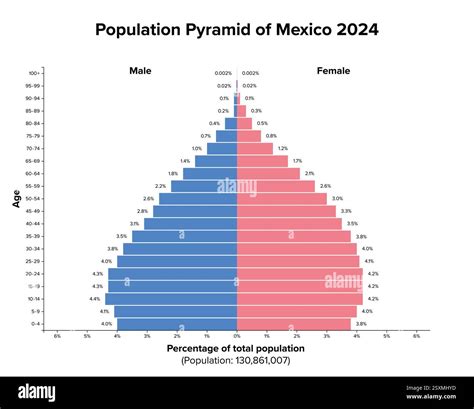
Mexico, officially known as the United Mexican States, is a country located in the southern portion of North America. It is a federation comprising 31 states and a special federal entity, Mexico City, which serves as the capital. The country's population is one of its most significant aspects, reflecting its economic, social, and cultural dynamics. As of the latest data available, Mexico's population presents several interesting facts that shed light on its demographic trends and characteristics.
Key Points
- Mexico's population is approximately 130 million people, making it the 10th most populous country in the world.
- The population growth rate has been declining, with a current annual rate of about 1.0%, reflecting trends in fertility rates and urbanization.
- Mexico City, the capital, is one of the most populous metropolitan areas globally, with over 21 million inhabitants, contributing significantly to the country's urban population.
- The average life expectancy at birth in Mexico is around 72 years for males and 77 years for females, indicating improvements in healthcare and living standards.
- Mexico experiences a significant migration phenomenon, both within its borders and internationally, particularly with the United States, which affects its demographic balance and economic landscape.
Population Size and Growth Rate
Mexico’s population has been steadily increasing over the years, though at a decelerating pace. With a population of approximately 130 million, Mexico ranks among the world’s most populous countries. The growth rate, however, has seen a notable decline, from peaks of over 3% in the mid-20th century to about 1.0% currently. This decrease is largely attributed to a decline in fertility rates, as the average number of children per woman has dropped significantly over the past few decades, moving closer to replacement levels.
Fertility Rates and Urbanization
The decline in fertility rates is a key factor in Mexico’s slowing population growth. The total fertility rate (TFR) has decreased substantially, from around 6.8 children per woman in 1970 to about 2.1 children per woman in recent years. This reduction is associated with increased access to education, especially for women, and improvements in family planning services. Urbanization also plays a crucial role, as urban dwellers tend to have fewer children than their rural counterparts. Mexico’s urban population constitutes a significant portion of its total population, with major cities like Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Monterrey being hubs for economic, cultural, and educational activities.
| Demographic Indicator | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Population (2023 estimate) | Approximately 130 million |
| Population Growth Rate (2023 estimate) | 1.0% per annum |
| Total Fertility Rate (TFR) | About 2.1 children per woman |
| Life Expectancy at Birth | 72 years for males, 77 years for females |

Migration Patterns

Mexico’s population dynamics are also influenced by migration, both internally and internationally. Internally, there is a significant movement of people from rural areas to urban centers in search of better economic opportunities. Internationally, Mexico is a country of origin, transit, and destination for migrants. The United States is a primary destination for Mexican migrants, with millions of Mexicans living and working there. This migration has economic, social, and political implications for both countries, including remittances, labor market dynamics, and border control policies.
Impact of Migration
The impact of migration on Mexico’s population is multifaceted. Remittances from abroad contribute significantly to the country’s economy, supporting families and communities. However, the loss of skilled and unskilled labor can have negative effects on certain sectors of the Mexican economy. Moreover, the return of migrants can bring back skills and experiences that can contribute to the country’s development, but it also poses challenges related to reintegration into the labor market and society.
In conclusion, Mexico's population facts reveal a complex and evolving demographic landscape. Understanding these trends is crucial for policymakers, economists, and social scientists to address the challenges and opportunities presented by population dynamics. By examining the interplay of factors such as fertility rates, urbanization, and migration, it is possible to develop more effective strategies for sustainable development and social welfare.
What is the current population of Mexico?
+Mexico’s population is approximately 130 million people as of the latest estimates.
What is the average life expectancy in Mexico?
+The average life expectancy at birth in Mexico is around 72 years for males and 77 years for females.
Why is Mexico’s population growth rate declining?
+The decline in Mexico’s population growth rate is largely due to a decrease in fertility rates, which have been influenced by factors such as increased access to education, especially for women, and improvements in family planning services.