Potassium permanganate, with the chemical formula KMnO4, is a versatile and highly effective compound used in various applications, ranging from water treatment and disinfection to chemical synthesis and analytical chemistry. Its unique properties, including its strong oxidizing capabilities, make it an essential reagent in many industrial, medical, and laboratory settings. Understanding the potassium permanganate formula and its applications is crucial for leveraging its potential across different fields.
Chemical Structure and Properties

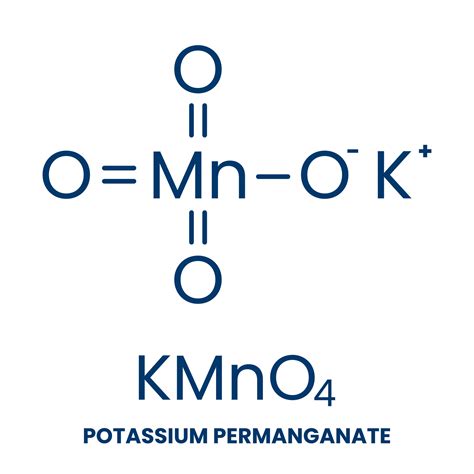
The potassium permanganate formula, KMnO4, indicates that one molecule of potassium permanganate consists of one potassium (K) atom, one manganese (Mn) atom, and four oxygen (O) atoms. This compound is characterized by its deep purple color and is highly soluble in water. The manganese atom in the permanganate ion (MnO4-) is in the +7 oxidation state, which confers its strong oxidizing properties. These properties make potassium permanganate a valuable agent for oxidation reactions, where it can accept electrons from other substances, thereby altering their chemical structure.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the significant applications of potassium permanganate is in water treatment, where it serves as a disinfectant and an oxidizing agent. It is effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, making it a critical component in ensuring the safety of drinking water. Additionally, potassium permanganate can oxidize iron and manganese compounds, as well as hydrogen sulfide, which can cause unpleasant odors and tastes in water. Its use in water treatment facilities involves careful dosing, as excessive amounts can lead to undesirable tastes and colors in the treated water.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Disinfection | Effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi |
| Oxidation of Inorganic Compounds | Removes iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide |
| Organic Compound Oxidation | Breaks down certain organic pollutants |

Medical and Laboratory Applications

Beyond water treatment, potassium permanganate has medical and laboratory applications. In medicine, it is used as an antiseptic and astringent, particularly in the treatment of wounds and skin conditions. Its antifungal properties make it useful for treating fungal infections of the skin and nails. In laboratory settings, potassium permanganate is utilized as a strong oxidizing agent in various chemical reactions and as a titrant in analytical chemistry, especially in the determination of the concentration of substances through redox titration.
Chemical Synthesis and Industry
In the realm of chemical synthesis, potassium permanganate is a valuable reagent for oxidation reactions. It can oxidize alkenes to form diols, oxidize primary alcohols to carboxylic acids, and perform other complex transformations that are crucial in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic compounds. Its application in industry extends to the manufacturing of saccharin, the production of benzene, and as a catalyst in the production of certain resins and polymers.
Key Points
- Potassium permanganate's formula, KMnO4, reflects its composition and oxidizing capabilities.
- It is widely used in water treatment for disinfection and the removal of inorganic and organic compounds.
- Medical applications include its use as an antiseptic and in the treatment of fungal infections.
- In laboratory settings, it serves as a strong oxidizing agent and titrant in analytical chemistry.
- Its industrial applications span chemical synthesis, manufacturing of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, and production of polymers.
In conclusion, the potassium permanganate formula, KMnO4, encapsulates the compound's versatility and potency. Its applications are diverse, ranging from ensuring the safety of drinking water to facilitating complex chemical syntheses. As a strong oxidizing agent, it plays a critical role in various industrial, medical, and laboratory processes, underscoring its importance in modern chemistry and technology.
What are the primary uses of potassium permanganate in water treatment?
+Potassium permanganate is primarily used for disinfection, removing iron and manganese, and oxidizing hydrogen sulfide, which can cause unpleasant odors and tastes in water.
How does potassium permanganate work as a medical antiseptic?
+It works by leveraging its strong oxidizing properties to kill bacteria, viruses, and fungi, thereby preventing infection and promoting healing in wounds and skin conditions.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling potassium permanganate?
+Due to its strong oxidizing properties and potential to cause skin and eye irritation, it is essential to wear protective clothing, including gloves and goggles, and to work in a well-ventilated area when handling potassium permanganate.