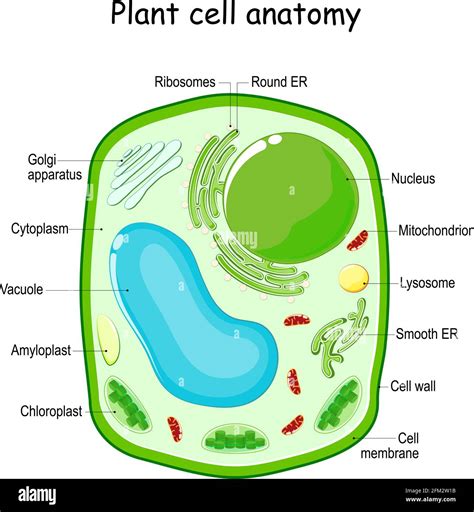
The plant cell is a complex and fascinating structure that plays a crucial role in the survival and growth of plants. Understanding the different components of a plant cell is essential for botanists, biologists, and anyone interested in the natural world. In this article, we will delve into the world of plant cells and explore their structure, function, and importance.
Introduction to Plant Cells
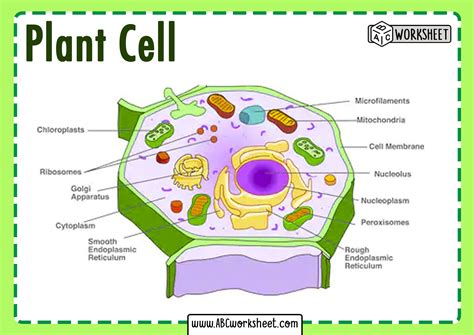
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that are characterized by the presence of a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. These cells are the building blocks of plants and are responsible for carrying out various functions such as photosynthesis, growth, and development. The plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall that provides support, protection, and maintains the cell’s shape.
Key Points
- The plant cell is a eukaryotic cell with a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole.
- The cell wall provides support, protection, and maintains the cell's shape.
- Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
- The large central vacuole plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell's turgor pressure and storing nutrients and waste products.
- The plant cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane that regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
Components of a Plant Cell
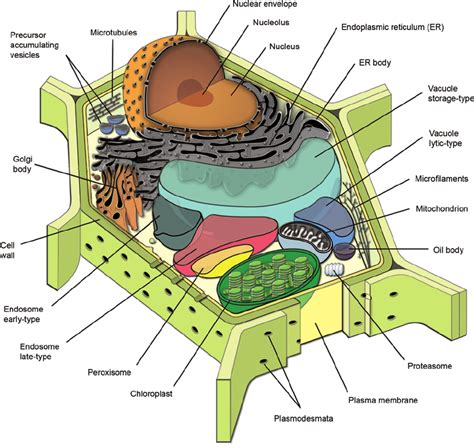
A plant cell is composed of several components, each with its unique function and characteristics. The main components of a plant cell include:
Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the plant cell and provides support, protection, and maintains the cell’s shape. It is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which are complex carbohydrates that give the cell wall its strength and rigidity.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy. They contain the pigment chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and plays a crucial role in absorbing light energy.
Large Central Vacuole
The large central vacuole is a prominent feature of plant cells and plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s turgor pressure and storing nutrients and waste products. It is a membrane-bound organelle that is filled with a solution called cell sap, which contains water, salts, and other substances.
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the plant cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell. It is semi-permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the plant cell and surrounds the organelles. It is composed of water, salts, and other substances and plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s shape and structure.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the plant cell and contains the cell’s genetic material, or DNA. It is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope and plays a crucial role in regulating the cell’s growth, development, and reproduction.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Provides support, protection, and maintains the cell's shape |
| Chloroplasts | Responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy |
| Large Central Vacuole | Maintains the cell's turgor pressure and stores nutrients and waste products |
| Plasma Membrane | Regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell |
| Cytoplasm | Maintains the cell's shape and structure |
| Nucleus | Contains the cell's genetic material, or DNA, and regulates the cell's growth, development, and reproduction |
Importance of Plant Cells
Plant cells play a crucial role in the survival and growth of plants. They are responsible for carrying out various functions such as photosynthesis, growth, and development. Without plant cells, plants would not be able to produce the energy they need to grow and thrive.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plant cells convert light energy into chemical energy. This process occurs in the chloroplasts and is essential for the production of glucose, which is used by the plant to fuel its growth and development.
Growth and Development
Plant cells play a crucial role in the growth and development of plants. They are responsible for producing the energy and nutrients needed for plant growth and development.
Response to Environment
Plant cells are able to respond to their environment in various ways. They can adjust their growth and development in response to changes in light, temperature, and water availability.
What is the main function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
+The main function of the cell wall in a plant cell is to provide support, protection, and maintain the cell's shape.
What is the role of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy.
What is the function of the large central vacuole in a plant cell?
+The large central vacuole plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell's turgor pressure and storing nutrients and waste products.
In conclusion, plant cells are complex and fascinating structures that play a crucial role in the survival and growth of plants. Understanding the different components of a plant cell and their functions is essential for appreciating the beauty and complexity of plant biology. By studying plant cells, we can gain a deeper understanding of how plants grow, develop, and respond to their environment.