Power series, a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the realm of calculus and analysis, have been a cornerstone for understanding functions and their behaviors. The study of power series dates back to the 17th and 18th centuries, with notable mathematicians such as Isaac Newton and Leonhard Euler contributing significantly to the field. In essence, a power series is an infinite series of the form $a_0 + a_1x + a_2x^2 + a_3x^3 + \ldots + a_nx^n + \ldots$, where $a_n$ are coefficients, and $x$ is the variable. This representation allows for the approximation of functions through a polynomial of infinite degree, enabling the analysis of functions that are otherwise complex or impossible to analyze directly.
Key Points
- The power series is a mathematical tool used to represent functions as an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the powers of the variable.
- The convergence of a power series is crucial and depends on the value of $x$; for some values, the series may converge absolutely, for others, it may diverge.
- Power series are essential in calculus for solving differential equations, representing functions in a compact form, and analyzing the properties of functions such as continuity, differentiation, and integration.
- The Taylor series and Maclaurin series are special types of power series that are used to approximate functions at a given point, with the Maclaurin series being a Taylor series centered at $x=0$.
- Understanding power series requires knowledge of calculus, particularly limits, differentiation, and integration, as these concepts are fundamental to analyzing and working with power series.
Understanding Power Series

To delve deeper into the concept of power series, it’s essential to understand their construction and behavior. The general form of a power series is f(x) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} a_nx^n = a_0 + a_1x + a_2x^2 + \ldots + a_nx^n + \ldots, where a_n are constants (coefficients of the series), and x is a variable. The series converges for certain values of x and diverges for others. The set of values for which the series converges is known as the interval of convergence, and the series diverges for x values outside this interval.
Convergence of Power Series
The convergence of a power series is determined by the coefficients a_n and the value of x. One method to determine the interval of convergence is by using the ratio test, which involves calculating the limit of the absolute value of the ratio of successive terms of the series as n approaches infinity. If this limit is less than 1, the series converges absolutely; if it is greater than 1, the series diverges; and if it equals 1, the test is inconclusive, requiring further analysis.
| Convergence Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Ratio Test | Determines convergence by evaluating the limit of $|\frac{a_{n+1}x^{n+1}}{a_nx^n}|$ as $n$ approaches infinity. |
| Root Test | Assesses convergence by examining the limit of $\sqrt[n]{|a_nx^n|}$ as $n$ approaches infinity. |
| Integral Test | Used for series of positive terms, compares the series with an improper integral to determine convergence. |
Applications of Power Series
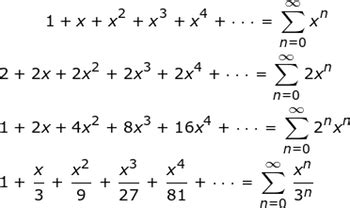
Power series have numerous applications across various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science. In calculus, they are used to solve differential equations, to represent functions in a more manageable form, and to study the properties of functions such as continuity, differentiation, and integration. The ability to approximate functions using power series expansions facilitates the analysis of complex systems and phenomena.
Taylor and Maclaurin Series
Two special types of power series are the Taylor series and the Maclaurin series. The Taylor series of a function f(x) centered at x=a is given by f(x) = f(a) + f'(a)(x-a) + \frac{f''(a)}{2!}(x-a)^2 + \frac{f'''(a)}{3!}(x-a)^3 + \ldots. When a=0, the Taylor series becomes the Maclaurin series, which is f(x) = f(0) + f'(0)x + \frac{f''(0)}{2!}x^2 + \frac{f'''(0)}{3!}x^3 + \ldots. These series are essential for approximating functions at a given point and are used extensively in numerical analysis and calculus.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, power series are a powerful tool in mathematics, allowing for the representation and analysis of functions in a compact and manageable form. Their applications are diverse, ranging from solving differential equations to approximating functions in numerical analysis. As mathematics and related fields continue to evolve, the understanding and application of power series will remain crucial for advancing our knowledge of complex systems and phenomena.
What is the main purpose of using power series in mathematics?
+The main purpose of using power series is to represent functions in a more manageable form, facilitating the analysis of their properties and behaviors, especially for complex functions that are difficult to analyze directly.
How do you determine the interval of convergence for a power series?
+The interval of convergence can be determined using various tests such as the ratio test, root test, or integral test. These tests evaluate the limit of the series terms as n approaches infinity to decide whether the series converges or diverges for different values of x.
What is the difference between a Taylor series and a Maclaurin series?
+A Taylor series is a power series representation of a function centered at any point x=a, while a Maclaurin series is a special case of the Taylor series centered at x=0. Thus, every Maclaurin series is a Taylor series, but not every Taylor series is a Maclaurin series.



