Logistic regression is a fundamental algorithm in machine learning, widely used for binary classification problems. It's a powerful tool for predicting the probability of an event occurring based on a set of input variables. Despite its simplicity, logistic regression can be tricky to implement and interpret, especially for those new to machine learning. In this article, we'll delve into five essential tips for getting the most out of logistic regression, covering everything from data preparation to model evaluation.
Key Points
- Understanding the problem and data is crucial before applying logistic regression.
- Feature scaling can significantly impact the performance of logistic regression models.
- Regularization techniques can help prevent overfitting in logistic regression.
- Evaluating the model using metrics beyond accuracy is essential for a comprehensive understanding of its performance.
- Interpreting the coefficients of a logistic regression model requires careful consideration of the odds ratio.
Tip 1: Understanding the Problem and Data

Before diving into logistic regression, it’s essential to have a deep understanding of the problem you’re trying to solve and the data you’re working with. This includes identifying the target variable, which should be binary (0/1, yes/no, etc.), and understanding the nature of your predictor variables. Are they categorical, numerical, or a mix? This knowledge will guide your data preprocessing steps, such as encoding categorical variables or scaling numerical ones. For instance, if you’re predicting whether a customer will buy a product based on their age, gender, and income, you need to decide how to represent gender in a numerical format that logistic regression can understand.
Importance of Data Quality
Data quality is paramount. Missing values, outliers, and skewed distributions can all impact the performance of your logistic regression model. It’s crucial to inspect your data thoroughly and clean it as necessary. This might involve imputing missing values, transforming variables to reduce skewness, or even removing outliers if they are deemed not representative of the underlying population. For example, if you’re dealing with income data that has a few extremely high values, you might consider using a logarithmic transformation to stabilize the variance.
Tip 2: Feature Scaling
Feature scaling is a critical step in preparing your data for logistic regression. Unlike some other algorithms, logistic regression is sensitive to the scale of the predictor variables. If one variable has a much larger range than the others, it can dominate the model, leading to poor predictions. Feature scaling, such as standardization or normalization, ensures that all variables are on the same scale, which can significantly improve the model’s performance and stability. Standardization (subtracting the mean and then dividing by the standard deviation for each variable) is a common approach, as it helps in the convergence of the model.
Choosing the Right Scaling Method
The choice between standardization and normalization depends on the distribution of your data and the presence of outliers. Normalization (usually between 0 and 1) can be more robust to outliers, but it may not be suitable if the data contains zeros or if the range of the data is not well-defined. On the other hand, standardization is more sensitive to outliers but preserves the shape of the distribution, which can be beneficial for many statistical analyses.
Tip 3: Regularization Techniques
Overfitting is a common issue in logistic regression, especially when dealing with a large number of predictor variables or complex interactions. Regularization techniques, such as L1 (Lasso) and L2 (Ridge) regularization, can help mitigate overfitting by penalizing large coefficients. L1 regularization can also be used for feature selection, as it sets the coefficients of non-important variables to zero. The choice between L1 and L2 regularization depends on the specific problem and the nature of the data. Cross-validation is a useful tool for determining the optimal regularization strength.
| Regularization Type | Description |
|---|---|
| L1 (Lasso) Regularization | Sets coefficients to zero, useful for feature selection. |
| L2 (Ridge) Regularization | Reduces coefficient values, prevents overfitting without eliminating variables. |
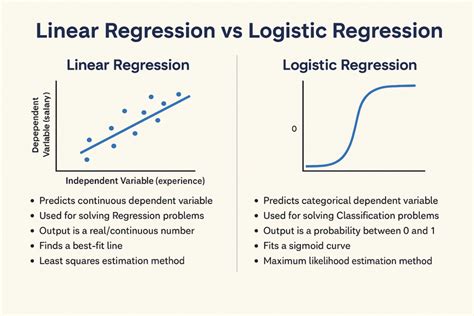
Tip 4: Evaluating the Model
Evaluating the performance of a logistic regression model goes beyond just looking at accuracy. While accuracy can give a general idea of how well the model is doing, it doesn’t tell the whole story, especially in imbalanced datasets. Other metrics, such as precision, recall, F1 score, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC), provide a more nuanced view of the model’s performance. Precision and recall are particularly useful for understanding the model’s ability to predict positive outcomes correctly and its ability to identify all instances of the positive class, respectively.
Understanding Evaluation Metrics
The AUC-ROC score, which ranges from 0 to 1, indicates the model’s ability to distinguish between the positive and negative classes. A score of 1 represents perfect separation, while a score of 0.5 indicates no better than random guessing. The F1 score, which is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, is useful for striking a balance between these two metrics. It’s essential to choose the evaluation metrics that align with the goals of your project and the nature of your data.
Tip 5: Interpreting Coefficients
Interpreting the coefficients of a logistic regression model requires understanding the concept of odds ratios. The coefficient represents the change in the log odds of the outcome variable for a one-unit change in the predictor variable, while holding all other predictor variables constant. To interpret these coefficients in a more intuitive way, it’s helpful to exponentiate them, which gives the odds ratio. An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that an increase in the predictor variable is associated with an increase in the odds of the positive outcome, while an odds ratio less than 1 indicates a decrease in the odds.
Real-World Applications
In real-world scenarios, understanding how to interpret logistic regression coefficients is vital for decision-making. For instance, in credit risk assessment, the coefficients can help determine how different factors (such as income, credit history, and debt-to-income ratio) influence the likelihood of a loan being approved. By understanding these relationships, financial institutions can make more informed decisions about lending.
What is the main difference between L1 and L2 regularization in logistic regression?
+L1 regularization (Lasso) sets the coefficients of non-important variables to zero, effectively performing feature selection, while L2 regularization (Ridge) reduces the coefficient values to prevent overfitting without eliminating any variables.
How do you evaluate the performance of a logistic regression model?
+Evaluating a logistic regression model involves looking beyond accuracy to metrics such as precision, recall, F1 score, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) to get a comprehensive understanding of the model's performance.
What is the purpose of feature scaling in logistic regression?
+Feature scaling ensures that all predictor variables are on the same scale, which can improve the model's performance and stability by preventing any single variable from dominating the model due to its large range.
In conclusion, logistic regression is a powerful tool for binary classification, but its effectiveness depends on careful consideration of several factors, including data preparation, feature scaling, regularization, model evaluation, and coefficient interpretation. By following these tips and understanding the nuances of logistic regression, practitioners can unlock its full potential and make more accurate predictions in a wide range of applications.