The concept of Positive Predictive Value (PPV) is crucial in various fields, including medicine, finance, and social sciences. It refers to the proportion of true positive results among all positive results obtained by a diagnostic test or a predictive model. In simpler terms, PPV answers the question: "If a test says I have a condition, what are the chances that I actually have it?" Understanding PPV is vital because it helps in making informed decisions, managing resources effectively, and avoiding unnecessary interventions. This article will delve into five ways PPV matters, exploring its significance, applications, and implications.
Key Points
- PPV is essential for evaluating the accuracy of diagnostic tests and predictive models.
- It helps in managing healthcare resources by identifying true positives and reducing false alarms.
- PPV plays a critical role in finance by assessing the reliability of credit scoring models and fraud detection systems.
- Understanding PPV is vital for policymakers to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
- PPV has significant implications for individuals, affecting their well-being, privacy, and access to services.
Medical Diagnosis and Treatment

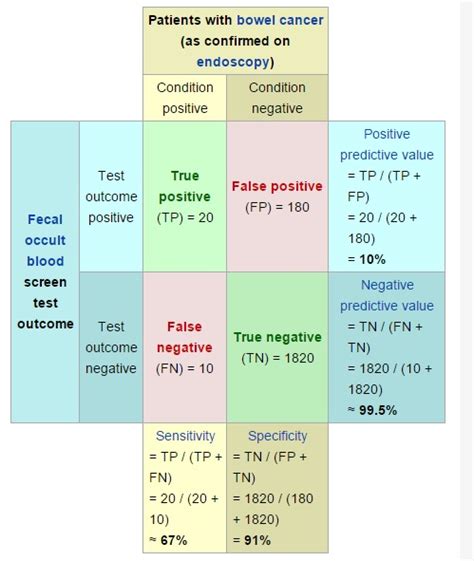
In the medical field, PPV is used to evaluate the effectiveness of diagnostic tests. For instance, a test for a rare disease may have high sensitivity (ability to detect true positives) but low specificity (ability to detect true negatives), resulting in a low PPV. This means that many people who test positive may not actually have the disease, leading to unnecessary anxiety, further testing, and potential harm from treatments. Understanding PPV helps clinicians interpret test results more accurately, making better-informed decisions about patient care and treatment.
PPV in Screening Programs
Screening programs for diseases like cancer or HIV rely heavily on PPV. A high PPV ensures that most individuals who test positive actually have the condition, allowing for timely and targeted interventions. Conversely, a low PPV can lead to overtreatment and unnecessary costs. For example, a study on breast cancer screening found that the PPV of mammography varies by age and risk factors, highlighting the need for personalized approaches to screening and diagnosis.
| Disease | Prevalence | Test Sensitivity | Test Specificity | PPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | 1% | 90% | 95% | 16.1% |
| Prostate Cancer | 2% | 80% | 90% | 15.4% |
| HIV | 0.5% | 99% | 99.5% | 90.9% |
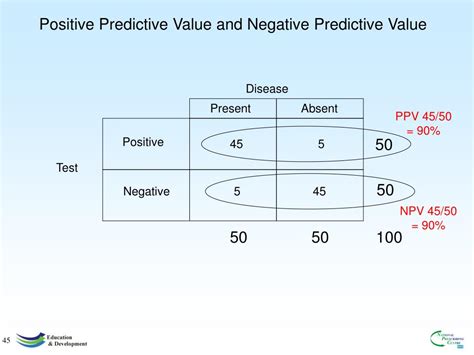
Financial Applications and Risk Assessment
In finance, PPV is crucial for assessing the reliability of credit scoring models and fraud detection systems. A high PPV in credit scoring indicates that individuals identified as high-risk are indeed more likely to default, allowing lenders to make informed decisions about loan approvals and interest rates. Similarly, in fraud detection, a high PPV means that most transactions flagged as suspicious are actually fraudulent, enabling timely interventions to prevent financial losses.
PPV in Credit Risk Assessment
A study on credit scoring models found that the PPV of default predictions varied significantly across different models and datasets. The results highlighted the importance of model validation and the need for ongoing monitoring of PPV to ensure that credit decisions are fair and accurate. By understanding PPV, financial institutions can optimize their risk assessment processes, minimize losses, and improve customer outcomes.
The implications of PPV extend beyond the financial sector, influencing policy decisions and resource allocation. Policymakers must consider the PPV of various interventions and programs to ensure that resources are allocated effectively and that policies are evidence-based. This requires a nuanced understanding of PPV and its applications, as well as the ability to communicate complex concepts to diverse stakeholders.
Policymaking and Resource Allocation
PPV plays a critical role in policymaking by helping to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and programs. For instance, in public health, understanding the PPV of disease surveillance systems is essential for identifying outbreaks and allocating resources to affected areas. Similarly, in education, PPV can help evaluate the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving student outcomes, allowing policymakers to make data-driven decisions about resource allocation.
PPV in Policy Evaluation
A key challenge in policy evaluation is the presence of confounding variables, which can affect the accuracy of PPV estimates. Researchers must use robust methodologies, such as propensity score matching or instrumental variables, to control for these variables and obtain unbiased estimates of PPV. By doing so, policymakers can develop more effective interventions and allocate resources more efficiently, ultimately leading to better outcomes for individuals and communities.
What is the difference between PPV and NPV?
+PPV (Positive Predictive Value) is the proportion of true positive results among all positive results, while NPV (Negative Predictive Value) is the proportion of true negative results among all negative results. Both measures are essential for evaluating the accuracy of diagnostic tests and predictive models.
How does PPV affect healthcare resource allocation?
+PPV helps healthcare providers allocate resources more effectively by identifying true positives and reducing false alarms. This leads to better patient outcomes, reduced costs, and more efficient use of healthcare resources.
What are the implications of PPV for individuals?
+PPV has significant implications for individuals, affecting their well-being, privacy, and access to services. A high PPV can provide reassurance and timely interventions, while a low PPV can lead to unnecessary anxiety, further testing, and potential harm from treatments.
In conclusion, Positive Predictive Value is a critical concept that has far-reaching implications across various fields. By understanding PPV, individuals and organizations can make more informed decisions, manage resources effectively, and improve outcomes. As the complexity of diagnostic tests and predictive models continues to evolve, the importance of PPV will only continue to grow, underscoring the need for ongoing education, research, and dialogue among stakeholders.