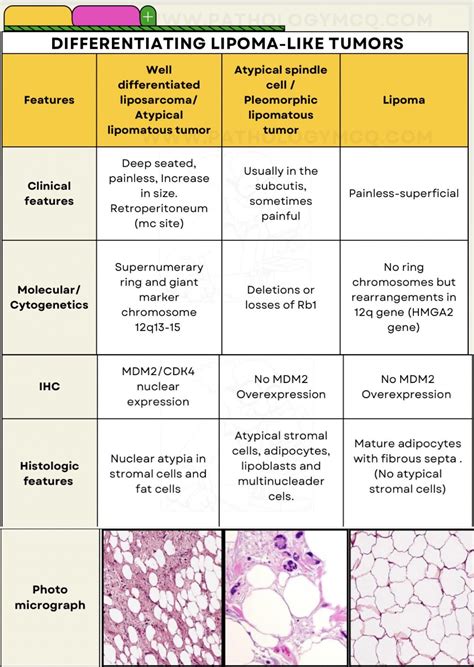
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of a lipoma is typically made through a physical examination. Healthcare providers look for characteristic signs such as a soft, movable mass under the skin. In some cases, especially if the lipoma is deep or if there’s a suspicion of a more serious condition like a liposarcoma, imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possibilities.
| Diagnostic Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Visual inspection and palpation to assess the size, mobility, and consistency of the mass. |
| Ultrasound | Use of high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal structures, helpful in distinguishing lipomas from other types of tumors. |
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | Produces detailed images of the internal structures using magnetic fields and radio waves, particularly useful for deep or complex lipomas. |
Treatment for lipomas is generally not necessary unless they cause discomfort, are in a location that interferes with movement, or are cosmetically bothersome. In such cases, surgical removal (excision) is the most common treatment. This procedure is typically straightforward and can be performed under local anesthesia. For larger lipomas or those in deeper tissues, more extensive surgery may be required.
Living with Lipomas
Most people with lipomas do not experience significant discomfort or impairment. However, large or strategically located lipomas can cause issues, such as limiting range of motion, pressing on nerves (leading to pain or numbness), or causing cosmetic concerns. In these situations, discussing treatment options with a healthcare provider is essential. It’s also important to note that while lipomas themselves are benign, any new or changing lump should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other conditions that may require more urgent attention.
What does a lipoma look like?
+A lipoma typically appears as a soft, movable lump under the skin. It can be small or large and may feel doughy or rubbery to the touch.
Are lipomas cancerous?
+No, lipomas are benign growths and are not cancerous. However, it's essential to have any new lump evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out other conditions.
How are lipomas treated?
+Treatment for lipomas usually involves surgical removal. For smaller lipomas, observation might be recommended if they do not cause symptoms.
In conclusion, while lipomas are common and generally harmless, understanding their appearance, types, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for those who develop these growths. By consulting with healthcare professionals and considering individual circumstances, individuals can make informed decisions about how to manage lipomas, ensuring the best possible outcomes in terms of comfort, function, and aesthetics.