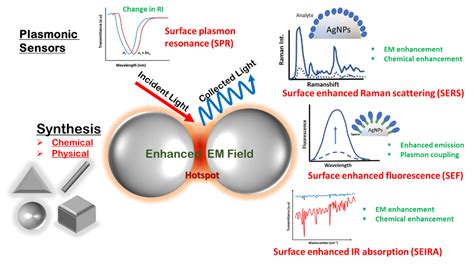
The field of plasmonics has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with plasmonic particles being at the forefront of this research. These particles have the ability to manipulate light at the nanoscale, leading to a wide range of applications in fields such as optics, electronics, and medicine. But how do plasmonic particles work? In this article, we will delve into the world of plasmonics and explore the 5 ways plasmonic particles work, highlighting their unique properties and potential applications.
Key Points
- Plasmonic particles can enhance local electromagnetic fields, leading to improved optical sensing and imaging capabilities.
- The surface plasmon resonance (SPR) phenomenon allows for the manipulation of light at the nanoscale, enabling applications such as biosensing and optical trapping.
- Plasmonic particles can be used to enhance the efficiency of solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
- The unique properties of plasmonic particles make them ideal for use in biomedical applications, such as cancer treatment and drug delivery.
- Plasmonic particles can be designed to exhibit specific optical properties, such as tunable resonance frequencies and enhanced nonlinear optical effects.
Enhancement of Local Electromagnetic Fields

One of the primary ways in which plasmonic particles work is by enhancing local electromagnetic fields. This is achieved through the excitation of surface plasmons, which are collective oscillations of electrons at the surface of the particle. When light is incident on the particle, it can cause the electrons to oscillate, leading to the formation of an enhanced electromagnetic field. This field can be used to improve optical sensing and imaging capabilities, as well as to enhance the efficiency of optoelectronic devices.
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
The surface plasmon resonance (SPR) phenomenon is a critical aspect of plasmonic particles. SPR occurs when the frequency of the incident light matches the natural frequency of the surface plasmons, leading to a significant enhancement of the local electromagnetic field. This phenomenon can be used to manipulate light at the nanoscale, enabling applications such as biosensing and optical trapping. For example, SPR-based biosensors can be used to detect biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA, with high sensitivity and specificity.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Resonance Frequency | 500-800 nm |
| Enhancement Factor | 10-100 |
| Detection Limit | 10^-12 M |
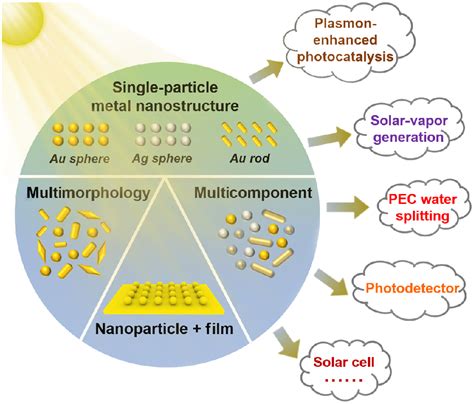
Enhancement of Optoelectronic Devices
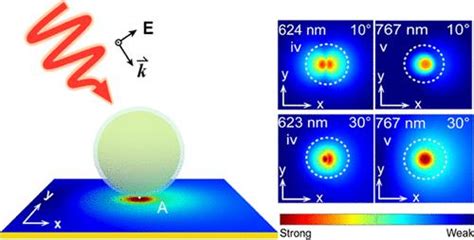
Plasmonic particles can also be used to enhance the efficiency of optoelectronic devices, such as solar cells and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). By incorporating plasmonic particles into these devices, researchers can improve their performance and efficiency, leading to increased energy conversion rates and reduced energy losses. For example, plasmonic particles can be used to enhance the absorption of light in solar cells, leading to increased energy conversion rates and improved device efficiency.
Biomedical Applications
The unique properties of plasmonic particles make them ideal for use in biomedical applications, such as cancer treatment and drug delivery. For example, plasmonic particles can be designed to target specific cells or tissues, allowing for the delivery of therapeutic agents or the destruction of cancer cells. Additionally, plasmonic particles can be used to enhance the contrast of medical images, allowing for improved diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Plasmonic particles have also been shown to have potential in the field of photothermal therapy, where they can be used to generate heat and destroy cancer cells. This is achieved through the excitation of surface plasmons, which can cause the particles to heat up, leading to the destruction of surrounding cells. The use of plasmonic particles in photothermal therapy has shown promising results, with studies demonstrating the ability to selectively target and destroy cancer cells while leaving healthy cells intact.
What are the potential applications of plasmonic particles in biomedical research?
+Plasmonic particles have a wide range of potential applications in biomedical research, including cancer treatment, drug delivery, and medical imaging. They can be designed to target specific cells or tissues, allowing for the delivery of therapeutic agents or the destruction of cancer cells.
How do plasmonic particles enhance the efficiency of optoelectronic devices?
+Plasmonic particles can enhance the efficiency of optoelectronic devices by improving the absorption of light, reducing energy losses, and increasing energy conversion rates. They can be incorporated into devices such as solar cells and LEDs to improve their performance and efficiency.
What is the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) phenomenon, and how is it used in plasmonic particles?
+The surface plasmon resonance (SPR) phenomenon occurs when the frequency of the incident light matches the natural frequency of the surface plasmons, leading to a significant enhancement of the local electromagnetic field. This phenomenon can be used to manipulate light at the nanoscale, enabling applications such as biosensing and optical trapping.
In conclusion, plasmonic particles work in a variety of ways, from enhancing local electromagnetic fields and manipulating light at the nanoscale to enhancing the efficiency of optoelectronic devices and enabling biomedical applications. By understanding the unique properties of plasmonic particles, researchers can design and develop new devices and systems that take advantage of their enhanced optical properties, leading to breakthroughs in fields such as optics, electronics, and medicine.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the 5 ways plasmonic particles work, from enhancing local electromagnetic fields to enabling biomedical applications, and learn about their unique properties and potential uses.”