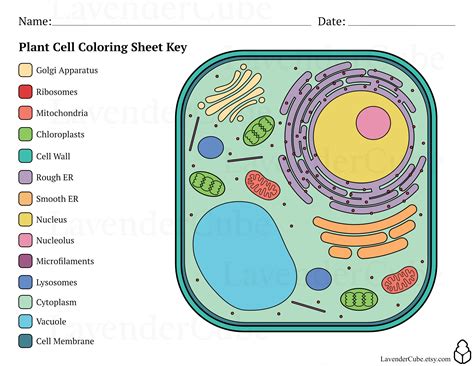
Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants, and understanding their structure is crucial for botanists, biologists, and students alike. One of the most effective ways to learn about plant cells is through coloring activities, which can help visualize the different components and their relationships. However, to get the most out of plant cell coloring, it's essential to approach it with a clear understanding of the cell's structure and the role of each component. In this article, we will delve into the world of plant cell coloring, providing tips and insights to enhance your learning experience.
Key Points
- Understanding the plant cell structure is crucial for effective coloring.
- Using a variety of colors can help differentiate between cell components.
- Labeling the cell components is essential for clarity and understanding.
- Attention to detail is key when coloring the plant cell's intricate structures.
- Practicing with different coloring techniques can enhance the learning experience.
Understanding Plant Cell Structure
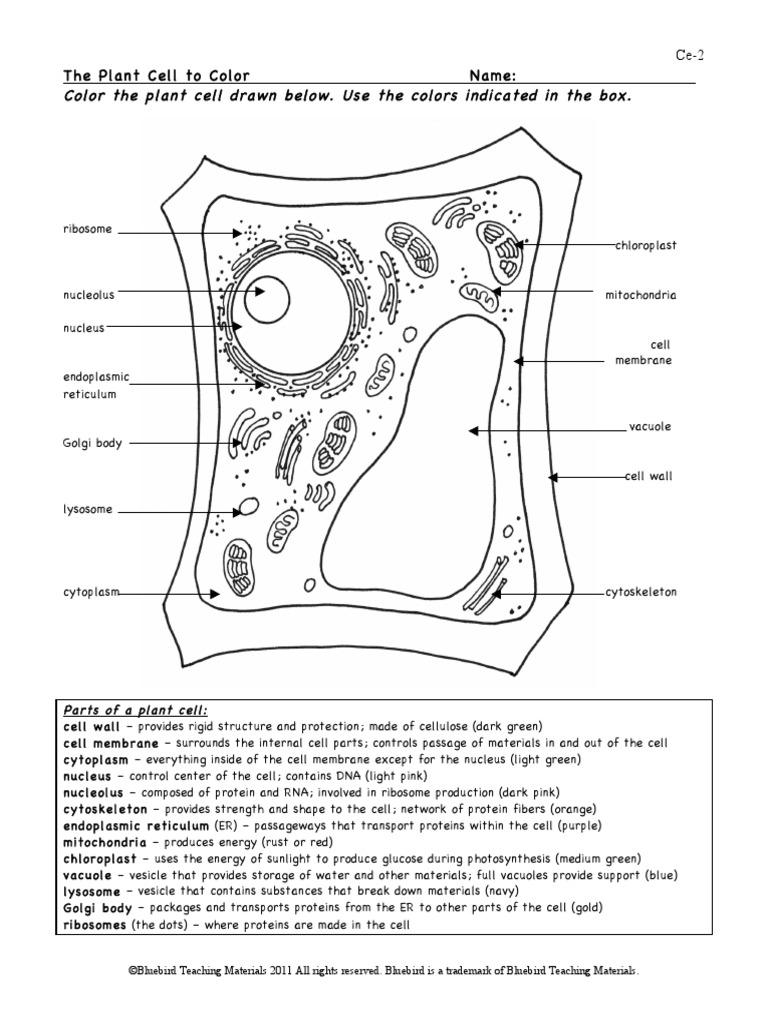
Before diving into coloring tips, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of the plant cell’s structure. A plant cell consists of several key components, including the cell wall, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, and vacuoles. Each of these components plays a vital role in the cell’s functioning, and understanding their relationships is crucial for effective coloring.
Tip 1: Use a Variety of Colors
Using a variety of colors can help differentiate between the various cell components, making it easier to visualize and understand their relationships. For example, the cell wall can be colored brown, the plasma membrane can be colored pink, and the cytoplasm can be colored blue. Chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, can be colored green, while the nucleus can be colored purple. By using a range of colors, you can create a visually appealing and informative diagram that enhances your understanding of the plant cell’s structure.
Tip 2: Label Cell Components
Labeling the cell components is essential for clarity and understanding. By labeling each component, you can ensure that you understand the role of each part and how they interact with each other. This is particularly important when coloring the plant cell’s intricate structures, such as the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondria. By taking the time to label each component, you can create a detailed and accurate diagram that reflects your understanding of the plant cell’s structure.
Tip 3: Pay Attention to Detail
Attention to detail is key when coloring the plant cell’s intricate structures. The plant cell has several complex components, such as the chloroplasts and the mitochondria, which require careful attention to detail. By taking the time to carefully color each component, you can create a detailed and accurate diagram that reflects your understanding of the plant cell’s structure. Additionally, paying attention to detail can help you identify any mistakes or inaccuracies in your diagram, allowing you to make corrections and improve your understanding.
| Cell Component | Function | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Provides support and protection | Brown |
| Plasma Membrane | Regulates the movement of materials | Pink |
| Cytoplasm | Site of metabolic processes | Blue |
| Chloroplasts | Site of photosynthesis | Green |
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material | Purple |
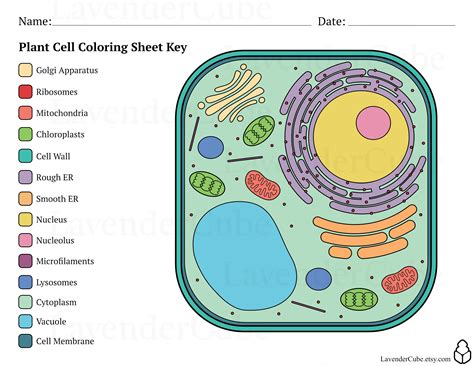
Practicing with Different Coloring Techniques
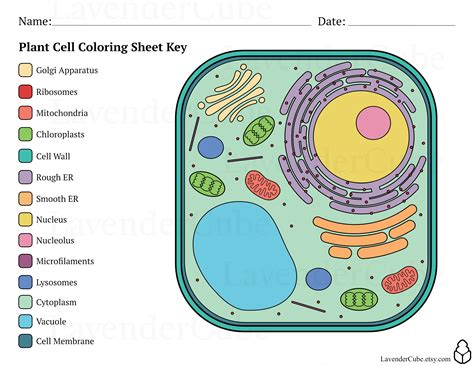
Practicing with different coloring techniques can enhance the learning experience and help you develop a deeper understanding of the plant cell’s structure. One technique is to use different shades of the same color to create a sense of depth and dimension. For example, you can use light blue for the cytoplasm and dark blue for the nucleus. Another technique is to use patterns and textures to add visual interest and create a sense of realism. By experimenting with different techniques, you can create a unique and informative diagram that reflects your understanding of the plant cell’s structure.
What is the function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
+The cell wall provides support and protection to the plant cell, maintaining its shape and structure.
What is the role of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
Why is labeling cell components important?
+Labeling cell components is essential for clarity and understanding, allowing you to identify and understand the role of each component in the plant cell's structure.
In conclusion, plant cell coloring is a valuable tool for learning about the structure and function of plant cells. By following these tips and practicing with different coloring techniques, you can create a detailed and accurate diagram that reflects your understanding of the plant cell’s structure. Remember to use a variety of colors, label cell components, pay attention to detail, and practice with different techniques to enhance your learning experience. With patience and practice, you can develop a deeper understanding of the plant cell’s structure and its role in the functioning of plants.