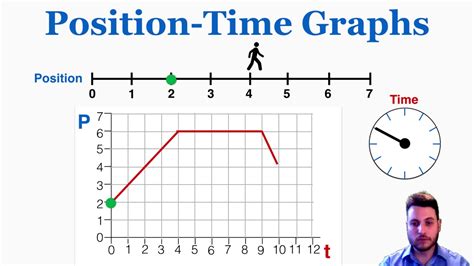
Position graphs are a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, used to describe the motion of objects. They provide a visual representation of an object's position over time, allowing us to analyze and understand its motion. In this article, we will explore five ways position graphs work, including their construction, interpretation, and application in real-world scenarios.
Key Points
- Position graphs are used to describe the motion of objects over time.
- The construction of position graphs involves plotting the object's position against time.
- Position graphs can be used to determine the velocity and acceleration of an object.
- There are different types of position graphs, including linear, quadratic, and sinusoidal graphs.
- Position graphs have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields.
Construction of Position Graphs
The construction of position graphs involves plotting the object’s position against time. This can be done using a variety of methods, including manual plotting, graphical software, or programming languages. The resulting graph provides a visual representation of the object’s motion, allowing us to identify patterns and trends. For example, a position graph can be used to show the motion of a car over a given period, with the x-axis representing time and the y-axis representing the car’s position.
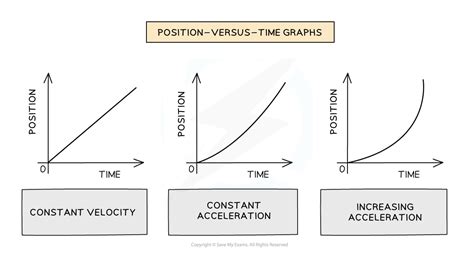
Types of Position Graphs
There are several types of position graphs, each with its own unique characteristics. Linear position graphs, for instance, represent motion at a constant velocity, while quadratic position graphs represent motion with a constant acceleration. Sinusoidal position graphs, on the other hand, represent periodic motion, such as the motion of a pendulum or a spring-mass system. Understanding the different types of position graphs is essential for analyzing and interpreting motion data.
| Type of Position Graph | Description |
|---|---|
| Linear | Represents motion at a constant velocity |
| Quadratic | Represents motion with a constant acceleration |
| Sinusoidal | Represents periodic motion |
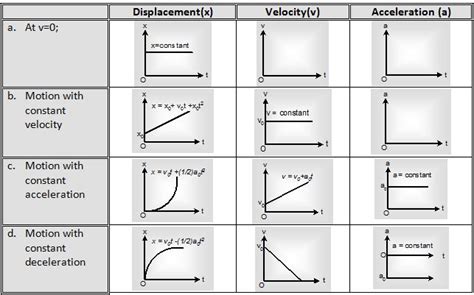
Interpretation of Position Graphs
Interpreting position graphs requires a thorough understanding of the underlying physics and mathematics. By analyzing the shape and features of the graph, we can determine the object’s velocity, acceleration, and other motion parameters. For example, the slope of a position graph represents the object’s velocity, while the curvature of the graph represents the object’s acceleration. Additionally, the graph can be used to identify key events, such as changes in direction or speed.
Applications of Position Graphs
Position graphs have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. They are used to analyze and design motion systems, such as robotics, automotive systems, and aerospace systems. Additionally, position graphs are used in scientific research, such as the study of particle motion, fluid dynamics, and biomechanics. By providing a visual representation of motion, position graphs enable researchers and engineers to develop more accurate models, optimize system performance, and improve safety.
Real-World Examples of Position Graphs
Position graphs are used in a wide range of real-world applications, from navigation systems to medical devices. For example, GPS navigation systems use position graphs to track a vehicle’s location and velocity, providing turn-by-turn directions and estimated arrival times. In medical devices, position graphs are used to analyze patient motion, such as the motion of a patient’s heart or lungs, providing critical information for diagnosis and treatment.
What is the purpose of a position graph?
+The purpose of a position graph is to provide a visual representation of an object's motion over time, allowing us to analyze and understand its motion parameters, such as velocity and acceleration.
How are position graphs constructed?
+Position graphs are constructed by plotting the object's position against time, using methods such as manual plotting, graphical software, or programming languages.
What are the different types of position graphs?
+There are several types of position graphs, including linear, quadratic, and sinusoidal graphs, each representing different types of motion, such as constant velocity, constant acceleration, and periodic motion.
In conclusion, position graphs are a powerful tool for analyzing and understanding motion. By providing a visual representation of an object’s position over time, position graphs enable us to determine velocity, acceleration, and other motion parameters, and have numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. Whether used in navigation systems, medical devices, or scientific research, position graphs play a critical role in helping us understand and describe the world around us.