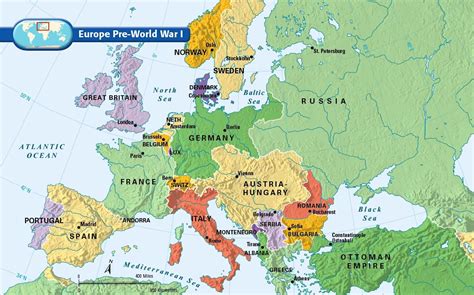
Understanding the complex geography and political landscape of pre-World War I Europe is crucial for grasping the events that led to the Great War. The early 20th century was marked by a delicate balance of power among European nations, with alliances, territorial disputes, and imperial ambitions all playing significant roles. Maps from this period offer valuable insights into the political, social, and economic conditions that characterized the continent on the eve of one of the most devastating conflicts in human history.
Introduction to Pre-WWI Europe
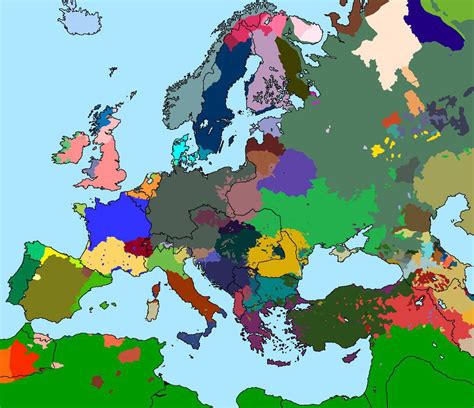
Pre-World War I Europe was a continent of contrasts, with industrialized nations like Britain, France, and Germany standing alongside less developed regions in Eastern Europe and the Balkans. The era was marked by nationalism, imperialism, and militarism, all of which contributed to an environment in which war became increasingly likely. The system of alliances, including the Triple Entente (France, Britain, and Russia) and the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy), divided Europe into two camps, setting the stage for a broader conflict.
Key Points
- The complex system of alliances in Europe, including the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance, played a significant role in the lead-up to WWI.
- Imperialism and the scramble for colonies contributed to tensions among European powers.
- Nationalism, especially in the Balkans, was a driving force behind the events leading to WWI.
- The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary in 1914 was the immediate trigger for the war.
- Maps of pre-WWI Europe help illustrate the political divisions, territorial disputes, and the balance of power among nations.
Maps of Pre-WWI Europe
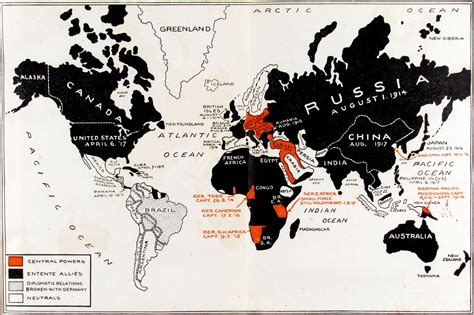
Maps from the pre-World War I era provide a visual representation of the political landscape, helping to clarify the complex relationships and territorial claims that characterized the period. Five significant maps from this era include:
1. The Map of Europe in 1914
This map highlights the political boundaries of Europe just before the outbreak of World War I. It shows the division of the continent into the two main alliance systems and illustrates the territorial claims and disputes that were significant factors leading to the war.
2. The Balkans in 1914
The Balkans were a region of significant turmoil in the years leading up to WWI, with various ethnic groups seeking independence or unity under different nations. A map of the Balkans in 1914 would show the complex political landscape, including the Ottoman Empire’s declining influence, the rise of nationalist movements, and the role of external powers like Austria-Hungary and Serbia.
3. Colonial Empires of European Powers
A map detailing the colonial empires of European powers in 1914 would illustrate the extent of imperialism and the scramble for Africa and other regions. This map would show how European nations had divided much of the world into colonies, protectorates, and spheres of influence, contributing to global tensions and rivalries.
4. The System of Alliances
A map focused on the system of alliances would visually represent the complex network of agreements and understandings among European nations. It would illustrate how the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance divided Europe and how these alliances contributed to the rapid escalation of the conflict following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
5. Territorial Changes After the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars of 1912-1913 led to significant territorial changes in the region, further destabilizing the political landscape of Europe. A map showing these changes would highlight the gains and losses of various nations, including the expansion of Serbia, the decline of the Ottoman Empire, and the implications of these shifts for the balance of power in Europe.
| Event | Date | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand | June 28, 1914 | Immediate trigger for WWI |
| Balkan Wars | 1912-1913 | Redrew the map of the Balkans, contributing to European instability |
| Formation of the Triple Entente and Triple Alliance | Early 20th century | Divided Europe into two opposing camps, increasing the risk of a broader conflict |

Conclusion
In conclusion, maps of pre-WWI Europe provide invaluable insights into the political, social, and economic conditions that led to one of the most significant conflicts of the 20th century. By examining these maps in the context of historical events and trends, it becomes clear how the complex system of alliances, the scramble for colonies, and the rise of nationalist movements all contributed to the outbreak of World War I. As we reflect on this period, we are reminded of the importance of understanding the past to navigate the complexities of the present and future.
What were the main causes of World War I?
+The main causes of World War I include the complex system of alliances, imperialism, militarism, and nationalism. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand served as the immediate trigger for the war.
How did the system of alliances contribute to the outbreak of WWI?
+The system of alliances divided Europe into two opposing camps, the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. When the conflict began, the alliances drew more nations into the war, leading to its rapid escalation.
What role did nationalism play in the lead-up to WWI?
+Nationalism, particularly in the Balkans, was a significant factor leading to WWI. Nationalist movements sought independence or unity, often with the support of external powers, contributing to regional instability and the outbreak of conflict.