The concept of a "Pilgrim in Progress" embodies a profound journey of self-discovery, spiritual exploration, and personal growth. This transformative path is characterized by a willingness to challenge one's assumptions, confront uncertainties, and embrace the complexities of human experience. As we delve into the depths of this journey, it becomes clear that the pilgrim's progress is not a linear or static phenomenon, but rather a dynamic and iterative process of learning, unlearning, and relearning.
Key Points
- The pilgrim's journey is marked by a series of trials, tribulations, and triumphs that shape their spiritual and personal identity.
- Self-reflection, introspection, and mindfulness are essential practices for navigating the complexities of the pilgrim's path.
- The journey is influenced by various factors, including cultural, social, and environmental contexts, which can either facilitate or hinder progress.
- The pilgrim's progress is often accompanied by a sense of paradox, ambiguity, and uncertainty, requiring the cultivation of wisdom, resilience, and adaptability.
- Ultimately, the pilgrim's journey is a testament to the human capacity for growth, transformation, and redemption, offering a powerful reminder of the importance of living a meaningful, purpose-driven life.
The Pilgrim’s Journey: A Historical and Cultural Context

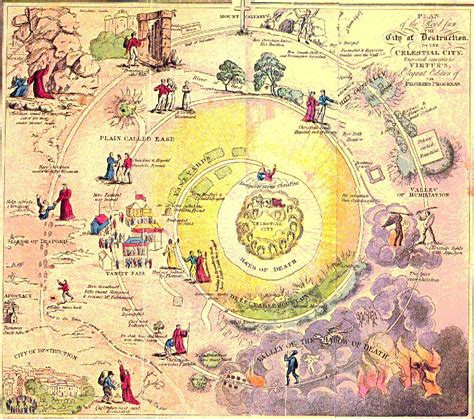
The idea of a pilgrim in progress has its roots in various spiritual and philosophical traditions, including Christianity, Buddhism, and Sufism. In John Bunyan’s classic allegory, “The Pilgrim’s Progress,” the protagonist, Christian, embarks on a perilous journey from the City of Destruction to the Celestial City, encountering numerous challenges and obstacles along the way. This seminal work has inspired countless adaptations, interpretations, and reinterpretations, cementing the pilgrim’s journey as a universal and timeless metaphor for personal transformation.
Psychological and Philosophical Perspectives
From a psychological perspective, the pilgrim’s journey can be seen as a process of individuation, where the individual integrates their opposites, confronts their shadow, and develops a more nuanced and compassionate sense of self. This journey is often marked by periods of crisis, chaos, and disorientation, which can serve as catalysts for growth, renewal, and rebirth. Philosophically, the pilgrim’s progress raises fundamental questions about the nature of reality, the human condition, and the meaning of life, inviting the traveler to embrace the mystery, ambiguity, and uncertainty of existence.
| Stage of Journey | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Initial Awakening | A sense of discontent, disillusionment, or restlessness, prompting the individual to embark on a journey of self-discovery. |
| Path of Trials | A series of challenges, obstacles, and setbacks that test the pilgrim's resolve, courage, and perseverance. |
| Dark Night of the Soul | A period of intense spiritual crisis, marked by feelings of despair, doubt, and existential anxiety. |
| Integration and Renewal | A process of healing, reconciliation, and rebirth, where the pilgrim integrates their experiences, and emerges transformed, renewed, and revitalized. |
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples

The pilgrim’s journey has numerous practical applications and real-world implications, from personal development and spiritual growth to social justice and community engagement. By embracing the principles of the pilgrim’s progress, individuals can cultivate a deeper sense of purpose, meaning, and direction, leading to more fulfilling, creative, and contributory lives. Moreover, the pilgrim’s journey can serve as a powerful framework for addressing social and environmental challenges, promoting empathy, understanding, and cooperation in the face of adversity.
Cultivating Mindfulness and Self-Reflection
Mindfulness and self-reflection are essential practices for navigating the pilgrim’s journey, allowing individuals to develop greater awareness, clarity, and insight into their thoughts, feelings, and actions. By cultivating these qualities, pilgrims can better navigate the twists and turns of their journey, making more informed decisions, and cultivating a deeper sense of inner peace, wisdom, and compassion.
What is the primary motivation for embarking on a pilgrim's journey?
+The primary motivation for embarking on a pilgrim's journey is often a sense of discontent, disillusionment, or restlessness, prompting the individual to seek a deeper sense of purpose, meaning, and direction in life.
How can individuals cultivate mindfulness and self-reflection on their journey?
+Individuals can cultivate mindfulness and self-reflection by practicing meditation, journaling, and engaging in regular periods of solitude and introspection, allowing them to develop greater awareness, clarity, and insight into their thoughts, feelings, and actions.
What are some common challenges and obstacles that pilgrims may encounter on their journey?
+Pilgrims may encounter a range of challenges and obstacles, including self-doubt, fear, and uncertainty, as well as external barriers, such as social, cultural, and environmental constraints, requiring them to cultivate resilience, adaptability, and creative problem-solving skills.
Meta description suggestion: “Embark on a transformative journey of self-discovery and spiritual exploration, navigating the complexities of the pilgrim’s path, and cultivating a deeper sense of purpose, meaning, and direction in life.” (149 characters)